Abstract
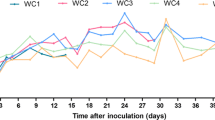
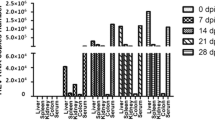
On the basis of the successful establishment of an animal model in tree shrews experimentally infected with human hepatitis B virus (HBV), a study on the hepatocarcinogenic effects of HBV and/or aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) was conducted. The results showed that the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was significantly higher in the animals both infected with HBV and exposed to AFB1 (52.94%) than in those solely infected with HBV (11.11%) or exposed to AFB1 (12.50%). No HCC of precancerous lesions were found in the controls that were neither HBV-infected nor AFB1-exposed. Precancerous lesions, including liver cell dysplasia and enzyme-altered hyperplastic hepatocyte foci, were observed before the occurrence of HCC, and the frequency of their appearance correlated well with the incidence of HCC. HBV DNA and the protein it encodes were detected in the cancer cells and/or the surrounding hepatocytes. Integration of HBV DNA inot the host liver genome was found during hepatocarcinogenesis among the animals infected by HBV. These results suggest that exposure to HBV and AFB1 may play a synergistic role in the development of HCC, and support the viewpoint of an aetiological relationship between HBV and HCC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCC :
-
hepatocellular carcinoma
- HBV :
-
human hepatitis B virus
- AFB1 :
-
aflatoxin B1
- GGT foci :
-
hyperplastic hepatocyte foci positive for γ-glutamyltranspeptidase
- LCD :
-
liver cell dysplasia
References
Beasley RP (1988) Hepatitis B virus. The major etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 61: 1942–1956
Beasley RP, Huang LY, Lin CC, Chien CS (1981) Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus: a prospective study of 22707 men in Taiwan. Lancet 2: 1129–1133
Chakraborty PR, Ruiz-Opago N, Shouval D, Shafritz DA (1980) Identification of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA and expression of viral RNA in an HBsAg-producing human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Nature 286: 531–533
Cova L, Wild CP, Mehrotra R, Turusov V, Shirai T, Lambert V, Jacquet C, Tomatis L, Trepo C, Montesano R (1990) Contribution of aflatoxin B1 and hepatitis B virus infection in the induction of liver tumors in ducks. Cancer Res 50: 2156–2163
Cova L, Mehrotra R, Wild CP, Chutimaewin S, Cao SF, Duflot A, Prace M, Yu SZ, Montesano R, Trepo C (1994) Duck hepatitis B virus infection, aflatoxin B1, and liver cancer in domestic Chinese ducks. Br J Cancer 69: 104–109
Cullen JM, Marion PL, Sherman GJ, Hong X, Newlold JE (1990) Hepatic neoplasms in aflatoxin B1-treated, congenital duck hepatitis B virus-infected, and virus-free Peking ducks. Cancer Res 50: 4072–4080
Dragani TA, Manenti G, Farza H, Porta GD, Tiollais P, Pourcel C (1989) Transgenic mice containing hepatitis B virus sequences are more susceptible to carcinogen-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 11: 953–956
Gerin JL (1990) Experimental WHV infection of woodchucks: an animal model of hepadnavirus-induced liver cancer. Gastroenterol-Jpn 25 [Suppl 2]: 38–42
Gu JR (1988) Molecular aspects of human hepatic carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 9: 697–703
Gyorkey F, Melnick JL, Mirkovic R, Cabral GA, Gyorkey P, Hollinger FB (1977) Experimental carcinoma of liver in Macaque monkeys exposed to diethylnitrosamine and hepatitis B virus. J Natl Cancer Inst 59: 1451–1467
Harris CC, Sun JT (1986) Interactive effects of chemical carcinogens and hepatitis B virus in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Surv 5: 765–780
Heilbronn R, Schlehofer JR, Yalkinoglu AO, Hausen H zur (1985) Selective DNA-amplification induced by carcinogens (initiators): evidence for a role of protease and DNA polymerase. Int J Cancer 36: 85–91
IARC/WHO (1987) Biennial report (1986–1987). IARC, Lyon, pp 41–43
Kew MC (1993) Mutant hepadnaviruses and hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrohepatol 8: 12–13
Kim CM, Koike K, Saito J, Miyamura T, Jay G (1991) HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in transgenic mice. Nature 351: 317–320
