Summary
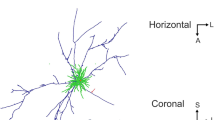
The early postnatal maturation of pyramidal neurons in layers II/III and V of the rat visual cortex has been examined in an attempt to elucidate some determinants of their mature morphology. Three indices have been quantified using Golgi-impregnated pyramidal cells: densities of spines along apical dendrites, numbers of primary basal dendrites and volumes of cell bodies. The mean density of spines on the apical dendrites of all pyramidal neurons increases in a stepwise fashion. The first significant increase occurs between days 6 and 9 and the second, between days 12 and 15; these increases may correlate with the arrival of geniculate afferents and with the opening of the eyes, respectively. In younger animals, the distribution of spines along the apical shafts is relatively even, whereas in older animals, spine density increases significantly over the proximal 125 μm portion and is relatively constant over the remaining distal portion. By day 21, layer V pyramidal cells have acquired more primary basal dendrites and larger somatic volumes than layer II/III cells. Furthermore, as the cells mature the rates of change in these characteristics are significantly different for neurons in layer II/III and in layer V. For both cell populations, the mean number of primary basal dendrites increases to a maximum before falling to a steady level, but for neurons in layer V, the maximum is higher and attained three days earlier than for layer II/III cells. Moreover, the increase in volume of cell bodies of layer V neurons begins three days before that of layer II/III cells. This three day phase difference in maturation may reflect the cell birth dates, since autoradiographic evidence indicates that layer V pyramidal neurons reach the cortical plate about three days prior to those which occupy layer II/III in the adult visual cortex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angevine, J. B., Jr &Sidman, R. L. (1961) Autoradiographic study of cell migration during histogenesis of cerebral cortex in the mouse.Nature 192, 766–8.
Angulo-Colmenares, A. G., Vaughan, D. W. &Hinds, J. W. (1979) Rehabilitation following early malnutrition in the rat: body weight, brain size and cerebral cortex development.Brain Research 169, 121–38.
Berry, M. &Rogers, A. W. (1965) The migration of neuroblasts in the developing cerebral cortex.Journal of Anatomy 99, 691–709.
Boothe, R. G., Greenough, W. T., Lund, J. S. &Wrege, K. (1979) A quantitative investigation of spine and dendrite development of neurons in visual cortex (Area 17) ofMacaca nemistrina monkeys.Journal of Comparative Neurology 186, 473–90.
Boulder Committee (1970) Embryonic vertebrate central nervous system: Revised terminology.Anatomical Record 166, 257–62.
Eayrs, J. T. &Goodhead, B. (1959) Postnatal development of the cerebral cortex of the rat.Journal of Anatomy 93, 385–402.
Fairén, A., Peters, A. &Saldanha, J. (1977) A new procedure for examining Golgi-impregnated neurons by light and electron microscopy.Journal of Neurocytology 6, 311–37.
Feldman, M. &Peters, A. (1979) A technique for estimating total spine numbers on Golgi-impregnated dendrites.Journal of Comparative Neurology 188, 527–42.
Globus, A. &Scheibel, A. B. (1967) Effects of visual deprivation on cortical neurons: A Golgi study.Experimental Neurology 19, 331–45.
Hicks, S. P. &D'Amato, C. J. (1968) Cell migration to the isocortex in the rat.Anatomical Record 160, 619–34.
Juraska, J. M., Elliott, C. &Wesa, J. (1980) A Golgi study of the development of pyramidal neurons in the rat visual cortex after eye opening.Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 6, 288.
Juraska, J. M. &Fifkova, E. (1979) A Golgi study of the early postnatal development of the visual cortex of the hooded rat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 183, 247–56.
Krieg, W. J. S. (1946) Connections of the cerebral cortex. I. The albino rat. B. Structure of the cortical areas.Journal of Comparative Neurology 84, 277–323.
Leuba, G. &Rabinowicz, T. (1979) Long-term effects of postnatal undernutrition and maternal malnutrition on mouse cerebral cortex. II. Evolution of dendritic branchings and spines in the visual region.Experimental Brain Research 37, 299–308.
