Summary
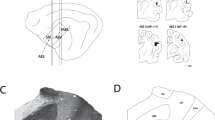
The thalamic reticular nucleus (TRN) is a sheet-like nucleus partially enclosing the dorsolateral and anterior aspects of the thalamus and traversed by the thalamo-cortical and cortico-thalamic fibre systems. This paper describes the cellular and synaptic organization of the TRN in adult albino rats on the basis of LM and EM studies of normal animals and experimental animals with injections of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and/or lesions in various parts of the brain. Particular attention was paid to the dorso-caudal part of the TRN, which establishes connections with visual centres.
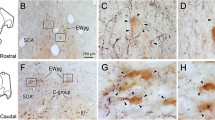
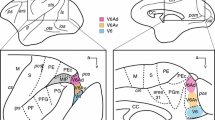
LM-HRP preparations show that the neurons of TRN project only to ipsilateral dorsal thalamus; no labelled cell bodies were found in TRN after injections into the cortex or any part of the brain stem caudal to the thalamus. Small injections into dorsal thalamus result in a small cluster of labelled neurons and an associated patch of terminal label in TRN. The dorso-caudal part of the nucleus projects to the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus, the ventro-caudal part to the medial geniculate nucleus and a large part of the nucleus anterior to the areas associated with the geniculate nuclei projects to the ventrobasal nucleus. No evidence was found for a widespread distribution of reticulo-thalamic axons and the connections between TRN and the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus and between TRN and the ventrobasal nucleus show a fine-grain topographical organization with more rostral and dorsal parts of TRN projecting to more rostral and dorsal parts of the dorsal lateral geniculate and ventrobasal nuclei.
The neurons of TRN are variable in size (range of somal diametersc. 10–20 μm), shape (cell bodies are most commonly ellipsoidal) and dendritic morphology (bitufted and bipolar arrangements most common), but no basis for subdividing them into more than one class was found with any of the techniques used. The cell body and dendrites are commonly aligned parallel to the surface of TRN and at right angles to the traversing fibre bundles. The dendrites do not branch extensively and are only moderately spinous. Long, hair-like spines corresponding to those described by Scheibel & Scheibel (1966) were not found: nor were dendritic bundles found to be as prominent in EM material as reported by these authors in LM-Golgi material. Plasma membranes of dendrites in small bundles and of contiguous somata were commonly in direct contact over large areas, but gap junctions between them were not seen.
The neuropil of TRN is simple with three major axon terminal types.D-type terminals (about 56% of all terminals in visual TRN) have closely packed spherical synaptic vesicles (42 nm diameter);L-type terminals (about 31%) are paler, slightly larger and have less densely packed synaptic vesicles (46 nm diameter); both terminal types make Gray type 1 synaptic contacts on dendritic spines and dendritic shafts and rarely also on cell bodies and axon hillocks.F-type terminals (about 8%) contain flattened synaptic vesicles in a dark matrix and make Gray type 2 contacts with dendrites, cell bodies and axon hillocks. In visual TRN, D-type terminals (but not all) degenerate after ablation of ipsilateral visual cortex and L-type terminals (but not all) degenerate after lesion of ipsilateral dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus; the density of degenerating terminals is higher after cortical than after geniculate lesions. Indirect evidence suggests that F-type terminals may be (or may include) collaterals of reticulo-thalamic projection cells, but no evidence was found for a widespread or dense plexus of such collaterals.
After injection of HRP into the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus, labelled axon terminals in visual TRN (many clearly L-type) were found in synaptic contact with retrogradely labelled dendrites of reticulo-geniculate projection cells. When HRP injection was combined with ablation of ipsilateral visual cortex, degenerating axon terminals (most of them identifiable as D-type) were also found in synaptic contact with retrogradely-labelled dendrites of reticulo-geniculate projection cells.
Thus, neurons of visual TRN in the rat receive monosynaptic, presumptively excitatory input from collaterals of cortico-geniculate and geniculo-cortical axons, and project in a topographically-organized manner to the ipsilateral dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (where they make Gray type 2 GABAergic and presumptively inhibitory synaptic contacts chiefly with the dendrites of geniculo-cortical projection cells). A similar pattern of organization is seen in other parts of the TRN and these data are compatible with the view that the TRN (and the perigeniculate nucleus of the cat thalamus, which is similar in several respects to visual TRN) forms part of a negative feed-back system by which the activity of thalamo-cortical projection neurons is regulated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlsén, G. &Lindström, S. (1982) Mutual inhibition between perigeniculate neurons.Brain Research 236, 482–6.
