Abstract
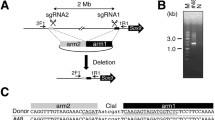
Spontaneous deletion mutants can be isolated from CHO cell lines heterozygous at the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus at frequencies up to 10−4, i.e., about 100-fold higher than spontaneous point mutations. Indirect evidence has suggested that most deletions were in the megabase range. We have fully characterized one such mutant, Del 155, and shown that it resulted from an illegitimate recombination that took place between overlapping tetranucleotides. Comparisons with sequences of other deletions at various loci revealed a number of similarities, most striking of which was a CHI-like motif found within 6 bp of the upstream breakpoint of Del 155 and breakpoints of 8/21 previously described short deletions at the CHO aprt locus. Homology also existed between the downstream breakpoint of Del 155 and breakpoints of retinoblastoma gene deletions (3/6 cases) and also a 20-bp stretch of an Alu sequence in which breakpoints at the low-density lipoprotein receptor locus have been shown to cluster. The magnitude of the deletion event in Del 155 was assessed by pulsed field (PF) gel analysis and found to be at least 2100 kb long. PF analysis also indicated that the downstream breakpoint was near a region of structural differences between the two chromosomes carrying aprt. These structural differences were probably not implicated in the mechanism of the high frequency event, since no indication of breakpoint clustering among a large collection of mutants was found either by conventional or PF electrophoretic analyses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Den Dunne, J.T., Grootscholten, P.M., Bakker, E., Blonden, L.A.J., Ginjaar, H.B., Wapenaar, M.C., Van Paassen, H.M.B., Van Broeckhoven, C., Pearsen, P.L., and Van Ommen, G.J.B. (1989).Am. J. Hum. Genet. 45835–847.
Gillard, E.F., Chamberlain, J.S., Murphy, E.G., Duff, C.L., Smith, B., Burghes, A.H.M., Thompson, M.W., Sutherland, J., Oss, I., Bodrug, S.E., Klamut, H.J., Ray, P.N., and Worton, R.G. (1989).Am. J. Hum. Genet. 45507–520.
Gillard, E.F., Affara, N.A., Yates, J.R.W., Goudie, D.R., Lambert, J., Aitken, D.A., and Ferguson-Smith, M.A. (1987).Nucleic Acids Res. 153977–3985.
Yen, P.H., Allen, E., Marsh, B., Mohandas, T., Wang, N., Taggart, R.T., and Shapiro, L.J. (1987).Cell 49443–454.
Friend, S.H., Bernards, R., Rogelj, S., Weinberg, R.A., Rapaport, J.M., Albert, D.M., and Dryja, T.P. (1986).Nature 323643–646.
Friend, S.H., Horowitz, J.M., Gerber, M.R., Wang, X.F., Bogenmann, E., Li, F.P., and Weinberg, R.A. (1987).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 849059–9063.
Fung, Y.K.T., Murphree, A.L., Tang, A., Qian, J., Hinrichs, S.H., and Benedict, W.F. (1987).Science 2361657–1661.
Goddard, A.D., Balakier, H., Canton, M., Dunn, J., Squire, J., Reyes, E., Becher, A., Phillips, R.A., and Gallie, B.L. (1988).Mol. Cell. Biol. 82082–2088.
Whang-Peng, J., Bunn, P.A., Kao-Shan, C.S., Lee, E.C., Carney, D.N., Gazdar, A., and Minna, J.D. (1982).Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 6119–134.
Dewyse, P., and Bradley, W.E.C. (1989).Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 1519–28.
Adair, G.M., Stallings, R.L., Nairn, R.S., and Siliciano, M.J. (1983).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 805961–5964.
Bradley, W.E.C., and Letovanec, D. (1982).Somat. Cell Genet. 851–66.
Simon, A.E., and Taylor, M.W. (1983).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80810–814.
Simon, A.E., Taylor, M.W., and Bradley, W.E.C. (1983).Mol. Cell. Biol. 31703–1710.
Siciliano, M.J., Stallings, R.L., and Adair, G.M. (1985). InMolecular Cell Genetics (ed.), Gottesman, M.M. Wiley, New York. pp. 95–135.
Worton, R.G., Ho, C.C., and Duff, C. (1977).Somat. Cell Genet. 327–45.
Monaco, A.P., and Kunkel, L.M. (1987).Trends Genet. 333–37.
Hansen, M.F., and Cavenee, W.K. (1988).Trends Genet. 4125–128.
Bradley, W.E.C., Belouchi, A., and Messing, K. (1988).Mutat. Res. 199199–131.
Dewyse, P., and Bradley, W.E.C. (1990).Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 16225–230.
Sager, R., and Kovac, P.E. (1978).Somat. Cell Genet. 4375–392.
Roufa, D.J., Sadow, B.N., and Caskey, C.T. (1973).Genetics 75515–530.
Murray, N. (1983). InLambda II (eds.) Hendrix, R., Roberts, J., Stahl, F., and Weisberg, R. (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York). pp. 395–432.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F., and Stambrook, J. (1982). Molecular Cloning. A Laboratory Manual. (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York).
