Summary
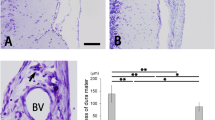
Using fluorescence histochemistry, 5-HT, histamine and heparin were colocalized in a large population of cells in the dura mater thereby identifying them as mast cells. In addition, because these cells were highly sensitive to compound 48/80 and were densely packed with granules of a consistent density, they were identified specifically as ‘connective tissue’ mast cells. Other types of mast cells, i.e. ‘mucosal’ or ‘neurolipomastocytes’, were not present in the rat dura mater. 5-HT immunohistochemistry was the best technique for demonstrating that there were two populations of mast cells, one associated with each of the two layers of dura. Although shaped differently the type of mast cell in each layer was the same. It was observed that mast cell shape is dependent on the contiguity, density and orientation of its surrounding elements, not its type. In general, mast cells in the outer layer were aligned parallel to the middle meningeal artery and those in the inner layer were parallel to trigeminal nerve branches that coursed obliquely across the middle meningeal artery. Examination of cross-sections of dura revealed that most mast cells also were aligned at the interface between the two dural layers. The linear orientation of mast cells in two planes of each layer suggests a programmed lamellar seeding of these cells during development of the dura. This study also demonstrated that the majority of dural mast cells were more closely related to other connective tissue elements than to blood vessels and nerves. These results (1) are compatible with the suggestion that dural mast cells play a non-obligatory role in the neuroinflammatory response, (2) leave open to question the role of the dural mast cell in headache or the regulation of blood flow, and (3) support evidence that dural mast cells play an important role in connective tissue related functions, e.g. development, inflammatory response to injury and wound repair.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andres, K. H. (1967) Über die Feinstruktur der Arachnoidea und Dura mater von Mammalia.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung 79, 272–95.
Andres, K. H., Von Düring, M., Muszynski, K. &Schmidt, R. F. (1987) Nerve fibres and their terminals of the dura mater encephali of the rat.Anatomy and Embryology 175, 289–301.
Appenzeller, O., Becker, W. J. &Ragaz, A. (1981) Cluster headache: ultrastructural aspects and pathogenetic mechanisms.Archives of Neurology 38, 302–6.
Arnold, W. &Huth, F. (1978) Electron microscopic findings in four cases of nasopharyngeal fibroma.Virchows Archiv A 378, 285–98.
Baraniuk, J. N., Kowalski, M. L., &Kaliner, M. A. (1990) Relationships between permeable vessels, nerves, and mast cells in rat cutaneous neurogenic inflammation.Journal of Applied Physiology 68, 2305–11.
Benditt, E. P., Wong, R. L., Arase, M. &Roeper, E. (1955) 5-Hydroxytryptamine in mast cells.Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine 90, 303–4.
Christoffersen, P. &Poulsen, H. (1979) Alcoholic liver disease. InPathology of the Liver (edited byMacSween, R. N. M., Anthony, P. P. &Scheuer, P. J.) pp. 232. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
Csaba, G. &Kovács, P. (1975) Demonstration of the heterogeneity of the mast cell population on the basis of the mucopolysaccharide content,Acta Morphologica Academy of Sciences of Hungary 23, 227–33.
Dabrowski, R. &Szczepanowska, A. (1985) Histamine and collagen levels in the lathyritic chick embryos after administration of 48/80.Agents and Actions 16, 3–4.
De La Torre, J. C. &Surgeon, J. W. (1976) A methodological approach to rapid and sensitive monoamine histofluorescence using a modified glyoxylic acid technique: the SPG method.Histochemistry 49, 81–93.
D'Ermo, F. &Cricchi, M. (1963) Sull'azione di farmaci istaminoliberatori sulle mastzellen di coroide di cavia.Giornale Italiano di Oftalmologia 16, 119–31.
Dimitriadou, V., Aubineau, P., Taxi, J. &Seylaz, J. (1987) Ultrastructural evidence for a functional unit between nerve fibers and type II cerebral mast cells in the cerebral vascular wall.Neuroscience 22, 621–30.
Dimlich, R. V. W. (1984) Electron microscopic examination of mast cells and nerve processes in hepatic portal areas of the rat. InProceedings of the 42nd Annual Meeting of the Electron Microscopy Society of America (edited byBailey, G. W.) pp. 230–1. San Francisco: San Francisco Press.
