Summary
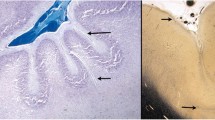
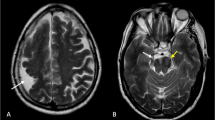
Unlayered polymicrogyria was analyzed in four patients with established lesions and in one 19- to 20-week-old fetus with lesions in a formative stage whose mother had suffered a serious accident two weeks before. Polymicrogyria occurred at the banks of porencephalic, sylvian clefts in three cases, and bilaterally in the watershed areas of the parieto-occipital lobes in a fourth case. Periventricular neuronal heteropias were found in these cases. Cortical lesions in the fetus were distributed along the watershed zones of the middle cerebral artery. Serial sections revealed that the appearance of microgyria was the result of radial tissue cleavage of the cerebral cortex, as shown by the increased numbers of blood vessels and astrocytes forming a tissue scar. Golgi studies disclosed that the different neuronal types were positioned at the apropriate cortical depths in the microgyric cortex. On the other hand, heterotopic nodules were composed of pyramidal and non-pyramidal neurons usually found in the upper cortical layers in the normal cortex. These features indicate that unlayered polymicrogyria is produced by circulatory failure occurring before the end of the period of neuroblast migration to the cortical plate. Circulatory failure in the radial and unbranched arteries that penetrate from the meningeal surface and vascularize the cerebral cortex at midgestation may result in radial tissue necrosis of the cortical mantle, whereas failure in the distal, terminal territories of these blood vessels may damage radial glial fibres and impair the last migration of neuroblasts. The particular morphology of this cortical abnormality finally depends on the imbalance in the tangential growth of adjoining cortical areas variably destroyed by tissue necrosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bankl J, Jellinger K (1967) Zentralnervöse Schäden nach fetaler Kohlenoxidvergiftung. Beitr Pathol Anat 135:350–376
Bar T (1980) The vascular system of the cerebral cortex. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 59:1–65
Barth PG (1987) Disorders of neuronal migration. Can J Neurol Sci 14:1–16
Barth PG, van der Harten JJ (1985) Parabiotic twin syndrome with topical isocortical disruption and gastroschisis. Acta Neuropathol 67:345–349
Bielchowsky M (1916) Über Mikrogyrie. J Psychol Neurol 22:1–47
Caviness VS, Williams RS (1979) Cellular pathology of developing human cortex. In: Katzman R (ed) Congenital and acquired cognitive disorders. Raven Press, New York, pp 69–89
Crome L (1952) Microgyria. J Pathol Bacteriol 64:479–495
Crome L, France NE (1959) Microgyria and cytomegalic inclusion disease in infancy. J Clin Pathol 12:427–434
Dekaban A (1965) Large defects in cerebral hemispheres associated with cortical dysgenesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 24:512–530
DeLeon GA (1972) Observations on cerebral and cerebellar microgyria. Acta Neuropathol 20:278–287
Duckett S (1971) The establishment of internal vascularization in the human telencephalon. Acta Anat 80:107–113
Evrard P, de Saint-Georges P, Kadhim HJ, Gadisseaux JF (1989a) Pathology of prenatal encephalopathies. in: Child neurology and developmental disabilities. Brookes, Baltimore London Sydney Toronto, pp 153–176
Evrard P, Kadhim HJ, de Sant-Georges P, Gadisseux JF (1989b) Abnormal development and destructive processes of the human brain durin the second half of gestation. In: Evrard P, Minkowski A (eds) Developmental Neurobiology. Nestle Nutrition Workshop Series (vol 12), Vevey Raven Press, New York, pp 21–41
Fairen A, DeFelipe J, Regidor J (1984) Nonpyramidal neurons: general account. In: Peters A, Jones EG (eds) Cerebral cortex Vol 1, Cellular components of the cerebral cortex. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 201–253
Ferrer I (1984) A Golgi analysis of unlayered polymicrogyria. Acta Neuropathol 65:69–76
Ferrer I, Sancho S (1987) Non-pyramidal neurons in layers II-III in the dog's cerebral cortex (Parietal lobe). Acta Anat 129:43–52
Ferrer I, Fabregues I, Condom E (1986) A Golgi study of the sixth layer of the cerebral cortex. III Neuronal changes during normal and abnormal cortical folding. J Anat 152:71–82
Ferrer I, Hernadez-Marti M, Bernet E, Galofre E (1988) Formation and growth of the cerebral convolutions. I Postnatal development of the median-suprasylvian gyrus and adjoining sulci in the cat. J Anat 160:89–100
Ferrer I, Hernandez-Marti M, Bernet E, Calopa M (1989) Formation and growth of the cerebral convolutions. II Cell death in the gyrus suprasylvius and adjoining sulci in the cat. Dev Brain Res 45:303–308
