Abstract
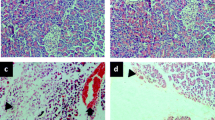
Ischemia has been considered to play a role in the development of acute pancreatitis. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of ischemia, caused by hemorrhagic shock, on cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. Acute pancreatitis was induced by the intravenous infusion of a supramaximally stimulating dose of cerulein (10 μg/kg/hr) for 6 hr. Hemorrhagic shock was induced by the removal of blood until the mean arterial blood pressure reached 35 mm Hg. This level was maintained for 30 min, after which time all the blood was reinfused. Hemorrhagic shock alone induced no morphological change in the pancreas. However, after the induction of hemorrhagic shock in animals treated with cerulein, hemorrhage and parenchymal necrosis were frequently observed in the pancreas. Seven of 20 rats (35%) receiving cerulein plus hemorrhagic shock had died by 48 hr after the start of cerulein infusion, whereas none of the rats in the cerulein or shock group died during this experiment. Cathepsin B activity in the pancreas of the cerulein plus shock group was significantly higher than in the other groups at 48 hr. These results suggest that ischemia may be a contributing factor in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feiner H: Pancreatitis after cardiac surgery. Am J Surg 131:684–688, 1976
Jones RT, Garcia JH, Mergner WJ, Pendergrass RE, Valingorsky JM, Trump BF: Effects of shock on the pancreatic acinar cell. Arch Pathol 99:634–644, 1975
Warshaw AL, O'Hara PJ: Susceptibility of the pancreas to ischemic injury in shock. Ann Surg 188:197–201, 1978
Gmaz-Nikulin E, Nikulin A, Plamenac P, Hegewald G, Gaon D: Pancreatic lesions in shock and their significance. J Pathol 135:223–236, 1981
Becker V, Stollhoff K: Shock and terminal pancreatitis. Pathol Res Pract 179:512–516, 1985
Takahashi T, Yaginuma N: Ischemic injury of the human pancreas. Its basic patterns correlated with the pancreatic microvasculature. Pathol Res Pract 179:645–651, 1985
Popper HL, Necheles H, Russell KC: Transition of pancreatic edema into pancreatic necrosis. Surg Gynecol Obstet 87:79–83, 1948
Spormann H, Sokolowski A, Letko G: Effect of temporary ischemia upon development and histological patterns of acute pancreatitis in the rat. Pathol Res Pract 184:507–513, 1989
Pfeffer RB, Lazzarini-Robertson A, Safadi D, Mixter G, Secoy CF, Hinton JW: Gradations of pancreatitis, edematous, through hemorrhagic, experimentally produced by controlled injection of microspheres into blood vessels in dogs. Surgery 51:764–769, 1962
Redha F, Uhlschmid G, Ammann RW, Freiburghaus AU: Injection of microspheres into pancreatic arteries causes acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis in the rat: A new animal model. Pancreas 5:188–193, 1990
Broe PJ, Zuidema GD, Cameron JL: The role of ischemia in acute pancreatitis: Studies with an isolated perfused canine pancreas. Surgery 91:377–382, 1982
Printz H, Saluja A, Leli U, Sengupta A, Steer M: Effects of hemorrhagic shock, aspirin, and ethanol on secretagogue-induced experimental pancreatitis. Int J Pancreatol 6:207–217, 1990
Klar E, Rattner DW, Compton C, Stanford G, Chernow B, Warshaw AL: Adverse effect of therapeutic vasoconstrictors in experimental acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg 214:168–174, 1991
Rao SS, Watt IA, Donaldson LA, Crocket A, Joffe SN: A serial histologic study of the development and progression of acute pancreatitis in the rat. Am J Pathol 103:39–46, 1981
Brackett KA, Crocket A, Joffe SN: Ultrastructure of early development of acute pancreatitis in the rat. Dig Dis Sci 28:74–84, 1983
Klar E, Endrich B, Messmer K: Microcirculation of the pancreas. A quantitative study of physiology and changes in pancreatitis. Int J Microcirc Clin Exp 9:85–101, 1990
Lampel M, Kern HF: Acute interstitial pancreatitis in the rat induced by excessive doses of a pancreatic secretagogue. Virchows Arch A 373:97–117, 1977
LaBarca C, Paigen K: A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem 102:344–352, 1980
Ceska M, Birath K, Brown B: A new and rapid method for the clinical determination of α-amylase activities in human serum and urine. Clin Chim Acta 26:437–444, 1969
Kurooka S, Okamoto S, Hashimoto M: A novel and simple colorimetric assay for human serum lipase. J Biochem 81:361–369, 1977
McDonald JK, Ellis S: On the substrate specificity of cathepsin B1 and B2 including a new fluorogenic substrate for cathepsin B1. Life Sci 17:1269–1276, 1975
Klar E, Messmer K, Warshaw AL, Herfarth C: Pancreatic ischaemia in experimental acute pancreatitis: Mechanism, significance and therapy. Br J Surg 77:1205–1210, 1990
Jones RT, Trump BF: Cellular and subcellular effects of ischemia on the pancreatic acinar cell. Virchows Arch B 19:325–336, 1975
Robert JH, Toledano AE, Toth LS, Premus G, Dreiling DA: Hypovolemic shock, pancreatic blood flow, and pancreatitis. Int J Pancreatol 3:283–292, 1988
Gurll NJ: Organ blood flow and metabolism in shock: Overview Prog Clin Biol Res 299:3–8, 1989
Anderson MC: Venous stasis in the transition of edematous pancreatitis to necrosis. JAMA 183:534–537, 1963
McCord JM: Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med 312:159–163, 1985
Granger DN: Role of xanthine oxidase and granulocytes in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol 255:H1269-H1275, 1988
Jarasch ED, Bruder G, Heid HW: Significance of xanthine oxidase in capillary endothelial cells. Acta Physiol Scand 548(suppl):39–46, 1986
Figarella C, Miszczuk-Jamska B, Barrett AJ: Possible lysosomal activation of pancreatic zymogens. Biol Chem Hoppe-Seyler 369(suppl):293–298, 1988
Spath JA, Gorczynski RJ, Lefer AM: Pancreatic perfusion in the pathophysiology of hemorrhagic shock. Am J Physiol 226:443–451, 1974
Saluja A, Hashimoto S, Saluja M, Powers RE, Meldolesi J, Steer ML: Subcellular redistribution of lysosomal enzymes during caerulein-induced pancreatitis. Am J Physiol 253:G508-G516, 1987
Papp M, Makara GB, Hajtman B, Csaki L: A quantitative study of pancreatic blood flow in experimental pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 51:524–527, 1966
Goodhead B: Acute pancreatitis and pancreatic blood flow. Surg Gynecol Obstet 129:331–340, 1969
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by a grant, Scientific Research B-03454319, from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture, and a grant from the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Japan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kyogoku, T., Manabe, T. & Tobe, T. Role of ischemia in acute pancreatitis. Digest Dis Sci 37, 1409–1417 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01296012
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01296012