Dimlich, R. V. W. (1990) ‘Neurolipomastocyte’ of the rat brain: a misnomer.Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 16, 246.
Dimlich, R. V. W., Meineke, H. A., Reilly, F. D. &McCuskey, R. S. (1980a) The fluorescent staining of heparin in mast cells using Berberine Sulphate: compatability with paraformaldehyde or o-phthalaldehyde induced fluorescence and metachromasia.Stain Technology 55, 217–23.
Dimlich, R. V. W., Reilly, F. D., Meineke, H. A. &McCuskey, R. S. (1980b) Characterization of intensely fluorescent cells in the liver of the rat. I. Histochemistry and 48/80-induced degranulation.Anatomical Record 198, 475–84.
Douglas, W. W. (1974) Involvement of calcium in exocytosis and the exocytosis-vesiculation sequence.Biochemical Society Symposium 39, 1–28.
Edvinsson, L., Cervós-Navarro, J., Larsson, L.-I., Owman Ch. &Rönnberg, A-L. (1977) Regional distribution of mast cells containing histamine, dopamine, or 5-hydroxytryptamine in the mammalian brain.Neurology 27, 878–83.
Enerbäck, L. (1966) Mast cells in rat gastrointestinal mucosa. 1. Effects of fixation.Acta Pathologica et Microbiologica Scandinavia 66, 289–302.
Enerbäck, L. (1974a) Berberine sulphate binding to mast cell polyanions: a cytofluorometric method for the quantitation of heparin.Histochemistry 42, 301–13.
Enerbäck, L. (1974b) Ultrastructure of mucosal mast cells in normal and compound 48/80-treated rats.Cell and Tissue Research 150, 95–105.
Faraci, F. M., Kadel, K. A., &Heistad, D. D. (1989) Vascular responses of dura mater.American Journal of Physiology 257, H157-H161.
Fawcett, D. W. (1955) An experimental study of mast cell degranulation and regeneration.Anatomical Record 121, 29–51.
Gabbiani, G., Badonnel, M. C. &Majno, G. (1970) Intra-arterial injections of histamine, serotonin, or bradykinin: a topographic study of vascular leakage.Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine 135, 447–52.
Galli, S. J. (1987) New approaches for the analysis of mast cell maturation, heterogeneity, and function.Federation Proceedings 46, 1906–14.
Galli, S. J. (1990) New insights into ‘the riddle of the mast cells’: microenvironmental regulation of mast cell development and phenotypic heterogeneity.Laboratory Investigation 62, 5–33.
Gamble, H. J. &Goldby, S. (1961) Mast cells in peripheral nerve trunks.Nature 189, 766–7.
Gietzen, K. (1983) Comparison of calmodulin anatagonists compound 48/80 and calmidazolium.Biochemical Journal 216, 611–16.
Gietzen, K., Adamczyk-Engelmann, P., Wuthrich, A., Konstantinova, A. &Bader, H. (1983) Compound 48/80 is a selective and powerful inhibitor of calmodulin-regulated functions.Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 736, 109–18.
Giordano-Lanza, G., Fusaroli, P., Bratina, F. &Cirino, L. V. (1972) Sulla innervazione della pachimeninge encefalica.Quaderni di Anatomia Pratica S. 28, 1–4.
Goldberg, B. &Rabinovitch, M. (1977) Connective tissue. InHistology (edited byWeiss, L. &Greep, R. O.) pp. 145–249. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Hals, E. (1970) Some methods for fluorochromatin and staining of rat mast cells with basic dyes.Scandinavian Journal of Dental Research 78, 301–10.
Hamilton, W. J. &Mossman, H. W. (1972)Human Embryology, p. 165. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins.
Heinrich, J. &Zimmermann, R. E. (1984) Compound 48/80 is a potent inhibitor of human platelet aggregation antagonizing the calmodulin-dependent platelet reactionin vitro.Thrombosis Research 36, 475–80.
Holmgren, H. &Wilander, O. (1937) Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Chemie und Funktion der Ehrlichschen Mastzellen.Zeitschrift für mikroskopisch-anatomische Forschung 42, 242–77.
