Summary
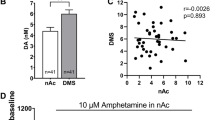
The effects of acute and chronic administration of lithium (Li) on the basal levels of dopamine (DA), dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC), homovanillic acid (HVA) and 5-hydroxy-indoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), and the amphetamine-induced DA increase were assessed in the Nucleus Accumbens (NAC) and Prefrontal Cortex (PFC) by brain dialysis in freely-moving rats. Acute Li (2meq/L) was locally administered by reverse dialysis. Chronic Li (2 meq/kg) was intragastrically administered for 14 days. No effect was observed after acute Li administration. However, after chronic Li administration, the basal levels of DOPAC and the amphetamine-induced DA increase in the NAC were significantly higher in the Li-treated rats than in the saline-treated controls. In the PFC, while the amphetamine-induced DA increase was not affected by chronic Li, the basal levels of DA and DOPAC were significantly decreased after Li administration. The effects of chronic Li in the NAC could be due to increased synthesis and/or decreased release of DA, whereas in the PFC the effects could be due to a decreased synthesis of DA. The absence of effects of acute Li administration is in agreement with the therapeutic inefficacy of the acute use of the cation. The changes observed after chronic treatment in the NAC and the PFC could be related to the effects of Li on mood disorders and cognitive functions, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baptista T, Hernández L, Burguera JL, Burguera M, Hoebel BG (1990) Chronic lithium administration enhances serotonin release in the lateral hypothalamus but not in the hippocampus in rats. A microdialysis study. J Neural Transm 82: 31–41
Berggren U (1985) Effects of chronic lithium treatment on brain monoamine metabolism and amphetamine-induced locomotor stimulation in rats. J Neural Transm 64: 239–250
Bliss EL, Ailion J (1970) The effect of lithium on brain neuroamines. Brain Res 24: 305–310
Bloom FE, Baetge G, Deyo S, Ettenberg A, Koda L, Magistretti PJ, Shoemaker WJ, Staunton DA (1983) Chemical and physiological aspects of the action of lithium and antidepressant drugs. Neuropharmacology 22: 359–365
Bowers MB, Rozitis A (1982) Dopamine metabolites and catalepsy after lithium and haloperidol. Eur J Pharmacol 78: 113–115
Bunney WE, Garland BL (1983a) A second generation catecholamine hypothesis. Pharmacopsychiatry 15: 111–115
Bunney WE, Garland BL (1983b) Possible receptor effects of chronic lithium administration. Neuropharmacology 22: 367–372
Camp DM, Robinson TE (1992) On the use of multiple probe insertions at the same time for repeated intracerebral microdialysis experiments in the nigrostriatal dopamine system in rats. J Neurochem 58: 1706–1712
Corrodi H, Fuxe K, Schou M (1969) The effect of prolonged lithium administration on cerebral monoamine neurons in the rat. Life Sci 8: 643–651
Ellison G, Eison M, Huberman H, Daniel F (1978) Long-term changes in dopaminergic innervation of caudate nucleus after continuous amphetamine administration. Science 201: 276–278
Friedman E, Gershon S (1973) Effect of lithium on brain dopamine. Nature 243: 520–521
Fuller R, Hemrick-Luecke S (1980) Long-lasting depletion of striatal dopamine by a single injection of amphetamine in iprindole-treated rats. Science 209: 305–307
Hernández L, Parada MA, Hoebel BG (1983) Amphetamine-induced hyperphagia and obesity caused by intraventricular or lateral hypothalamic injections in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227: 524–530
Hernández L, Stanley BG, Hoebel BG (1986) A small, removable microdialysis probe. Life Sci 39: 2629–2637
Hernández L, Lee F, Hoebel BG (1987) Simultaneous microdialysis and amphetamine infusion in the nucleus accumbens and striatum of freely moving rats: increase in extracellular dopamine and serotonin. Brain Res Bull 19 (6): 623–628
Ho AK, Loh HH, Cravevs F, Hitzemann RJ, Gershon S (1970) The effect of prolonged lithium treatment on the synthesis rate and turnover of monoamines in brain regions of rats. Eur J Pharmacol 10: 72–78
Kersten L (1987) The gastrointestinal system. In: Johnson FN (ed) Depression and mania. Modern lithium therapy. IRL Press, Oxford, pp 196–201
Kupfermann I (1991) Localization of higher cognitive and affective functions: the association cortices. In: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM (eds) Principles of neural science. Elsevier Science Publishing Co, New York, pp 823–838
McIntyre IM, Kuhn C, Demitriou S, Fucek FR, Stanley M (1983) Modulating role of lithium on dopamine turnover, prolactin release, and behavioral supersensitivity following haloperidol and reserpine. Psychopharmacology 81: 150–154
Müller-Oerlinghausen B (1987) Mental functioning. In: Johnson FN (ed) Depression and mania. Modern lithium therapy. IRL Press, Oxford, pp 246
Otero-Losada ME, Rubio MC (1985) Striatal dopamine and motor activity changes observed shortly after lithium administration. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 330: 169–174
Paxinos G, Watson Ch (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego
Pert A, Rosenblatt JE, Sivit C, Pert CB, Bunney WE (1978) Long-term treatment with lithium prevents the development of dopamine receptor supersensitivity. Science 201: 171–173
Pittman KJ, Jakubovic A, Fibiger HC (1984) The effects of chronic lithium on behavioral and biochemical indices of dopamine receptor supersensitivity in the rat. Psychophar-macology 82: 371–377
Poitou P, Bohuon C (1975) Catecholamine metabolism in the rat brain after short- and long-term lithium administration. J Neurochem 25: 535–537
Porot M, Francois MA, Francoism A, Planche R, Aubin B, Ganclus F, Merat VPM (1980) ivité anndépressive de l'amineptine. Etude controleé á double insu. Therapie 35: 733–742
Post R (1989) Mood disorders: somatic treatment. In: Kaplan HI, Sadock BJ (eds) Comprehensive textbook of psychiatry/V, chapter 17.4. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 913–931
Poust RI (1987) Kinetic and tissue distribution. In: Johnson FN (ed) Depression and mania. Modern lithium therapy. IRL Press, Oxford, pp 73–74
Reches A, Jackson-Lewis V, Fahn S (1984) Chronic lithium administration has no effect on haloperidol-induced supersensitivity of pre- and postsynaptic dopamine receptors in rat brain. Brain Res 246: 172–177
Rocks BF, Sherwood RA, Riley C (1982) Direct determination of therapeutic concentrations of lithium in serum by flow-injection analysis with atomic absorption spectroscopic detection. Clin Chem 28: 440–443
Schildkraut JJ (1965) The catecholamine hypothesis of affective disorders: a review of supporting evidence. Am J Psychiatry 122: 509–513
Schubert J (1973) Effect of chronic lithium treatment on monoamine metabolism in rat brain. Psychopharmacology 32: 301–311
Staunton DA, Magistretti PJ, Shoemaker WJ, Deyo SN, Bloom FE (1982) Effects of chronic lithium treatment on dopamine receptors in the rat corpus striatum. II. No effect on denervation or neuroleptic-induced supersensitivity. Brain Res 232: 401–412
Waldmeier PC (1987) Is there a common denominator for the antimanic effect of lithium and anticonvulsivants? Pharmacopsychiatry 20: 37–47
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baptista, T., Teneúd, L., Contreras, Q. et al. Effects of acute and chronic lithium treatment on amphetamine-induced dopamine increase in the nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex in rats as studied by microdialysis. J. Neural Transmission 94, 75–89 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01245002
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01245002