Benton, W.D., and Davis, R.W. (1977).Science 196180–182.
Riley, D.E. (1989).Gene 75193–196.
Zhang, H., Scholl, R., Browse, J., and Somerville, C. (1988).Nucleic Acids Res. 161220.
Schwartz, D.C., and Cantor, C.R. (1984).Cell 3767–75.
Fasel, N., Buetti, E., Firzlaff, J., Pearson, K., and Diggelmann, H. (1983).Nucleic Acids Res. 116943–6955.
Fowler, R.F., Stringfellow, L.A., and Skinner, D.M. (1988).Gene 71165–176.
Cockerill, P.N., and Garrard, W.T. (1986).Cell 44273–282.
Been, M.D., Burgess, R.R., and Champoux, J.J. (1984).Nucleic Acids Res. 123097–3114.
Smith, G.R., Kunes, S.M., Schultz, D.W., Taylor, A., and Triman, K.L. (1981).Cell 24429–436.
Krowczynska, A.M., Rudders, R.A., and Krontiris, T.G. (1990).Nucleic Acids Res. 181121–1127.
Meuth, M. (1989). InMobile DNA, (eds.) Berg, D.E., and Howe, M.M. (Washington, D.C.), pp. 833–860. American Society of Microbiology.
Sargent, G., Phear, G., and Meuth, M. (1989).New Biol. 1205–213.
Nalbantoglu, J., Hartley, D., Phear, G., Tear, G., and Meuth, M. (1986).EMBO J. 51199–1204.
Phear, G., Armstrong, W., and Meuth, M. (1989).J. Mol. Biol. 209577–582.
Nalbantoglu, J., Miles, C., and Meuth, M. (1988).J. Mol. Biol. 200449–459.
Bookstein, R., Lee, E., Peccei, A., and Lee, W.-H. (1989).Mol. Cell. Biol. 91628–1634.
Canning, S., and Dryja, T.P. (1989).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 865044–5048.
Lee, E., Bookstein, R., Young, L.-J., Lin, S.-J., Rosenfeld, M.G., and Lee, W.-H. (1988).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 856017–6021.
Lehrman, M.A., Goldstein, J.L., Russell, D.W., and Brown, M.S. (1987).Cell 48827–835.
De Jong, P.J., Grosovsky, A.J., and Glickman, B.W. (1988).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 853499–3503.
Nalbantoglu, J., and Meuth, M. (1986).Nucleic Acids Res. 148361–8371.
Nalbantoglu, J., Phear, G., and Meuth, M. (1987).Mol. Cell. Biol. 71445–1449.
Jennings, M.W., Jones, R.W., Wood, W.G., and Weatherall, D.J. (1985).Nucleic Acids Res. 132897–2906.
Vnencak-Jones, C.L., Phillips, J.A., III, Chen, E.Y., and Seeburg, P.H. (1988).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 855615–5619.
Mendoza, A.U., Chuw, J.Y., Lee, E., Bookstein, R., and Lee, W.-H. (1988).Hum. Pathol. 19487–489.
Myerowitz, R., and Hogikyan, N.D. (1987).J. Biol. Chem. 26215396–15399.
Henthorn, P.S., Smithies, O., and Mager, D.L. (1990).Genomics 6226–237.
Konopka, A.K. (1988).Nucleic Acids Res. 161739–1758.
Gasser, S.M., and Laemmli, U.K. (1987).Trends Genet. 317–21.
Gasser, S.M., and Laemmli, U.K. (1986).Cell 46521–530.
Sander, M., and Hsieh, T. (1985).Nucleic Acids Res. 131057–1072.
Nikaido, T., Nakai, S., and Honjo, T. (1981).Nature 292845–848.
Majors, J.E., and Varmus, H.E. (1981).Nature 289253–257.
Squires, C.H., DeFelice, M., Devereux, J., and Calvo, J.M. (1983).Nucleic Acids Res. 115299–5313.
Lehrman, M.A., Russell, D.W., Goldstein, G.L., and Brown, M.S. (1987).J. Biol. Chem. 2623354–3362.
Lehrman, M.A., Schneider, W.J., Sudhof, T.S., Brown, M.S., Goldstein, G.L., and Russell, D.W. (1985).Science 227140–146.
Lehrman, M.A., Russell, D.W., Goldstein, G.L., and Brown, M.S. (1986).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 833679–3683.
Vanin, E.F., Henthorn, P.S., Kioussis, D., Grosveld, F., and Smithies, O. (1984).Cell 35701–709.
Nicholls, R.D., Fishel-Ghodsian, N., and Higgs, D.R. (1987).Cell 49369–378.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dewyse, P., Bradley, W.E.C. A very large spontaneous deletion ataprt locus in CHO cells: Sequence similarities with smallaprt deletions. Somat Cell Mol Genet 17, 57–68 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01233205
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01233205