Abstract
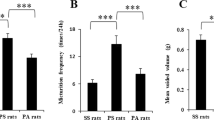
The effects of acoustic stress (AS) on gastrointestinal motility and their prevention by previous treatment with naloxone, phentolamine, propranolol, muscimol, and diazepam were investigated in intact and vagotomized fasted dogs fitted with chronically implanted strain gauges on the antrum at 10 cm from pylorus and on the jejunum at 70 and 140 cm from the pylorus. These effects were compared to those produced by intracerebroventricular administration of ovine corticotropin releasing factor (oCRF). Beginning 40–50 min after the occurrence of a gastric migrating motor complex (MMC), a 1-hr hearing of prerecorded intense music through earpieces (<100 dB) delayed the occurrence of the next gastric MMC observed after 2.8±1.2 hr, while jejunal MMC were still present at a normal frequency. During AS, heart rate and plasma cortisol were significantly increased by 32.7 and 215%, respectively, 10–15 min after the beginning of hearing. The AS-induced lengthening of the gastric MMC cycle as well as cortisol increase were abolished after previous administration of diazepam (0.5 mg/kg intramuscular) or muscimol (10 μg/kg intravenous), while they were still present after naloxone (0.1 mg/kg intravenous), phentolamine (0.2 mg/kg intravenous), or propranolol (0.1 mg/kg intravenous). CRF administered intracerebroventricularly (100 ng/kg) also delayed the occurrence of gastric MMC without affecting jejunal motility, and this effect was not antagonized by previous treatment with diazepam or muscimol. Both the effects of AS and CRF were abolished after bilateral thoracic vagotomy. These results suggest that the selective inhibition of gastric motility induced by noise in dog is due to the CNS release of CRF which affects, in turn, the vagal output to the stomach. The suppressive action of diazepam or GABA agonist on noise-induced gastric hypomotility may be related to blockade of the AS-induced CRF release.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thompson DG, Richelson E, Malagelada JR: Perturbation of gastric emptying and duodenal motility through the central nervous system. Gastroenterology 83:1200–1206, 1982
Thompson DG, Richelson E, Malagelada JR: Perturbation of upper gastrointestinal function by cold stress. Gut 24:277–283, 1983
Stanghellini V, Malagelada JR, Zinsmeister AR, Go VLW, Lao PC: Stress-induced gastroduodenal motor disturbances in humans: Possible humoral mechanisms. Gastroenterology 85:83–91, 1983
Stanghellini V, Malagelada JR, Zinsmeister AR, Go VLM, Kao PC: Effect of opiate and adrenergic blockers on the gut motor response to centrally acting stimuli. Gastroenterology 87:1104–1113, 1984
McRae S, Thompson DG, Wingate DL, Younger K: Changes in the pattern of fasting jejunal motor activity during mental stress. J Physiol (London) 308:25P, 1980
Kumar D, Wingate D: The irritable bowel syndrome: A paroxysmal motor disorder. Lancet 2:973–977, 1985
O'Brien JD, Thompson DG, Day S, Burnham WR, Walker E: Stress-induced disturbances of human postprandial antroduodenal motility and orocecal transit. The contribution of adrenergic pathways. Dig Dis Sci 30-785A, 1985
Cohen M, Pickar D, Dubois M, Roth YF, Naber D, Bunney WE: Surgical stress and endorphins. Lancet 1:213–214, 1981
Kopin KJ, Lake RC, Ziegler M: Plasma levels of norepinephrine. Ann Intern Med 88:671–680, 1978
Bortz WM, Angwin P, Mefford IN, Boarder MR, Noyce N, Barchas JD: Catecholamines, dopamine and endorphin levels during extreme exercise. N Engl J Med 1305:466–467, 1981
Rivier C, Rivier J, Vale W: Inhibition of adrenocorticotropic hormone secretion in the rat by immunoneutralisation of corticotropin releasing factor. Science 218:377–379, 1982
Brown MR, Fisher LA, Spiess J, Rivier C, Rivier J, Vale W: Corticotropin-releasing factor: Actions on the sympathetic nervous system and metabolism. Endocrinology 111:928–932, 1982
