Summary
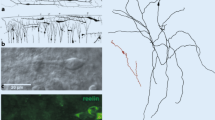
The ontogenesis of Retzius-Cajal cells, a unique feature of developing cortical layer I in a variety of mammalian species, was examined with the electron microscope in coronal or tangential sections of the visual cortex of rats whose ages were closely spaced in time between day 17 of gestation and adulthood. At 17 days of gestation, Retzius-Cajal cells already display a characteristic appearance and some of the cytoplasmic organelles by which they are identified in the perinatal period. At birth they are recognized by their large size, horizontally oriented long processes, dark cytoplasmic ground substance and abundance of tightly packed organelles. One feature which is most typical of these cells at this, and later stages of development, is the presence in the cytoplasm of numerous wide cisterns of granular endoplasmic reticulum filled with electron-opaque material. Synapses are rarely seen on the perikarya and processes during the first week of postnatal life but become more frequent later in development. A pattern of modifications becomes noticeable in the morphology of these cells during the first postnatal week with the appearance of growth cone-like differentiations and new processes of varying sizes. Furthermore, their cytoplasm slowly acquires a lighter appearance, and the thickness of the characteristically long processes diminishes. The frequency of Retzius-Cajal cells decreases with age and at the end of the third postnatal week only very few can be recognized with certainty. Careful examination of a large series of sections during subsequent days revealed that the morphological characteristics of Retzius-Cajal cells continue to change until these cells can no longer be distinguished from classical layer I nonpyramidal neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baron, M. &Gallego, A. (1971) Cajal cells of the rabbit cerebral cortex.Experientia 27, 430–32.
Bradford, R., Parnavelas, J. G. &Lieberman, A. R. (1977) Neurons in layer I of the developing occipital cortex of the rat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 176, 121–32.
Cajal, S. Ramon y (1891) Sur la structure de l'écorce cérébrale de quelques mammifères.Cellule 7, 123–76.
Cajal, S. Ramon y (1911)Histologie du Système Nerveux de l'Homme et des Vertébrés. Tome II. Paris: Maloine.
Cajal, S. Ramon y (1960)Studies on Vertebrate Neurogenesis (translated byGuth, L.), pp. 336–46. Springfield, Illinois: Charles C. Thomas.
Duckett, S. &Pearse, A. G. E. (1968) The cells of Cajal-Retzius in the developing human brain.Journal of Anatomy 102, 183–7.
Fairen, A., Peters, A. &Saldanha, J. (1977) A new procedure for examining Golgi impregnated neurons by light and electron microscopy.Journal of Neurocytology 6, 311–37.
Fox, M. W. &Inman, O. (1966) Persistence of Retzius-Cajal cells in developing dog brain.Brain Research 3, 192–4.
Gray, E. G. (1959) Axo-somatic and axo-dendritic synapses in the cerebral cortex: An electron microscopic study.Journal of Anatomy 93, 420–33.
Henrikson, C. K. &Vaughn, J. E. (1974) Fine structural relationships between neurites and radial glial processes in developing mouse spinal cord.Journal of Neurocytology 3, 659–75.
König, N. (1978) Retzius-Cajal or Cajal-Retzius cells?Neuroscience Letters 9, 361–3.
König, N., Hornung, J. -P. &Van Der Loos, H. (1981) Identification of Cajal-Retzius cells in immature rodent cerebral cortex: A combined Golgi-EM study.Neuroscience Letters 27, 225–9.
König, N. &Marty, R. (1981) Early neurogenesis and synaptogenesis in cerebral cortex.Bibliotheca Anatomica 19, 152–60.
König, N. &Schachner, M. (1981) Neuronal and glial cells in the superficial layers in early postnatal mouse neocortex: immunofluorescence observations.Neuroscience Letters 26, 227–31.
König, N., Valat, J., Fulcrand, J. &Marty, R. (1977) The time of origin of Cajal-Retzius cells in the rat temporal cortex. An autoradiographic study.Neuroscience Letters 4, 21–6.