Koike K (1993) Transgenic mouse model for hepatocellular carcinoma in human hepatitis B virus infection. Nippon-Rinsho 51: 536–541
Lai MY, Chen DS, Chen PJ, Lee SC, Sheu JC, Huang GT, Wu TC, Lee CS, Yu SC, Hsu HC, Sung JL (1988) Status of hepatitis B virus DNA in tumor and nontumor liver tissues. J Med Virol 25: 249–258
Lavi S (1981) Carcinogen-mediated amplification of viral DNA sequences in simian virus 40-transformed Chinese hamster embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78: 6144–6148
Lin JJ, Liu C, Svoboda DJ (1974) Long term effects of aflatoxin B1 and viral hepatitis on marmoset liver. Int Acad Pathol 30: 267–278
Marion PL, Van Davelaar MJ, Knight SS, Salazar FH, Garcia G, Popper H, Robinson WS (1986) Hepatocellular carcinoma in ground squirrels persistently infected with ground squirrel hepatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 4543–4546
Muchmore E, Popper H, Peterson DA, Miller MF, Lieberman HM (1988) Non-A, non-B hepatitis-related hepatocellular carcinoma in a chimpanzee. J Med Primatol 17: 235–246
Muchmore E, Socha WW, Krawczynski C (1990) HCC in chimpanzees. In: Sun JL, Chen DS (eds) Viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Excerpta Medica, Hong Kong, pp 698–702
Okuda K (1992) Hepatocellular carcinoma: recent progress. Hepatology 15: 948–963
Popper H, Roth L, Purchell RH, Tennant BC, Gerin JL (1987) Hepatocarcinogenicity of the woodchuck hepatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 866–870
Rajagopalan MS, Busch MP, Blum HE, Vyas GN (1986) Interaction of aflatoxin and hepatitis B virus in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Life Sci 39: 1287–1290
Reddy JK, Svoboda DJ, Rao MS (1976) Induction of liver tumors by aflatoxin B1 in the tree shrews (Tupaia glis), a nonhuman primate. Cancer Res 36: 151–160
Rogler CE (1990) Recent advance in hepatitis B virus and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cells 2: 366–369
Rogler CE, Chisari FV (1992) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis. Semin Liver Dis 12: 265–278
Rose RK, Yuan JM, Yu CC, Wogan GN, Qian GS, Tu TT, Groodman JD, Gao YT, Henderson BE (1992) Urinary aflatoxin biomarkers and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 339: 9343–9346
Seager C, Baldwin B, Hornbuckle WE, Yeager AE, Tennant BC, Cote P, Ferrell L, Ganem D, Varmus HE (1991) Woodchuck hepatitis virus is a more efficient oncogenic agent than ground squirrel hepatitis virus in a common host. J Virol 65: 1673–1679
Sell S, Hunt JM, Dunsford HA, Chisari FV (1991) Synergy between hepatitis B virus expression and chemical hepatocarcinogens in transgenic mice. Cancer Res 51: 1278–1285
Sherker AH, Marion PL (1991) Hepadnavirus and hepatocellular carcinoma. Annu Rev Microbiol 45: 475–508
Wild CP, Shrestha SM, Anwar WA, Montesano R (1992) Field studies of aflatoxin exposure, metabolism and induction of genetic alteration in relation to HBV infection and hepatocellular carcinoma in The Gambia and Thailand. Toxicol Lett 64–65: 455–461
Wild CP, Jansen LM, Cova L, Montesano R (1993) Molecular dosimetry of aflatoxin exposure: contribution to understanding the multifactorial aetiopathogenesis of primary hepatocellular carcinoma (PHC) with particular reference to hepatitis B virus. Env Health Perspect 99: 115–122
Wogan GN (1992) Aflatoxins as risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma in human. Cancer Res 52 7 [Suppl] 2114s-2118s
Yan RQ, Su JJ, Huang DR, Gan YC, Yang C, Huang GH (1996) Human hepatitis B virus and hepatocellular carcinoma. I. Experimental infection of tree shrews with hepatitis B virus. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 122: 283–288
Yeh FS, Mo CC, Yan RQ (1984) Epidemiology and pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma in Guangxi, China. Acta Hepatol Jpn 102: 934–935
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, R.Q., Su, J.J., Huang, D.R. et al. Human hepatitis B virus and hepatocellular carcinoma II. Experimental induction of hepatocellular carcinoma in tree shrews exposed to hepatitis B virus and aflatoxin B1. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 122, 289–295 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01261405
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01261405