Summary
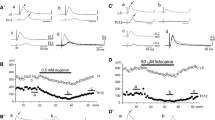
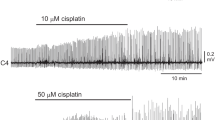
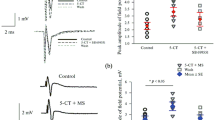
The porphyrin precursorsδ-aminolevulinic acid (δ-ALA) and porphobilinogen (PBG) which accumulate, and are excreted in the urine in increased amounts during acute attacks of porphyria, were tested for their effects on reflex activity in the isolated hemisected spinal cords ofXenopus laevis. The two compounds were found to exert an inhibitory effect on monosynaptic ventral root responses, as well as on dorsal root responses (DRR) and dorsal root potentials (DRP). The latent period for inhibition of the monosynaptic response was longer than that for the DRR and DRP. The sensitivity of the preparations to the effect of the porphyrin precursors was subject to some seasonal variation.δ-ALA and PBG did not effect conduction in isolated sciatic nerves at a concentration of 1 mg/ml.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balcar, V.J., andG. A. R. Johnson: High affinity uptake of transmitters: Studies on the uptake of L-aspartate, GABA, L-glutamate and glycine in cat spinal cord. J. Neurochem.20, 529–539 (1973).
Becker, D. M.: Ph. D. Thesis. Porphyrin precursors and their relationship to some aspects of membrane function, pp. 113–140. Johannesburg: Witwatersrand University. 1972.
Becker, D. M., J. D. Viljoen, andS. Kramer: The inhibition of red cell and brain ATPase byδ-aminolevulinic acid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta225, 26–34 (1971).
Becker, D. M., J. D. Viljoen, andS. Kramer:δ-Aminolevulinic acid uptake by slices of rabbit brain cerebral cortex. J. Neurochem. (in press).
Biempica, L., N. Kosower, andA. Novikoff: Cytochemical and ultrastructural changes in rat liver in experimental porphyria. Lab. Invest.17, 171–189 (1967).
Campbell, J. A. H.: The pathology of South African genetic porphyria. S. Afr. J. Lab. Clin. Med.9, 197–203 (1963).
Cavanagh, J. B., andR. S. Mellick: On the nature of peripheral nerve lesions associated with acute intermittent porphyria. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.28, 320–327 (1965).
Cerf, J. A., andG. Carels: Multiple sclerosis: serum factor producing reversible alterations in bioelectric responses. Science152, 1066–1068 (1966).
Curtis, D. R.: Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies (Jasper et al., ed.), p. 105. Boston: Little Brown. 1969.
Curtis, D. R., andJ. C. Watkins: The excitation and depression of spinal neurons by structurely related amino acids. J. Neurochem.6, 117–141 (1960).
Davidoff, R. A., R. P. Shank, L. T. Graham, M. H. Aprison, andR. Werman: Is Glycine a Neurotransmitter? Nature214, 680–681 (1967).
Davidoff, R. A.: Gamma-aminobutyric acid antagonism and presynaptic inhibition in the frog spinal cord. Science175, 331–333 (1972).
De Matteis, F.: Les Maladies du Metabolisme des porphrines 2c Colloque International de Biologie de Saclay (1962).
Denny-Brown, D., andD. Sciarra: Changes in nervous system in acute porphyria. Brain68, 1–16 (1945).
Drury, R. A. B.: A nerve biopsy in acute intermittent porphyria. J. Path. Bact.71, 511 (1956).
Eales, L., E. B. Dowdle, andG. D. Sweeney: The acute porphyric attack. 1. The electrolyte disorder of the acute porphyric attack and the possible role of delta-aminolaevulinic acid. S. Afr. Med. J.17, 89–97 (1971).
Eccles, J. C., andJ. L. Malcolm: Dorsal root potentials of spinal cord. J. Neurophysiol.9, 139–160 (1946).
Feldman, D. S., R. D. Levere, andJ. S. Lieberman: Neuromuscular effects of the porphyrin precursor delta-aminolevulinic acid. J. Clin. Invest.47, 33 A (1968).
