Summary
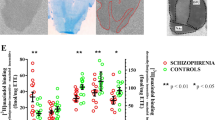
The dopamine-rich regions of post-mortem brains from 6 schizophrenics and 7 controls were analyzed. There were no significant changes in dopamine concentrations in basal ganglia and nucleus accumbens of schizophrenics compared with controls. Schizophrenic basal ganglia (putamen and caudate) showed significantly higher levels of homovanillic acid, and tyrosine hydroxylase activity. Among the schizophrenic patients, markedly high activity of tyrosine hydroxylase was measured in a patient diagnosed as catatonic type. He had not taken antipsychotic drugs for 3 months prior to death. In his relatives, three other schizophrenics were found to the second degree. A remarkable low level of dopamine and a high level of homovanillic acid measured indicate this case would have had an increased turnover rate of dopamine in the dopaminergic nerve terminals. Among the schizophrenic patients, there might be one group whose enzyme activity of dopamine synthesis in the brain is exceptionally high.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolfsson, R., Gottfries, C.-G., Roos, B.-E., Winblad, B.: Post-mortem distribution of dopamine and homovanillic acid in human brain, variations related to age, and a review of the literature. J. Neural Transm.45, 81–105 (1979).
Bacopoulos, N. C., Spokes, E. G., Bird, E. D., Roth, R. H.: Antipsychotic drug action in schizophrenic patients: effect on cortical dopamine metabolism after long-term treatment. Science205, 1405–1407 (1979).
Bird, E. D., Crow, T. J., Iversen, L. L., Longden, A., Mackay, A. V. P., Riley, G. J., Spokes, E. G.: Dopamine and homovanillic acid concentration in the post-mortem brain in schizophrenia. J. Physiol.293, 36–37 (1979).
Carlsson, A., Adolfsson, R., Aquilonius, S.-M., Gottfries, C.-G., Oreland, L., Svennerholm, L., Winblad, B.: Neuroendocrine and neuropsychiatric aspects. In: Ergot Compounds and Brain Function (Goldstein, M., Calne, D. B., Lieberman, A., Tborner, M. O., eds.), pp. 295–304. New York: Raven Press. 1980.
Crow, T. J., Baker, H. F., Cross, A. J., Joseph, M. H., Lofthouse, R., Longden, A., Owen, F., Riley, G. J., Glover, V., Killpack, W. S.: Monoamine mechanisms in chronic schizophrenia: post-mortem neurochemical findings. Brit. J. Psychiat.134, 249–256 (1979).
De Armond, S. J., Fusco, H. M., Dewey, M. M.: Structure of Human Brain. London: Oxford Univ. Press. 1974.
Farley, I. J., Shannak, K. S., Hornykiewicz, O.: Brain monoamine changes in chronic paranoid schizophrenia and their possible relation to increased dopamine receptor sensitivity. In: Receptors for Neurotransmitters and Peptide Hormones (Pepeu, G., Kuhar, M. J., Enna, S. J., eds.), pp. 427–433. New York: Raven Press. 1980.
Lee, T., Seeman, P., Tourtellotte, W. W., Farley, I. J., Hornykiewicz, O.: Binding of3H-neuroleptics and3H-apomorphine in schizophrenic brains. Nature274, 879–900 (1978).
Livrea, P., de Reda, N., de Blasi, A., Bertolino, A.: Homovanillic acid (HVA) and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) in human brain areas at autopsy. Effect of predeath conditions with special attention to the state of consciousness and metabolic diseases. Acta Neurol. (Napoli)33, 487–500 (1978).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem.193, 265–275 (1951).
Mackay, A. V. P., Doble, A., Bird, E. D., Spokes, E. G., Quik, M., Iversen, L. L.:3H-spiperone binding in normal and schizophrenic post-mortem human brain. Life Sci.23, 527–532 (1978).
Nagatsu, T., Oka, K., Kato, T.: Highly sensitive assay for tyrosine hydroxylase activity by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr.163, 247–252 (1978).
Owen, F., Cross, A. J., Crow, T. J., Longden, A., Paulter, M., Riley, G. J.: Increased dopamine-receptor sensitivity in schizophrenia. Lancet1978, 223–225.
Reynolds, G. P., Reynolds, L. M., Riederer, P., Jellinger, K., Gabriel, E.: Dopamine receptors and schizophrenia: drug effect or illness. Lancet1980, 1251.
Riley, H. A.: An Atlas of the Basal Ganglia, Brain Stem and Spinal Cord-Based on Myelin-stained Material. Hafner Publishing Company. 1960.
Sedvall, G. C., Wode-Helgodt, B.: Aberrant monoamine metabolite levels in CSF and family history of schizophrenia. Their relationships in schizophrenic patients. Arch. Gen. Psychiat.37, 1113–1116 (1980).
Stevens, J.: Striatal function and schizophrenics. In: Psychobiology of the Striaturri (Cools, A. R., Lohman, A. H. M., van den Bercken, J. H. L., eds.), pp. 173–194. Amsterdam: Elsevier. 1977.
Toru, M., Malaga, N., Takashima, M., Nishikawa, T.: Enhancement of haloperidol-induced increase in rat striatal or mesolimbic 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and homovanillic acid by pretreatment of chronic methamphetamine. Psychopharmacol.74, 316–320 (1981).
Watanabe, S., Toru, M., Ichiyama, A., Kataoka, T.: The activity of rat pineal and brain tyrosine hydroxylase during the daily cycle of light and darkness as determined by the modified14CO2 assay method. J. Neurochem.36, 266–275 (1981).
Westerink, B. H. C.: Further studies on the sequence of dopamine metabolism in the rat brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol.56, 313–322 (1979).
Winblad, B., Bucht, G., Gottfries, G., Roos, B.-E.: Monoamines and monoamine metabolites in brains from demented schizophrenics. Acta psychiat. scand.60, 17–28 (1979).
Yarden, P. E., Discipio, W. J.: Abnormal movements and prognosis in schizophrenia. Amer. J. Psychiat.128, 317–323 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toru, M., Nishikawa, T., Mataga, N. et al. Dopamine metabolism increases in post-mortem schizophrenic basal ganglia. J. Neural Transmission 54, 181–191 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01254928
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01254928