Abstract
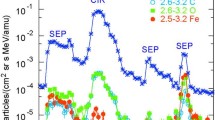
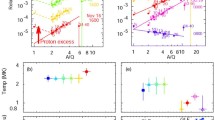
The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft include instrumentation that makes comprehensive ion (E ≳ 28 keV) and electron (E ≳ 22 keV) measurements in several energy channels with good temporal, energy, and compositional resolution. Data collected over the past decade (1977–1988), including observations upstream and downstream of four planetary bow shocks (Earth, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus) and numerous interplanetary shocks to ∼ 30 AU, are reviewed and analyzed in the context of the Fermi and shock drift acceleration (SDA) models. Principal findings upstream of planetary bow shocks include the simultaneous presence of ions and electrons, detection of “tracer” ions characteristic of the parent magnetosphere (O, S, O+), power-law energy spectra extending to ≳ 5 MeV, and large (up to 100:1) anisotropies. Results from interplanetary shocks include observation of acceleration to the highest energies ever seen in a shock (≳ 22 MeV for protons, ≳ 220 MeV for oxygen), the “saturation” in energy gain to ≳ 300 keV at quasi-parallel shocks, the observation of shock-accelerated relativistic electrons, and separation of high-energy (upstream) from low-energy (downstream) populations to within ∼ 1 particle gyroradius in a near-perpendicular shock. The overall results suggest that ions and electrons observed upstream of planetary bow shocks have their source inside the parent magnetosphere, with first order Fermi acceleration playing a secondary role at best. Further, that quasi-perpendicular interplanetary shocks accelerate ions and electrons most efficiently to high energies through the shock-drift process. These findings suggest that great care must be exercised in the application of concepts developed for heliosphere shocks to cosmic ray acceleration through shocks at supernova remnants.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Anagnostopoulos, G., E. T. Sarris, and S. M. Krimigis (1986), Magnetospheric origin of energetic upstream ions (E ≥ 50 keV): the October 31, 1977 event,J. Geophys. Res.,91, 3020–3028.
Anderson, K. A. (1981), Measurements of bow shock particles far upstream from the earth,J. Geophys. Res.,86, 4445.
Armstrong, T. P., S. M. Krimigis, and K. W. Behannon (1970), Proton fluxes at 300 keV associated with propagating interplanetary shock waves,J. Geophys. Res.,75, 5980–5988.
Armstrong, T. P., M. E. Pesses, and R. B. Decker (1985) Shock Drift Acceleration, inCollisionless Shocks in the Heliosphere: Reviews of Current Research, Tsurutani and Stone, editors, pp. 271–286, AGU Monograph No. 35.
Armstrong, T. P., G. Chen, E. T. Sarris and S. M. Krimigis (1977) Acceleration and modulation of electrons and ions by propagating interplanetary shocks.Study of Travelling Interplanetary Phenomena, M. A. Shea et al., eds. D. Reidel Pub. Co., Dordrecht, Holland, 367–389.
Asbridge, J. R., S. J. Bame, and I. B. Strong (1968) Observed flow of protons from the earth's bow shock,J. Geophys. Res.,73, 5777.
Baker, D. N., R. D. Zwickl, S. M. Krimigis, J. F. Carbary and M. H. Acuña (1984), Energetic particle transport in the upstream region of Jupiter: Voyager Results,J. Geophys. Res.,89, 3735–3746.
Decker, R. B., M. E. Pesses, and S. M. Krimigis (1981), Shock-associated low energy ion enhancements observed by Voyagers 1 and 2,J. Geophys. Res.,86, 8819–8831.
Decker R. B., S. M. Krimigis, and D. Venkatesan (1987), Latitudinal gradient of energetic particles in the outer heliosphere during 1985–1986,J. Geophys. Res.,92, 3375–3379.
Decker, R. B. (1988a), The role of drifts in diffusive shock acceleration,Ap. J., 324, 566.
Decker, R. B. (1988b), Computer modeling of test particle acceleration at oblique shocks,Space Sci. Rev.,48, 195–262.