Marin-Padilla, M. (1972) Prenatal ontogenetic history of the principal neurons of the neocortex of the cat (Felix domestica). A Golgi study. II. Developmental differences and their significances.Zeitschrift für Anatomie und Entwicklungs-Geschichte 136, 125–42.
Noback, C. R. &Purpura, D. P. (1961) Postnatal ontogenesis of neurons in cat neocortex.Journal of Comparative Neurology 117, 291–308.
Parnavelas, J. G., Sullivan, K., Lieberman, A. R. &Webster, K. E. (1977) Neurons and their synaptic organization in the visual cortex of the rat. Electron microscopy of Golgi preparations.Cell and Tissue Research 183, 499–517.
Persinger, M. A. &Robb, N. I. (1976) Cajal-Retzius cells as electrostatic guides for migrating neurons.Psychological Reports 39, 651–5.
Peters, A. (1970) The fixation of central nervous tissue and the analysis of electron micrographs of the neuropil with special reference to the cerebral cortex. InContemporary Research Methods in Neuroanatomy (edited byNauta, W. J. H. &Ebbesson, S. O. E.), pp. 56–76. New York, Heidelberg, Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Peters, A. (1971) Stellate cells in the rat parietal cortex.Journal of Comparative Neurology 141, 345–74.
Peters, A. &Fairén, A. (1978) Smooth and sparsely-spined stellate cells in the visual cortex of the rat: A study using a combined Golgi-electron microscope technique.Journal of Comparative Neurology 181, 129–72.
Peters, A., Palay, S. &Webster, H. deF (1976)The Finé Structure of the Nervous System: The Neurons and Supporting Cells. Philadelphia, London, Toronto: W. B. Saunders Company.
Raedler, E. &Raedler, A. (1978) Autoradiographic study of early neurogenesis in rat neocortex.Anatomy and Embryology 154, 267–84.
Raedler, A. &Sievers, J. (1975) The development of the visual system of the albino rat.Advances in Anatomy Embryology and Cell Biology 50, Fasc. 3.
Raedler, A. &Sievers, J. (1976) Light and electron microscopical studies on specific cells of the marginal zone in the developing rat cerebral cortex.Anatomy and Embryology 149, 173–81.
Retzius, G. (1981) Über den Bau der Oberflächenschicht der Grosshirnrinde bei Menschen und bei den Säugetieren.Verhandlungen biologische Vereins (Stockholm) 3, 90–102.
Retzius, G. (1893) Die Cajalschen Zellen der Grosshirnrinde bei Menschen und bei Säugethieren.Biologische Untersuchungen Neue Folge 5, 1–8.
Rickmann, M., Chronwall, B. M. &Wolff, J. R. (1977) On the development of non-pyramidal neurons and axons outside the cortical plate: The early marginal zone as a palliai anlage.Anatomy and Embryology 151, 285–307.
Sas, E. &Sanides, F. (1970) A comparative Golgi study of Cajal foetal cells.Zeitschrift für mikroskopisch-anatomische Forschung 82, 385–96.
Shoukimas, G. M. &Hinds, J. W. (1978) The development of the cerebral cortex in the embryonic mouse: An electron microscopic serial section analysis.Journal of Comparative Neurology 179, 795–830.
Sievers, J. &Raedler, A. (1981) Light and electron microscopical studies on the development of the horizontal cells of Cajal-Retzius.Bibliotheca Anatomica 19, 161–6.
Veratti, E. (1897) Über einige Structureigentümlichkeiten der Hirnrinde bei den Säugetieren.Anatomischer Anzeiger 13, 379–89.
Wolff, J. R. &Rickmann, M. (1977) Cytological characteristics of early stages of glial differentiation in the neocortex.Folia Morphologica 25, 235–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edmunds, S.M., Parnavelas, J.G. Retzius-Cajal cells: an ultrastructural study in the developing visual cortex of the rat. J Neurocytol 11, 427–446 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01257987
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01257987