Sutton RE, Koob GG, Lemoal M, Rivier J, Vale W: Corticotropin releasing factor produces behavioural activation in rats. Nature 297:331–333, 1982
Ramade F, Bayle JD: Influence du muscimol (GABA-agoniste) sur une boucle de régulation thalamohypothalamique à efference corticotrope (modéle thalamique). CR Soc Biol 179:383–388, 1985
Narducci F, Snape WJ, Battle WH, London RL, Cohen S: Increased colonic motility during exposure to a stressful situation. Dig Dis Sci 30:40–44, 1985
Buéno L, Ferré JB, Ruckebusch Y, Genton M, Pascaud X: Continuous electrical and mechanical activity recording in the gut of the conscious rat. J Pharmacol Methods 6:129–136, 1981
Alvinerie M, Toutain PL: Simultaneous determination of corticosterone, hydrocortisone and dexamethasone in dog plasma using high-performance liquid chromatography. J Pharm Sci 71:816–818, 1982
Fargeas MJ, Fioramonti J, Buéno L: Time-related effects of benzodiazepines on intestinal motility in conscious dogs. J Pharm Pharmacol 36:130–132, 1984
Fioramonti J, Fargeas MJ, Buéno L: Different targets for ICV vs IV administered morphine for its effects on colonic motility in dogs. Eur J Pharmacol 111:1418–1420, 1985
Buéno L, Fioramonti J, Primi MP: Influence of corticotrophin releasing factor, corticotrophin and cortisol on normal and motilin induced gastrointestinal motility in dogs. Dig Dis Sci 30-761A, 1985
Erckenbrecht JF, Schoepe-Stillel A, Borgos J, Rehm S, Weinbeck M: The effects of mental stress by noise on motility and fluid absorption in the human upper small bowel. Dig Dis Sci 30-768A, 1985
Curtis DR, Johnston GAR: Amino-acid transmitters in the mammalian central nervous system. Ergebn Physiol 69:97–188, 1974
Jessen RK, Mirsky R, Dennison ME, Burnstock G: GABA may be a neurotransmitter in the vertebrate peripheral nervous system. Nature 281:71–74, 1979
Olsen RW: Drug interactions at the GABA receptor ionophore complex. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 22:245–277, 1982
Mennini T, Garattini S: Benzodiazepine receptors: Correlation with pharmacological responses including animals. Life Sci 31:2025–2035, 1982
Williford DJ, Ormsbee HS, Norman W, Harmon JW, Garvey TQ, Dimicco JA, Gillis RA: Hindbrain GABA receptors influence parasympathetic outflow to the stomach. Science 214:193–195, 1981
Goto Y, Tache Y, Debas H, Novin D: Gastric acid and vagus nerve response to GABA agonists baclofen. Life Sciences 36:2471–2475, 1985
Buckingham JC, Hodges JR: Hypothalamic receptors influencing the secretion of corticotrophin releasing hormone in the rat. J Physiol (London) 290:421–431, 1979
Makara GB, Stark E: Effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and GABA antagonist drugs on ACTH release. Neuroendocrinology 16:178–190, 1974
Ninan DJ, Insel TM, Cohen RM, Cook JM, Skolnick P, Paul SM: Benzodiazepine receptor-mediated experimental “anxiety” in primates. Science 218:1332–1334, 1982
Minano FJ, Serrano JS, Duran A, Sancibrian M: Protective effect of GABA and sodium valproate on stress-induced gastric lesions in guinea pigs. J Pharm Pharmacol 37:675–677, 1985
Gibbs D, Vale W: Presence of corticotropin releasing factor-like immunoreactivity in hypophysiol portal blood. Endocrinology 111:1418–1420, 1982
Tache Y, Goto Y, Gunion M, Rivier J, Debas H: Inhibition of gastric acid secretion in rats and dogs by corticotropin releasing factor. Gastroenterology 86:281–286, 1984
Sakaguchi T, Ohtake M: Inhibition of gastric motility induced by activation of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Brain Res 335:365–367, 1985
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gue, M., Fioramonti, J., Frexinos, J. et al. Influence of acoustic stress by noise on gastrointestinal motility in dogs. Digest Dis Sci 32, 1411–1417 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01296668
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01296668