Decker, R. B., Particle acceleration at shocks with surface ripples,J. Geophys. Res.,95, A8, 11993–12,003, 1990.
Ellison, D. C. (1985), Shock acceleration of diffuse ions at the earth's bow shock: Acceleration efficiency and A/Z enhancements,J. Geophys. Res.,90, 29.
Gleeson, L. J., and W. I. Axford (1967) Cosmic rays in the interplanetary medium,Astrophys. J.,149, L115.
Gold, R. E., R. B. Decker, L. J. Lanzerotti, C. G. Maclennan, and S. M. Krimigis (1988), Latitude and radial dependence of shock acceleration in the heliosphere,J. Geophys. Res.,93, 991–996.
Goldstein, M. L., H. K. Wong, A. F. Vinas, and C. W. Smith (1985), Large amplitude MHD waves upstream of the Jovian bow shock: Reinterpretation,J. Geophys Res.,90, 302.
Hamilton, D. C., G. Gloeckler, S. M. Krimigis, and L. J. Lanzerotti (1981), Composition of non-thermal ions in the Jovian magnetosphere,J. Geophys. Res.,86, 8301–8318.
Ipavich, F. M., G. Gloeckler, C. Y. Fan, L. A. Fisk, D. Hovestadt, B. Klecker, J. J. O'Gallagher, and M. Scholer (1979), Initial observations of low energy charged particles near the earth's bow shock on ISEE-1,Space Sci. Rev.,23, 93.
Ipavich, F. M. M. Scholer, and G. Gloeckler (1981), Temporal development of composition, spectra, and anisotropies during upstream particle events,J. Geophys. Res.,86, 11153.
Kennel, C. F., F. V. Coroniti, F. L. Scarf, W. A. Livesey, C. T. Russell, E. J. Smith, K. P. Wenzel, and M. Scholer (1986), A test of Lee's quasi-linear theory of ion acceleration by interplanetary traveling shocks,J. Geophys. Res.,91, 11917–11928.
Krimigis, S. M., T. P. Armstrong, W. I. Axford, C. O. Bostrom, C. Y. Fan, G. Gloeckler, and L. J. Lanzerotti (1977), The Low Energy Charged Particle (LECP) experiment on the Voyager spacecraft,Space Sci. Rev.,21, 329–354.
Krimigis, S. M., J. F. Carbary, E. P. Keath, C. O. Bostrom, W. I. Axford, G. Gloeckler, L. J. Lanzerotti, and T. P. Armstrong (1981), Characteristics of hot plasma in the Jovian magnetosphere: Results from the Voyager spacecraft,J. Geophys. Res.,86, 8227–78257.
Krimigis, S. M., J. F. Carbary, E. P. Keath, T. P. Armstrong, L. J. Lanzerotti, and G. Gloeckler (1983), General characteristics of hot plasma and energetic particles in the Saturnian magnetosphere: Results from the Voyager spacecraft,J. Geophys. Res.,88, 8871.
Krimigis, S. M., R. D. Zwickl, and D. N. Baker (1985), Energetic ions upstream of Jupiter's bow shock,J. Geophys. Res., 3947–3960.
Krimigis, S. M., G. Sibeck, and R. W. McEntire (1986), Magnetospheric particle injection and the upstream ion event of September 5, 1984,Geophys. Res. Lett.,13, 1376–1379.
Krimigis, S. M. (1986), Energetic ions upstream of planetary bow shocks: Fermi acceleration or leakage? Comparative Study of Magnetospheric Systems, CNES Editor, CEPADUES Editions, Toulouse, France, 99–124.
Krimigis, S. M., E. P. Keath, B. H. Mauck, A. F. Cheng, L. J. Lanzerotti, R. P. Lepping, and N. F. Ness (1988), Observations of energetic ion enhancements and fast neutrals upstream and downstream of Uranus' bow shock by the Voyager 2 spacecraft,Planetary & Space Sci.,36, 311–328.
Krimigis, S. M., T. P. Armstrong, W. I. Axford, C. O. Bostrom, A. F. Cheng, G. Gloeckler, D. C. Hamilton, E. P. Keath, L. J. Lanzerotti, B. H. Mauk, and J. A. Van Allen, Hot plasma and energetic particles in Neptune' magnetosphere,Science,246, 1483–1494, 1989.