Lund, J. S., Boothe, R. G. &Lund, R. D. (1977) Development of neurons in the visual cortex (area 17) of the monkey (Macaca nemistrina). A Golgi study from fetal day 127 to postnatal maturity.Journal of Comparative Neurology 176, 149–88.
Lund, R. D. &Mustari, M. J. (1977) Development of the geniculocortical pathway in rats.Journal of Comparative Neurology 173, 289–306.
Marin-Padilla, M. &Stibitz, G. R. (1968) Distribution of the apical dendrite spines of layer V pyramidal cells of the hamster neocortex.Brain Research 11, 580–92.
McAllister, J. P., Levine, M. S., Hull, C. D. &Adinolfi, A. M. (1980) Computer-assisted quantification of dendritic maturation in the kitten caudate nucleus.Society for Neurosciences Abstracts 6, 806.
Miller, M. (1980) A Golgi study of the postnatal development of pyramidal neurons in the rat visual cortex.Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 6, 821.
Parnavelas, J. G. &Lieberman, A. R. (1979) An ultrastructural study of the maturation of neuronal somata in the visual cortex of the rat.Anatomy and Embryology 157, 311–28.
Peters, A. &Feldman, M. (1973) The cortical plate and molecular layer of the late rat fetus.Zeitschrift für Anatomie und Entwicklungeschichte 141, 3–37.
Peters, A., Proskauer, C. C., Feldman, M. L. &Kimerer, L. (1979) The projection of the lateral geniculate nucleus to area 17 of the rat cerebral cortex. V. Degenerating axon terminals synapsing with Golgi impregnated neurons.Journal of Neurocytology 8, 331–57.
Rakic, P. (1971) Guidance of neurons migrating to the fetal monkey neocortex.Brain Research 33, 471–6.
Ramón Y Cajal, S. (1911)Histologie du Système Nerveux de l'Homme et des Vertebres Vd. 2 (translated byAzoulay, L.) Paris: Maloine.
Ramón Y Cajal, S. (1929)Studies on Vertebrate Neurogenesis (translated byGuth, L.) Springfield, Ill: Charles C. Thomas.
Reese, T. S. &Karnovsky, M. J. (1967) Fine structural localization of a blood-barrier to exogeneous peroxidase.Journal of Cell Biology 34, 207–18.
Schober, W. &Winkelmann, E. (1975) Der visuelle kortex der ratte cytoarchitektonik und stereotaktische parameter.Zeitschrift für mikroskopische Anatomische Forschung 89, 431–46.
Shoukimas, G. M. &Hinds, J. W. (1978) The development of the cerebral cortex in the embryonic mouse: An electron microscopic serial section analysis.Journal of Comparative Neurology 179, 795–830.
Valverde, F. (1967) Apical dendritic spines of the visual cortex and light deprivation in the mouse.Experimental Brain Research 3, 337–52.
Valverde, F. (1970) The Golgi method. A tool for comparative structural analyses. InContemporary Research Methods in Neuroanatomy (edited byNauta, W. J. H. &Ebbesson, S. O. E.), pp. 11–31. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Valverde, F. &Ruiz-Marcos, A. (1968) Dendritic spines in the visual cortex of the mouse: Introduction to a mathematical model.Experimental Brain Research 3, 269–83.
Van Der Loos, H. (1965) The ‘improperly’ oriented pyramidal cell in the cerebral cortex and its possible bearing on neuronal growth and cell orientation.Bulletin of the Johns Hopkins Hospital 117, 228–50.
Vaughan, D. W. (1977) Age-related deterioration of pyramidal cell basal dendrites in rat auditory cortex.Journal of Comparative Neurology 171, 501–16.
Winer, B. J. (1962)Statistical Principles in Experimental Design. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Wise, S. P., Fleshman, J. W. &Jones, E. G. (1979) Maturation of pyramidal cell form in relation to developing afferent and efferent connections of rat somatic sensory cortex.Neuroscience 4, 1275–97.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, M. Maturation of rat visual cortex. I. A quantitative study of Golgi-impregnated pyramidal neurons. J Neurocytol 10, 859–878 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01262658
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01262658