Hsu, S.-M., Raine, L. &Fanger, H. (1981) Use of avidinbiotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabelled antibody (PAP) procedures.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 29, 577–80.
Humanson, G. L. (1967)Animal Tissue Techniques, p. 18. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman.
Ibrahim, M. Z. M., Al-Wirr, M. E. &Bahuth, N. (1979) The mast cells of the mammalian central nervous system. III. Ultrastructural characteristics in the adult rat brain.Acta Anatomica 104, 134–54.
Johnson, M. D., Kamso-Pratt, J., Federspiel, C. F. &Whetsell, W. O. (1989) Mast cell and lymphoreticular infiltrates in neurofibromas: comparison with nerve sheath tumors.Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine 113, 1263–70.
Juhlin, L. Shelley, W. B. (1966) Detection of histamine by a new fluorescent o-phthaladehyde stain.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 14, 525–8.
Keller, J. T., Marfurt, C. F., Dimlich, R. V. W. &Tierney, B. E. (1989) Sympathetic innervation of the supratentorial dura mater of the rat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 290, 310–21.
Kiernan, J. A. (1976) A comparative survey of the mast cells of the mammalian brain.Journal of Anatomy 121, 303–11.
Kimura, S. (1979) Mast cells in solitary glomus tumors: a possible algogenic role.Acta Dermatovener 59, 415–19.
Kitamura, Y., Go, S. &Hatanaka, S. (1978) Decrease of mast cells in W/W mice and their increase by bone marrow transplantation.Blood 52, 447–52.
Lagunoff, D. (1972) Contributions of electron microscopy to the study of mast cells.Journal of Investigative Dermatology 58, 296–311.
Lagunoff, D. &Chi, E. Y. (1978) Mast cell secretion: membrane events.Journal of Investigative Dermatology 71, 81–4.
Liberski, P. P. &Prusiński, A. (1982) Further observations on the mast cells over the painful region in cluster headache patients.Headache 22, 115–17.
Markowitz, S., Saito, K., Buzzi, M. G. &Moskowitz, M. A. (1989) The development of neurogenic plasma extravasation in the rat dura mater does not depend upon the degranulation of mast cells.Brain Research 477, 157–65.
Markowitz, S., Saito, K. &Moskowitz, M. A. (1987) Neurogenically mediated leakage of plasma protein occurs from blood vessels in dura mater but not brain.Journal of Neuroscience 7, 4129–36.
Marom, Z. &Casale, T. B. (1983) Mast cells and their mediators.Annals of Allergy 50, 367–70.
Matsuura, N. &Zetter, B. R. (1989) Stimulation of mast cell chemotaxis by interleukin 3.Journal of Experimental Medicine 170, 1421–6.
Michels, N. A. (1938) The mast cells.Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 103, 232–372.
Moskowitz, M. A. (1984) The neurobiology of vascular head pain.Annals of Neurology 16, 157–68.
Moskowitz, M. A., Markowitz, S. &Saito, K. (1987) Ergot alkaloids specifically block neurogenically-induced plasma extravasation in rat dura: mechanism of action in vascular headaches.Federation Proceedings 46, 634.
Moskowitz, M. A., Reinhard, J. F., Romero, J., Melamed, E. &Pettibone, D. J. (1979) Neurotransmitters and the fifth cranial nerve: is there a relation to the headache phase of migraine?Lancet ii, 883–5.
Mota, I., Beraldo, W. T. &Junqueira, L. C. U. (1953) Protamine-like property of compounds 48/80 and stilbamidine and their action on mast cells.Proceedings of the Society of Experimental Biology and Medicine 83, 455–7.
Motavkin, P. A., Chertok, V. M. &Shul'ga, S. D. (1979) Effect of acetylcholine on mast cells of the dura mater.Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine 22, 518–21.
Newson, B., Dahlström, A., Enerbäck, L. &Ahlman, H. (1983) Suggestive evidence for a direct innervation of mucosal mast cells. An electron microscopic study.Neuroscience 10, 565–70.
Norrby, K. (1981) On the 48/80-induced secretion of tissue mast cells and its mitogenic effect on nearby cells in the intact rat.Virchows Archiv B 38, 57–65.
Olsson, Y. (1968) Mast cells in the nervous system.International Review of Cytology 24, 27–70.
