Summary
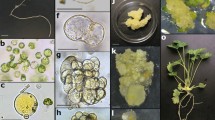
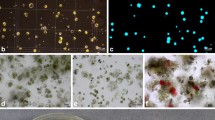
Protoplasts were isolated from embryogenic cell suspension cultures derived from proliferating shoot segments of a 20-year-old sandalwood tree (Santalum album Linn.). Under appropriate conditions, isolated protoplasts divided in liquid culture medium and produced embryogenic cell aggregates and globular embryos. Plating of cell aggregates on a fresh medium facilitated the differentiation of somatic emryos which further developed into plantlets.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAP:
-
6-benzylaminopurine
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- GA3 :
-
Gibberellic acid
- IAA:
-
indoleacetic acid
- IBA:
-
indolebutrytic acid
- MES:
-
2-(N-morpholino)ethane sulfonic acid
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog's medium as modified in the text
References
Backs-Hüsemann, D., Reinert, J., 1970: Embryobildung durch isolierte Einzelzellen aus Gewebekulturen vonDaucus carota. Protoplasma70, 49–60.
Bapat, V. A., Rao, P. S., 1979: Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet formation in tissue cultures of sandalwood (Santalum album L.). Ann. Bot.44, 629–630.
— —, 1984: Regulatory factors forin vitro multiplication of sandalwood tree (Santalum album L.) I. Shoot bud regeneration and somatic embryogenesis in hypocotyl cultures. Proc. Indian natn. Sci. Acad. (Plant Sci.)93, 19–27.
Binding, H., 1974: Regeneration von haploiden und diploiden Pflanzen aus Protoplasten vonPetunia hybrida L. Z. Pflanzenphysiol.74, 327–356.
Button, J., Kochba, J., Bornman, C. H., 1974: Fine structure and embryoid development from embryogenic ovular callus of “Shamouti” orange (Citrus sinensis Osb.) J. exp. Bot.25, 446–457.
Dodds, J. H., Roberts, L. W., 1982: Experiments in plant tissue culture. London: Cambridge Univ. Press.
Gamborg, O. L., Miller, R. A., Ojima, K., 1968: Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp. Cell. Res.50, 151–158.
Galun, E.,Aviv, D.,Raveh, D.,Vardi, A.,Zelcer, A., 1977: Protoplasts in studies of cell genetics and morphogenesis. In: Proc. Life Sci. (Reinhard, E.,Alfermann, A. W., eds.), pp. 301–312. Berlin.
Haccius, B., 1978: Question of unicellular origin of non-zygotic embryos in callus cultures. Phytomorphology28, 74–81.
Konar, R. N., Thomas, E., Street, H. E., 1972: Origin and structure of embryoids arising from epidermal cells of the stem ofRanunculus sceleratus L. J. Cell. Sci.11, 77–93.
Lakshmi Sita, G., Raghava Ram, N. V., Vaidyanathan, C. S., 1979: Differentiation of embryoids and plantlets from shoot callus of sandalwood. Plant Sci. Lett.15, 265–270.
— — —, 1980 a: Triploid plants from endosperm cultures of sandalwood by experimental embryogenesis. Plant Sci. Lett.20, 63–69.
—,Shoba, G., Vaidyanathan, C. S., 1980 b: Regeneration of whole plants by embryogenesis from cell suspension cultures of sandalwood. Curr. Sci.49, 196–198.
Murashige, T., Skoog, F., 1962: A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant.15, 473–497.
Rangaswamy, N. S., Rao, P. S., 1963: Experimental studies onSantalum album L.—establishment of tissue culture of endosperm. Phytomorphology13, 450–454.
Rao, P. S., 1965:In vitro induction of embryonal proliferation inSantalum album L. Phytomorphology15, 165–167.
—, 1982: Protoplast culture. In: Experimental embryology of vascular plants (Johri, B. M., ed.), pp. 231–262. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer.
—,Rangaswamy, N. S., 1971: Morphogenic studies in tissue cultures of the parasiteSantalum album L. Biol. Plant. (Praha)13, 200–206.
—,Bapat, V. A., 1978: Vegetative propagation of sandalwood plants through tissue culture. Can. J. Bot.56, 1153–1156.
— —, 1980: Morphogenetic investigations in tissue and organ cultures of sandalwood tree. In: Plant tissue culture, genetic manipulation and somatic hybridization of plant cells (Rao, P. S., Heble, M. R., Chadha, M. S., eds.), pp. 206–215. Proc. Natl. Symp., Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, Bombay.
Rao, P. S., Raghava Ram, N. V., 1983: Propagation of sandalwood (Santalum album L.) using tissue and organ culture technique. In: Plant cell culture in crop improvement (Sen, S. K., Giles, K. L., eds.), pp. 419–422. New York: Plenum Publishing Corporation.
—,Bapat, V. A., Mhatre, M., 1984: Regulatory factors forin vitro multiplication of sandalwood tree (Santalum album L.) II. Plant regeneration in nodal and internodal stem explants and occurence of somaclonal variations in tissue culture raised plants. Proc. Indian natn. Sci. Acad.B50, 148–154.
Redenbaugh, K., Karnosky, D., Westfall, R. D., 1981: Protoplast isolation and fusion in threeUlmus species. Can. J. Bot.59, 1436–1443.
Schieder, O., Vasil, I. K., 1980: Protoplast fusion and somatic hybridization. In: Perspectives in plant cell and tissue culture (Vasil, I. K., ed.), pp. 21–46. Int. Rev. Cytol. Suppl. 11 B. New York: Academic Press.
Smith, M. A., McCown, B. H., 1982: A comparison of source tissue for protoplast isolation from three woody plant species. Plant Sci. Lett.28, 149–156.
Tisserat, B., Esan, E. B., Murashige, T., 1979: Somatic embryogenesis in angiosperms. Hort. Rev.1, 1–78.
Vardi, A., Spiegel-Roy, P., Galun, E., 1975:Citrus cell culture: isolation of protoplasts, plating densities, effect of mutagens and regeneration of embryos. Plant Sci. Lett.4, 231–236.
— —, 1982: Plant regeneration fromCitrus protoplasts: variability in methodological requirements among cultivars and species. Theor. appl. Genet.62, 174–176.
Vasil, I. K., Vasil, V., 1980: Isolation and culture of protoplasts. In: Perspectives in plant cell and tissue culture (Vasil, I. K., ed.), pp. 1–19. Int. Rev. Cytol. Suppl. 11 B. New York: Academic Press.
Vasil, V., Vasil, I. K., 1982: Characterization of an embryogenic cell suspension culture derived from cultured inflorescences ofPennisetum americanum (pearl millet,Gramineae). Amer. J. Bot.69, 1441–1449.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, P.S., Ozias-Akins, P. Plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis in protoplast cultures of sandalwood (Santalum album L.). Protoplasma 124, 80–86 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01279726
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01279726