Summary
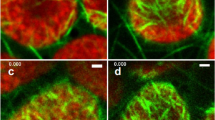
The birefringent fibrils in thin-spread plasmodium ofPhysarum polycephalum have been investigated with both polarizing and electron microscopes. The birefringent fibrils were classified into three groups by polarized light microscopy. The first type of fibril is observed in the advancing frontal region as a mutual orthogonal array. The birefringence changes rhythmically in accordance with the shuttle streaming. The second type of birefringent fibril is located in the strand region and runs parallel or somewhat oblique to the strand axis. The third type is observed in the strand region always perpendicular to the streaming axis. Electron microscopy confirmed that all these fibrils are composed of microfilaments, which range in densities in the cross view of the fibril from 1.2 to 1.7 × 103/μm2 (1.5 × 103/(xm2 on the average).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alléra, A., Beck, R., Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K. E., 1971: Weitreichende fibrilläre Protoplasmadifferenzierungen und ihre Bedeutung für die Protoplasmaströmung. Cytobiologie4, 437–449.
Fleischer, M., Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K. E., 1975: Correlation between tension force generation, fibrillogenesis and ultrastructure of cytoplasmic actomyosin during isometric and isotonic contractions of protoplasmic strands. Cytobiologie10, 339–365.
Hasegawa, T., Takahashi, S., Hayashi, H., Hatano, S., 1980: Fragmin: A calcium ion sensitive regulatory factor on the formation of actin filaments. Biochemistry19, 2677–2683.
Hatano, S., Oosawa, F., 1966: Isolation and characterization of plasmodial actin. Biochim. biophys. Acta127, 488–498.
—,Tazawa, M., 1968: Isolation, purification and characterization of myosin B from myxomycete plasmodium. Biochim. biophys. Acta154, 507–519.
Hinssen, H., 1981 a: An actin-modulating protein fromPhysarum polycephalum. I. Isolation and purification. Eur. J. Cell Biol.23, 225–233.
—, 1981 b: An actin-modulating protein fromPhysarum polycephalum. II. Ca++ -dependence and other properties. Eur. J. Cell Biol.23, 234–240.
Hülsmann, N., Haberey, M., Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K. E., 1974: Vitalmikroskopische Darstellung cytoplasmatischer Actomyosin-Fibrillen. Microscopica Acta76, 38–47.
Isenberg, G., Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K. E., 1976: Transformation of cytoplasmic actin. Importance for the organization of the contractile gel reticulum and the contraction-relaxation cycle of cytoplasmic actomyosin. Cell Tiss. Res.173, 495–528.
Kamiya, N., 1940: Control of protoplasmic streaming. Science92, 462–463.
- 1973: Contractile characteristics of the myxomycete plasmodium. Proc. IV Internat. Biophysics Congress, Moscow, pp. 447–465.
—,Kuroda, K., 1965: Movement of the myxomycete plasmodium. I. A study of glycermated models. Proc. Japan Acad.41, 837–841.
Kato, T., Tonomura, Y., 1975 a: Ca++-sensitivity of actomyosin ATPase purified fromPhysarum polycephalum. J. Biochem., Tokyo77, 1127–1134.
— —, 1975 b:Physarum tropomyosin-troponin complex. J. Biochem., Tokyo78, 583–588.
Kortzfleisch, D. von, 1976: Elektronenmikroskopische Darstellung der Topographie cytoplasmatischer Actomyosin-Fibrillen in Protoplasmaadern vonPhysarum polycephalum. Protistologica12, 399–413.
Nagai, R., Kato, T., 1975: Cytoplasmic filaments and their assembly into bundles inPhysarum plasmodium. Protoplasma86, 141–158.
—,Yoshimoto, Y., Kamiya, N., 1975: Changes in fibrillar structures in the plasmodial strand in relation to the phase of contraction-relaxation cycle. Proc. Japan Acad.51, 38–43.
— — —, 1978: Cyclic production of tension force in the plasmodial strand ofPhysarum polycephalum and its relation to microfilament morphology. J. Cell Sci.33, 205–225.
Nakajima, H., Allen, R. D., 1965: The changing pattern of birefringence on plasmodia of the slime mold,Physarum polycephalum. J. Cell Biol.25, 361–374.
Ogihara, S., Kuroda, K., 1979: Identification of a birefringent structure which appears and disappears in accordance with the shuttle streaming inPhysarum plasmodia. Protoplasma100, 167–177.
Reynolds, E. S., 1963: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol.17, 208–212.
Spurr, A. R., 1969: A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res.26, 31–43.
Taylor, D. L., Wong, Y.-L., 1978: Molecular cytochemistry. Incorporation of fluorescently labeled actin into living cells. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (U.S.A.)64, 289–310.
Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K. E., 1964: Differentiations of the ground cytoplasm and their significance for the generation of the motive force of ameboid movement. In: Primitive motile systems in cell biology (Allen, R. D., Kamiya, N., eds.), pp. 79–109. New York-London: Academic Press.
—, 1975: Weitreichende fibrilläre Protoplasmadifferenzierungen und ihre Bedeutung für die Protoplasmaströmung. X. Die Anordnung der Actomyosin-Fibrillen in experimentell unbeeinflußten Protoplasmaadern vonPhysarum polycephalum in situ. Protistologica11, 19–30.
Yoshimoto, Y., Kamiya, N., 1978 a: Studies on contraction rhythm of the plasmodial strand. I. Synchronization of local rhythm. Protoplasma95, 89–99.
— —, 1978 b: Studies on contraction rhythm of the plasmodial strand. IV. Site of active oscillation in an advancing plasmodium. Protoplasma95, 123–133.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishigami, M., Nagai, R. & Kuroda, K. A polarized light and electron microscopic study of the birefringent fibrils inPhysarum plasmodia. Protoplasma 109, 91–102 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01287632
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01287632