O'Rahilly, R. &Müller, F. (1986) The meninges in human development.Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 45, 588–608.
Orr, E. L. (1984) Dural mast cells: source of contaminating histamine in analyses of mouse brain histamine levels.Journal of of Neurochemistry 43, 1497–9.
Paff, G. M. &Mergenthaler, D. D. (1955). Vacuolation in normal mast cells treated with protamine sulphate.Anatomical Record 121, 579–92.
Pearce, F. L. (1983) Mast cell heterogeneity.Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 4, 165–7.
Pearse, A. G. E. (1968)Histochemistry, Vol. 1, pp. 667–8. Boston: Little Brown.
Pease, D. C. &Schultz, R. L. (1958) Electron microscopy of rat cranial meninges.American Journal of Anatomy 102, 301–21.
Rao, P. V. S., Friedman, M. M., Atkins, R. M. &Metcalfe, D. D. (1983) Phagocytosis of mast cell granules by cultured fibroblasts.Journal of Immunology 130, 341–9.
Reilly, F. D., Dimlich, R. V. W., Cilento, E. V. &McCuskey, R. S. (1983) Hepatic microvascular regulatory mechanisms. III. Aminergic mechanisms as related to mast cells.International Journal of Microcirculation: Clinical Experiments 2, 61–73.
Rice, W. R. &Whitsett, J. A. (1984) Inhibition of surfactant release from isolated Type II cells by compound 48/80.Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 805, 261–7.
Riley, J. F. (1953) The effects of histamine-liberators on the mast cells of the rat.Journal of Pathology and Bacteriology 65, 471–9.
Riley, J. F. (1959)The Mast Cells. Edinburgh and London: E. & S. Livingstone.
Riley, J. F. &West, G. B. (1952) Histamine in tissue mast cells.Journal of Physiology 117, 72P-73P.
Riley, J. F. &West, G. B. (1953) The presence of histamine in tissue mast cells.Journal of Physiology 120, 528–37.
Röhlich, P., Anderson, P. &Uvnäs, B. (1971) Electron microscopic observations on Compound 48/80-induced degranulation in rat mast cells.Journal of Cell Biology 51, 465–83.
Rosenblum, W. I. (1973) A possible role for mast cells in controlling the diameter of arterioles on the surface of the brain.Brain Research 49, 75–82.
Sagher, F. &Even-Paz, Z. (1967)Mastocytosis and the Mast Cell, pp. 10–324. Chicago: Yearbook Medical Publisher.
Selye, H., Gabbiani, G. &Nielsen, K. (1963) The ‘periosteal spread’ technic for study of mast cells.Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine 112, 460–3.
Selye, H. (1965)The Mast Cells. Washington: Butterworths.
Skofitsch, G., Savitt, J. M. &Jacobowitz, D. M. (1985) Suggestive evidence for a functional unit between mast cells and substance P fibers in the rat diaphragm and mesentery.Histochemistry 82, 5–8.
Smith, D. E. (1963) Electron microscopy of normal mast cells under various experimental conditions.Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 103, 40–52.
Spicer, S. S. (1962) Basic protein visualized histochemically in mucinous secretions.Experimental Cell Research 28, 480–8.
Stevens, R. L. &Austen, K. F. (1989) Recent advances in the cellular and molecular biology of mast cells.Immunology Today 10, 381–6.
Tharp, M. D. (1989) The interaction between mast cells and endothelial cells.Journal of Investigative Dermatology 93, 107S-112S.
Theoharides, T. C. (1983) Mast cells and migraines.Perspectives in Biology and Medicine 26, 672–5.
Theoharides, T. C. (1990) Mast cells: the immune gate to the brain.Life Sciences 46, 607–17.
Waggener, J. D. &Beggs, J. (1967) The membranous coverings of neural tissues: an electron microscopy study.Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 26, 412–26.
Wienser-Menzel, L., Schulz, B., Vakilzadeh, F. &Czarnetzki, B. M. (1981) Electron microscopical evidence for a direct contact between nerve fibres and mast cells.Acta Dermatovener 61, 465–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dimlich, R.V.W., Keller, J.T., Strauss, T.A. et al. Linear arrays of homogenous mast cells in the dura mater of the rat. J Neurocytol 20, 485–503 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01252276
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01252276