Ahlsén, G., Lindström, S. &Lo, F.-S. (1982) Functional distinction of perigeniculate and thalamic reticular neurons in the cat.Experimental Brain Research 46, 118–26.
Altman, J. &Bayer, S. A. (1979) Development of the diencephalon in the rat. VI. Re-evaluation of the embryonic development of the thalamus on the basis of thymidine-radiographic datings.Journal of Comparative Anatomy 188, 501–24.
Angel, A. (1983) The functional interrelations between the somatosensory cortex and the thalamic reticular nucleus: their role in the control of information transfer across the specific somatosensory thalamic relay nucleus. InSomatosensory Integration in the Thalamus (edited byMacchi, G., Rustioni, A. &Spreafico, R.), pp. 221–39. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers.
Barrionuevo, G., Benoit, O. &Tempier, P. (1981) Evidence for two types of firing pattern during the sleep-waking cycle in the reticular thalamic nucleus of the cat.Experimental Neurology 72, 486–501.
Berry, D. J., Jeffery, G., Lieberman, A. R. &Ohara, P. T. (1983) Relationships between the thalamic reticular nucleus and the brain stem reticular formation in the rat: a retrograde and anterograde tracing study using horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and wheat germ agglutin-HRP (WGA-HRP).Journal of Physiology 341, 54P.
Burke, W. &Cole, A. M. (1978) Extraretinal influences on the lateral geniculate nucleus.Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry & Pharmacology 80, 106–66.
Cajal, S. R. Y. (1911) Histologie du système nerveux de l'homme et des vertébrés, Vol. II. Translated by S. Azoulay. Reprinted Madrid: Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas, 1952.
Carman, J. B., Cowan, W. M. &Powell, T. P. S. (1964) Cortical connexions of the thalamic reticular nucleus.Journal of Anatomy 98, 587–98.
Crick, F. (1984) Function of the thalamic reticular complex: the searchlight hypothesis.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 81, 4586–90.
Deschênes, M., Paradis, M., Roy, J. P. &Steriade, M. (1984) Electrophysiology of neurons of lateral thalamic nuclei in cat: resting properties and burst discharges.Journal of Neurophysiology 51, 1196–219.
Dubin, M. W. &Cleland, B. G. (1977) Organization of visual inputs to interneurons of lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat.Journal of Neurophysiology 40, 410–27.
Frassoni, C., Spreafico, R. &Battaglia, G. (1984) Afferent and efferent connections of the nucleus reticularis thalami of the rat: an HRP study.Neuroscience Letters Supplement 18, S51.
French, C. R., Sefton, A. J. &Mackay-Sim, A. (1984) The inhibitory role of the visually responsive region of the thalamic reticular nucleus in the rat.Experimental Brain Research 57, 471–9.
Friedlander, M. J., Lin, C.-S., Stanford, L. R. &Sherman, S. M. (1981) Morphology of functionally identified neurons in lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat.Journal of Neurophysiology 46, 80–129.
Frigyesi, T. L. &Schwartz, R. (1972) Cortical control of thalamic sensorimotor relay activities in the cat and squirrel monkey. InCorticothalamic Projections and Sensorimotor Activities (edited byFrigyesi, T. L., Rinvik, E. &Yahr, M. D.), pp. 161–91. New York: Raven.
Graham, J., Lin, C.-S. &Kaas, J. H. (1979) Subcortical projections of six visual cortical areas in the owl monkey,Aotus trivirgatus.Journal of Comparative Neurology 187, 557–80.
Grofova, I., Ottersen, O. P. &Rinvik, E. (1978) Mesencephalic and diencephalic afferents to the superior colliculus and periaqueductal gray substance demonstrated by retrograde axonal transport of horseradish peroxidase in the cat.Brain Research 146, 205–20.
Grossman, A., Lieberman, A. R. &Webster, K. E. (1973) A Golgi study of the rat dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus.Journal of Comparative Neurology 150, 441–65.
Hale, P. T., Sefton, A. J., Baur, L. A. &Cottee, L. J. (1982) Interrelations of the rat's thalamic reticular and dorsal lateral geniculate nuclei.Experimental Brain Research 45, 217–29.
Hanberry, J., Ajmone-Marsan, C. &Dilworth, M. (1954) Pathways of non-specific thalamo-cortical projection system.Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology 6, 103–18.