Friede RL (1989) Dysplasias of the cerebral cortex. In: Development neuropathology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 330–346
Friede RL, Mikolasek J (1978) Postencephalitic porencephaly, hydranencephaly and polymicrogyria. A review. Acta Neuropathol 43:161–168
Fukuyama Y, Oshawa M, Suzuki H (1981) Congenital progressive muscular dystrophy of the Fukuyama type. Clinical, genetic and pathological considerations. Brain Dev 3:1–29
Hallervorden J (1949) Ueber eine Kohlenoxydvergiftung im Fetalleben mit Entwicklungsstörung der Hirnrinde. Allg Z Psychiatr 124:289–298
Jones EG (1975) Varieties and distribution of non-pyramidal cells in the somatic sensory cortex of the squirrel monkey. J Comp Neurol 160:205–268
Jones EG, Hendry SHC (1984) Basket cells. In: Peters A, Jones EJ (eds) Cerebral cortex (vol 1) Cellular components of the cerebral cortex. Plenum Press, New York, pp 309–336
Kier EL (1974) Fetal cerebral arteries; a phylogenetic and ontogenetic study. In: Newton TH, Potts DG (eds) Pathology of the skull and brain. (vol 2) Mosby, St. Louis, pp 1089–1130
Kuban KCK, Gilles FH (1985) Human telencephalic angiogenesis. Ann Neurol 17:539–548
Larroche JC (1984) Malformations of the nervous system. In: Hume Adams J, Corsellis JAM, Duchen LW (eds) Greenfields's neuropathology. Arnold, London, pp 385–450
Levine DN, Fisher MA, Caviness VS (1974) Porencephaly with microgyria: a pathological study. Acta Neuropathol 29:99–113
Lyon G, Robain O (1967) Etude comparative des encéphalopathies circulatoires prénatales et paranatales (hydranencéphalies, porencéphalies et encéphalomalacies kystiques de la substance blanche). Acta Neuropathol 9:79–98
Nieuwhuijse P (1913) Zur Kenntnis der Mikrogyrie. Psychiatr Neurol BI (Amst) 17:9–53
Norita M, Kawamura K (1981) Non-pyramidal neurons in the medial bank (Clare-Bishop area) of the middle suprasylvian sulcus: a golgi study of the cat. J Hirnforsch 22:9–28
Norman MG (1980) Bilateral encephaloclastic lesions in a 26 week gestation fetus: effect on neuroblast migration. Can J Neurol Sci 7:191–194
Norman MG, O'Kusky JR (1986) The growth and development of microvasculature in human cerebral cortex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 45:222–232
Peters A, Saint-Marie RL (1984) Smooth and sparsely spinous nonpyramidal neurons forming local and axonal plexuses. In: Cerebral cortex (vol 1) Cellular components of the cerebral cortex. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 419–445
Rakic P (1972) Mode of cell migration to the superficial layers of fetal monkey neocortex. J Comp Neurol 145:61–84
Rakic P (1974) Neurons in the rhesus monkey visual cortex: systematic relation between time of origin and eventual disposition. Science 183:425–427
Rakic P (1981) Developmental events leading to laminar and areal organization of the neocortex. In: Schmitt FO, Worden FG, Adelman G, Dennis SG (eds) The organization of the cerebral cortex. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 7–28
Rakic P (1988) Specification of cerebral cortical areas. Science 241:170–176
Richman DP, Stewart RM, Caviness VS (1974) Cerebral microgyria in a 27-week fetus: an architectonic and topographic analysis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 33:374–384
Smart IHM, McSherry GM (1986a) Gyrus formation in the cerebral cortex in the ferret. I Description of the external changes. J Anat 146:141–152
Smart IHM, McSherry GM (1986b) Gyrus formation in the cerebral cortex of the ferret. II Description of the internal histological changes. J Anat 147:27–43
Takada K, Nakamura H, Takashima S (1988) Cortical dysplasia in Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy (FCMD): a Golgi and angioarchitectonic analysis. Acta Neuropathol 76:170–178
Towfighi J, Sassani JW, Suzuki K, Ladda RL (1984) Cerebroocular dysplasia-muscular dystrophy (COD-MD) syndrome. Acta Neuropathol 65:110–123
Urich H (1976) Malformations of the nervous system, perinatal damage and related conditions in early life. In: Blackwood W, Corsellis JAN (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology. Arnold, Edinburgh, pp 361–469
Williams RS, Ferrante RJ, Caviness VS (1976) The cellular pathology of microgyria. Acta Neuropathol 36:269–283
Williams RS, Swisher CN, Jennings M, Ambler M, Caviness VS (1984) Cerebro-ocular dysgenesis (Walker-Warburg syndrome): neuropathological and etiologic analysis. Neurology 34:1531–1541
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrer, I., Catalá, I. Unlayered polymicrogyria : structural and developmental aspects. Anat Embryol 184, 517–528 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01236058
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01236058