Summary
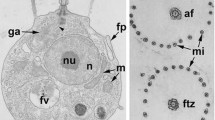
Flagellation ofPhysarum polycephalum amoebae (Myxomycete) involves the formation around the two kinetosomes of a flagellar apparatus leading to a modification in the shape of the amoeba and its nucleus. A tridimensional ultrastructural model of the flagellar apparatus is proposed, based upon observation of the isolated nucleo-flagellar apparatus complex. The flagellar apparatus is composed of a non-microtubular structure (the posterior para-kinetosomal structure), five microtubular arrays and two flagella: a long anterior flagellum and a short flagellum directed backwards. The asymmetry of the flagellar apparatus is due mainly to the presence of the posterior para-kinetosomal structure on the right side of the posterior kinetosome and of the two asymmetrical microtubular arrays 3 and 4. Thus, the flagellar apparatus is right-handed. This asymmetry implies also some spatial constraints on two other microtubular arrays (2 and 5). Except in the case of the microtubular array 1 which links the proximal end of the anterior kinetosome to the nuclear membrane, the number of microtubules of each microtubular array seems to be well defined: 39, 5–6, 7–9, and 2+2 for the microtubular arrays 2, 3, 4, and 5 respectively. All the elements of the nucleo-flagellar apparatus complex are linked either directly or indirectly through bridges. Furthermore, the microtubules which composed the microtubular array 3 are linked through bridges while the microtubules of the microtubular arrays 2, 3, and 4 seem to be linked through a reticulate material. All these spatial relationships lead to a great cohesion of the nucleo-flagellar apparatus complex which appears to be a well defined structure. This suggests thatPhysarum amoebal flagellation can be a promising system to study the morphogenesis of an eucaryotic cell.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PIPES:
-
Piperazine-N,N′-bis [2-ethane-sulfonic acid]
- EGTA:
-
[Ethylenebis(oxyethylenenitrile)]tetraacetic acid
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
References
Aldrich, H. C., 1968: The development of flagella in swarm cells of the MyxomycetePhysarum flavicomum. J. gen. Microbiol.50, 217–222.
Bloodgood, R. A., 1978: Genetic approaches to the study of motility in eukaryotic cells. Cell Biol. Int. Rep.2, 299–302.
Cooke, D. J., Dee, J., 1975: Methods for the isolation and analysis of plasmodial mutants inPhysarum polycephalum. Genet. Res. Camb.24, 175–187.
Dancker, P., Löw, I., Hasselbach, W., Wieland, Th., 1975: Interaction of actin with phalloidin: polymerization and stabilization of F-actin. Biochim. biophys. Acta400, 407–414.
Del Castillo, L., Oustrin, M. L., Wright, M., 1978: Characterization of thermosensitive mutants ofPhysarum polycephalum: plasmodial screening methods for cell cycle mutants defective in late G 2, mitosis or S phase. Mol. gen. Genet.164, 145–154.
Elliott, E. W., 1948: The swarm-cells of Myxomycetes. J. Wash. Acad. Sci38, 133–137.
—, 1949: The swarm-cells of Myxomycetes. Mycologia41, 141–170.
Gabbiani, G., Montesano, R., Tuchweber, B., Salas, M., Orci, L., 1975: Phalloidininduced hyperplasia of actin filaments in rat hepatocytes. Lab. Invest.33, 562–569.
Gibbons, I. R., Grimstone, A. V., 1960: On flagellar structure in certain flagellates. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.7, 697–715.
Gray, W. D., Alexopoulos, C. J., 1968: Biology of the Myxomycetes. New York: The Ronald Press Co.
Haskins, E. F., 1978: A study on the amoebo-flagellate transformation in the slime moldEchinostelium minutum de Bary. Protoplasma94, 193–206.
Kerr, S. J., 1972: Inhibition of flagellum morphogenesis in the true slime mould,Didymium nigripes. J. gen. Microbiol.72, 419–427.
Locquin, M., 1949: Recherches sur les simblospores de Myxomycetes. Bull. Soc. Linnéenne Lyon18, 43–46.
Lustig, S., Kosower, N. S., Pluznik, D. H., Kosower, E. M., 1977: Inhibition of cytokinesis in Friend Leukemia cells by membrane mobility agents. Proc. natl. Acad. Sci. (U.S.A.)74, 2884–2888.
Mante, S. D., Flashner, M., Tanenbaum, S. W., 1978 a: Effects of cytochalasin A on the morphology of plasmodia and sclerotia ofPhysarum polycephalum. Cytobiologie17, 10–22.
— — —, 1978 b: Combined effect of cytochalasin A and adenosine triphosphate onPhysarum polycephalum. Protoplasma96, 235–246.
Mir, L., Wright, M., 1977: Action of antimicrotubular drugs onPhysarum polycephalum. Microbios Lett.5, 39–44.
—,del Castillo, Wright, M., 1979: Isolation ofPhysarum amoebal mutants defective in flagellation and associated morphogenetic processes. FEMS microbiology letters5, 43–46.
Pickett-Heaps, J. D., 1969: The evolution of the mitotic apparatus: an attempt at comparative ultrastructural cytology in dividing plant cells. Cytobios3, 257–280.
Ross, I. K., 1957: Syngamy and plasmodium formation in the Myxogastres. Amer. J. Bot.44, 843–850.
Schuster, F. L., 1965: Ultrastructure and morphogenesis of solitary stages of true slime molds. Protistologica1, 49–62.
Stockem, W., Weber, K., Wehland, J., 1978: The influence of microinjected phalloidin on locomotion, protoplasmic streaming and cytoplasmic organization inAmoeba proteus andPhysarum polycephalum. Cytobiologie18, 114–131.
Warr, J. R., 1974: Genetic approaches to the study of microtubule structure and function. Sub-Cell. Biochem.3, 149–154.
Wakasugi, M., Ohta, J., 1973: Studies on the amoebo-flagellate transformation inPhysarum polycephalum. Bot. Mag. Tokyo86, 299–308.
Wehland, J., Osborn, M., Weber, K., 1977: Phalloidin induced actin polymerization in the cytoplasm of culture cells interferes with cell locomotion and growth. Proc. natl. Acad. Sci. (U.S.A.)74, 5613–5617.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wright, M., Moisand, A. & Mir, L. The structure of the flagellar apparatus of the swarm cells ofPhysarum polycephalum . Protoplasma 100, 231–250 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01279314
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01279314