Lee, M. A. (1982), Coupled hydromagnetic wave excitation and ion acceleration upstream of the earth's bow shock,J. Geophys. Res.,87, 5063.
Lee, M. A. (1983), The association of energetic particles and shocks in the heliosphere,Rev. Geophys.,21, 324.
Lin, R. P., C.-I. Meng, and K. A. Anderson (1974) 30 to 100 keV protons upstream from the earth's bow shock,J. Geophys. Rs.,79, 489.
Moebius, E., D. Hovestadt, B. Klecker, M. Scholer, F. M. Ipavich, C. W. Carlson, and R. P. Lin (1986), A burst of energetic O+ ions during an upstream particle event,Geophys. Res. Lett.,13, 1372–1375.
Rosner,R., E. L. Chupp, G. Gloeckler, D. J. Gorney, S. M. Krimigis, Y.Mok, R. Ramaty, D. W. Swift, L. Vlahos, and E. G. Zweibel (1984), Particle acceleration, inSolar-Terrestrial Physics: Present and Future, D. Bulter and K. Papadopoulos, eds., NASA-RP-1120.
Sards, E. T., and S. M. Krimigis (1985), Quasi-perpendicular shock acceleration of ions of ∼ 200 MeV and electrons to ∼ 2 MeV observed by Voyager-2,Astrophys. J.,298, 676–683.
Sarris, E. T., S. M. Krimigis, and T. P. Armstrong (1976), Observations of magnetospheric bursts of high-energy protons and electrons at ∼ 36 RE with IMP 7,J. Geophys. Res.,81, 2341.
Sarris, E. T., S. M. Krimigis, C. O. Bostrom, and T. P. Armstrong (1978), Simultaneous multispacecraft observations of energetic proton bursts inside and outside the magnetosphere,J. Geophys. Res.,83, 4289.
Sarris, E. T., G. C. Anagnostopoulos, and S. M. Krimigis (1987), Simultaneous measurements of energetic ion (≥ 50 keV) and electron (> 220 keV) activity upstream of earth's bow shock and inside the plasma sheet: Magnetospheric source for the November 3 and December 3, 1977 upstream events,J. Geophys. Res.,92, 12,083–12,096.
Scholer, M., (1985) Diffusive Acceleration, inCollisionless Shocks in the Heliosphere, B. T. Tsuruanti, and R. G. Stone, Editors., pp. 287–301, A. G. U. Monograph, Washington, D. C., U.S.A.
Scholer, M., D. Hovestadt, F. M. Ipavich, and G. Gloeckler (1981), Upstream energetic ions and electrons: Bow shock-associated or magnetospheric origin?J. Geophys. Res.,86, 9040.
Sibeck, D. G., R. W. McEntire, S. M. Krimigis, and D. N. Baker (1988), The magnetosphere as a sufficient source for upstream ions on November 1, 1984,J. Geophys. Res.,93, 14328.
Smith, E. J., and J. H. Wolfe (1979), Fields and plasmas in the outer solar system,Space Sci. Rev.,23, 217.
Somogyi, A. J., and 33 co-authors (1986), First observations of energetic particles near comet Halley,Nature,321, 285–288.
Zwickl, R. D., S. M. Krimigis, T. P. Armstrong, and L. J. Lanzerotti (1980), Ions of Jovian origin observed by Voyager 1 and 2 in interplanetary space,Geophys. Res. Lett.,1, 453.
Zwickl, R. D., S. M. Krimigis, J. F. Carbary, E. P. Keath, T. P. Armstrong, D. C. Hamilton, and G. Gloeckler (1981), Energetic particle events (>30 keV) of Jovian origin observed by Voyager 1 and 2 in interplanetary space,J. Geophys. Res., 86, 8125.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krimigis, S.M. Voyager energetic particle observations at interplanetary shocks and upstream of planetary bow shocks: 1977–1990. Space Sci Rev 59, 167–201 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01262539
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01262539