Feldman, D. S., R. D. Levere, J. S. Lieberman, R. A. Cardinal, andC. J. Watson: Presynaptic neuromuscular inhibition by porphobilinogen and porphobilin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.68, 383–386 (1971).
Gibson, J. B., andA. Goldberg: The neuropathology of acute porphyria. J. Path. Bact.71, 495–509 (1956).
Goldberg, A., W. D. M. Paton, andJ. W. C. Thompson: Pharmacology of the porphyrins and porphobilinogen. Brit. J. Pharmacol.9, 91–94 (1954).
Holemans, K. C., H. S. Meij, andB. J. Meyer: The existence of a monosynaptic reflex are in the spinal cord of the frog. Exp. Neurol.14, 175–186 (1966).
Holemans, K. C., H. S. Meij, B. J. Meyer, andJ. M. Loots: The use of the South African frog (Xenopus laevis) in the study of spinal reflex physiology. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res.34, 619–631 (1967).
Holemans, K. C., andH. S. Meij: An analysis of some inhibitory mechanisms in the spinal cord of the frog (Xenopus laevis). Pflueger Arch.303, 289–310 (1968).
Isaacson, L. C., R. Douglas, andL. Eales: Inhibition of sodium and water transport byδ-aminolevulinic acid (ALA). S. Afr. Med. J.45, 97–99 (1971).
Jarret, A., C. Rimington, andD. A. Willoughby:δ-Aminolaevulinic acid and Porphyria. Lancet1, 125–127 (1956).
Kandel, E. R., andD. Gardner: The synaptic action mediated by the different branches of a single neuron. Res. Publ., A.R.N.M.D.50, 91 to 146 (1972).
Kosower, N. S., andR. A. Rock: Seizures in experimental porphyria. Nature (London)217, 565–567 (1968).
Loots, J. M., andH. S. Meij: Monosynaptic testing of synaptic efficiency and motoneurone excitability. S. Afr. Med. J.46, 203–207 (1972).
Marcus, R. L., L. Wetterberg, A. Yuwiler, andW. D. Winters: Electroencephalographie and behavioral effects of experimental porphyria in the rat. Electroencephalog. and Clin. Neurophys.29, 602–607 (1970).
Mason, V. R., C. Courville, andE. Ziskind: Porphyrias in human disease. Medicine (Baltimore)12, 355–439 (1933).
McGillion, F. B., M. R. Moore, andA. Goldberg: The effect ofδ-aminolevulinic acid on the spontaneous activity of mice. Scot. Med. J.18, 133 (1973).
Otsuka, M.: The Structure and Function of Nervous Tissue (Bourne, G. H., ed.), pp. 249–289, Vol. IV. New York: Academic Press. 1972.
Shanley, B. C., J. J. F. Taljaard, W. M. Deppe, andS. M. Joubert: Deltaaminolaevulinic acid in acute porphyria. S. Afr. Med. J.46, 84 (1972).
Sweeney, V. P., M. A. Pathak, andA. K. Asbury: Acute intermittent porphyria. Increased ALA-synthetase activity during an acute attack. Brain93, 369–380 (1970).
Taddeini, L., andC. J. Watson: The Clinical Porphyrias. Seminars in Haematology5, 335–369 (1968).
Tebecis, A. K., andJ. W. Phillis: Experiments in Physiology and Biochemistry (Kerkut, G. A., ed.). New York: Academic Press. 1969.
Tschudy, D. P.: Acute intermittent Porphyria. Seminars in Haematology5, 370–379 (1968).
Yuwiler, A., L. Wetterberg, andE. Geller: Tryptophan pyrolase: Tryptophan and tyrosine transaminase changes during allylisopropylacetamide-induced porphyria in the rat. Biochem. Pharmacol.19, 189 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loots, J.M., Becker, D.M., Meyer, B.J. et al. The effect of porphyrin precursors on monosynaptic reflex activity in the isolated hemisected frog spinal cord. J. Neural Transmission 36, 71–81 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01243439
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01243439