Summary
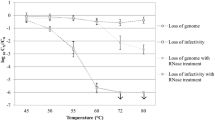
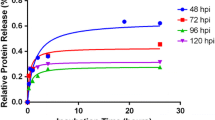
Using conventional procedures of extraction with diethyl ether to remove phenol, the infective poliovirus RNA titer was found to be 5 to 100 times greater when the virus stock was diluted about one-hundredfold into certain diluents prior to treatment with phenol (560 mM) than when undiluted stock was treated. Diluents giving this result were calcium-free, magnesium-free, mildly alkaline (pH 7–11) solutions, notably, e. g., 10 mM NaHCO3. The milieu afforded by such diluents was not necessary for the treatment with phenol but was necessary primarily to prevent “inactivation” of the poliovirus RNA by the ether; however, even without exposure to ether and with no extractions to remove phenol, mildly acid conditions or a moderate concentration of Ca++ resulted in some loss of infective RNA titer. Assay of ethereal phase detected no infectivity. Even with added base and chelating agent, extractions of phenol-treated essentially undiluted virus stocks with ether resulted in large loss of infective RNA titer. Extractions with benzene in place of ether had little or no effect on RNA titer using diluted systems; but with undiluted systems, a large titer loss was found. Treatment with ether without extractions with ether also inactivated RNA. Using heat shock (70° C, 20 seconds) in place of phenol to obtain infective RNA, the nature of the diluent required to give high infective RNA titer was very different from that required for the prephenol dilution when the conventional extractions with ether were employed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, S. G., andG. L. Ada: “Murray Valley Encephalitis Virus: Preparation of an Infective ‘Ribonucleic Acid’ Fraction.” Aust. J. exp. Biol. med. Sci.37, 353–364 (1959).
Dubes, G. R., M. Chapin, andO. Tolbert: “The Genetic Relationship Between Thermostability of Poliovirus and Itsin vivo Response to Cystine.” Arch. ges. Virusforsch.10, 315–334 (1960).
Dubes, G. R., F. H. Faas, D. G. Kelly, M. Chapin, R. D. Lamb, andT. A. Lucas: “A Study of the Facilitation of Infection with Surviving Poliovirus Units.” J. infect. Dis.114, 346–358 (1964).
Dubes, G. R., andE. A. Klingler, Jr.: “Facilitation of Infection of Monkey Cells with Poliovirus ‘Ribonucleic Acid’.” Science133, 99–100 (1961).
Dubes, G. R., andH. Rouhandeh: “Interference Between Poliovirus Ribonucleic Acids.” Arch. ges. Virusforsch.14, 87–98 (1963).
Dulbecco, R., andM. Vogt: “Plaque Formation and Isolation of Pure Lines of Poliomyelitis Viruses.” J. exp. Med.99, 167–182 (1954).
Fraenkel-Conrat, H.: “The Infectivity of Tobacco Mosaic Virus Nucleic Acid”, pp. 217–225, “Cellular Biology, Nucleic Acids, and Viruses”. ed. v. St. Whitelock, New York Academy of Sciences, New York, 1957.
Gierer, A., andG. Schramm: “Infectivity of Ribonucleic Acid from Tobacco Mosaic Virus.” Nature (Lond.)177, 702–703 (1956).
Klingler, E. Jr., M. Chapin, andG. R. Dubes: “Relationship Between Inactivation of Poliovirus by Phenol and Appearance of Ribonucleaselabile Infectivity.” Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.)101, 829–832 (1959).
Lamb, R. D., M. Chapin, andG. R. Dubes: “Factors Affecting the Titer of Infective RNA Present After Treatment of Lysates of Poliovirus-infected Cells with Phenol or Heat.” Genetics49, 263–264 (1964).
Lamb, R.D., andG. R. Dubes: “Chromatography of Enteroviral Ribonucleic Acids on Hydromagnesite.” Analyt. Biochem.7, 152–163 (1964).
Rouhandeh, H., andG. R. Dubes: “Destruction of Enteroviral Ribonucleic Acid Infectivity by Phosphodiesterase.” Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.)116, 133–136 (1964).
Rouhandeh, H., andG. R. Dubes: “A Study of the Nature of the Interfering Material in Preparations of Poliovirus Ribonucleic Acid.” Arch. ges. Virusforsch.15, 1–6 (1964).
Tolbert, O., andR. Engler: “Isolation of Infectious Poliovirus Ribonucleic Acid from Supernatant Fluids after Ultracentrifugation.” Nature (Lond.)200, 498–499 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Aided by a grant from the National Foundation. Part of these results were presented on August 25, 1964, at a meeting of the Genetics Society of America at the University of Colorado, Boulder.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamb, R.D., Chapin, M. & Dubes, G.R. Effect of ether and Ca++ on infectivity of poliovirus RNA. Archiv f Virusforschung 15, 486–499 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01245240
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01245240