Hassler, R. (1959) Anatomy of the thalamus. InIntroduction to Stereotaxis with an Atlas of the Human Brain (edited bySchaltenbrand, G. &Bailey, P.), pp. 230–90. Stuttgart: Thieme-Verlag.
Hirsch, J. C., Fourment, A. E. &Marc, M. E. (1982) Electrophysiological study of the perigeniculate region during natural sleep in the cat.Experimental Neurology 77, 436–54.
Houser, C. R., Vaughn, J. E., Barber, R. P. &Roberts, E. (1980) GABA neurons are the major cell type of the nucleus reticularis thalami.Brain Research 200, 341–54.
Ide, L. S. (1982a) The fine structure of the perigeniculate nucleus in the cat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 210, 317–34.
Ide, L. S. (1982b) Fine structure of the thalamic reticular nucleus in the cat.Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 8, 261.
Jahnsen, H. &Llinas, R. (1984a) Electrophysiological properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones: anin vitro study.Journal of Physiology 349, 205–26.
Jahnsen, H. &Llinas, R. (1984b) Ionic basis for the electroresponsiveness and oscillatory properties of guinea-pig thalamic neuronesin vitro.Journal of Pliysiology 349, 227–47.
Jasper, H. (1949) Diffuse projection systems: the integrative action of the thalamic reticular system.Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology 1, 405–20.
Jones, E. G. (1975) Some aspects of the organization of the thalamic reticular complex.Journal of Comparative Neurology 162, 285–308.
Jones, E. G. (1981) Functional subdivisions and synaptic organization of the mammalian thalamus. InNeurophysiology IV. International Review of Physiology, Vol. 25 (edited byPorter, R.), pp. 173–245, Baltimore: University Park Press.
Jones, E. G. (1983) The thalamus. InChemical Neuroanatomy (edited byEmson, P. C.), pp. 257–93. New York: Raven Press.
König, J. F. R. &Klippel, R. A. (1963)The rat brain. A stereotaxic atlas of the forebram and lower parts of the brain stem. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins Co.
Krieg, W. J. S. (1946) Connections of the cerebral cortex. I. The albino rat. A. Topography of the cortical areas.Journal of Comparative Neurology 84, 221–76.
Lashley, K. S. (1941) Thalamo-cortical connections of the rat's brain.Journal of Comparative Neurology 75, 67–122.
Laties, A. M. &Sprague, J. M. (1966) The projection of optic fibers to the visual centres in the cat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 127, 35–70.
LaVail, J. H. &LaVail, M. M. (1974) The retrograde intraaxonal transport of horseradish peroxidase in the chick visual system: a light and electron microscopic study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 157, 303–58.
Lieberman, A. R. &Webster, K. E. (1972) Presynaptic dendrites and a distinctive class of synaptic vesicle in the rat dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus.Brain Research 42, 196–200.
Lindström, S. (1982) Synaptic organization of inhibitory pathways to principal cells in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat.Brain Research 234, 447–53.
Mackay-Sim, A., Sefton, A. J. &Martin, P. R. (1983) Subcortical projections to lateral geniculate and thalamic reticular nuclei in the hooded rat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 213, 24–35.
McLardy, T. (1951) Diffuse thalamic projection to cortex: anatomical critique.Electroèncephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology 3, 183–8.
Marks, G. A., Stabrowski, A. &Roffwarg, H. P. (1983) Disinhibition of dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus following lesion of the thalamic reticular nucleus.Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 9, 815.
Massion, J. (1968) Etude d'une structure motrice thalamique, le noyau ventro-lateral, et de sa regulation par les afférences sensorielles. Thèse de doctorat d'Etat en sciences naturelles. Faculté de Science de Paris.
Mesulam, M. M. (1978) Tetramethyl benzidine for horseradish peroxidase neurohistochemistry: a noncarcinogenic blue reaction product with superior sensitivity for visualizing neuronal afferents and efferents.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 26, 106–17.
Minderhoud, J. M. (1971) An anatomical study of the efferent connections of the thalamic reticular nucleus.Experimental Brain Research 12, 435–46.
Montero, V. M. (1983) Ultrastructural identification of axon terminals from the thalamic reticular nucleus in the medial geniculate body in the rat: an EM autoradiographic study.Experimental Brain Research 51, 338–42.
Montero, V. M., Guillery, R. W. &Woolsey, C. N. (1977) Retinotopic organization within the thalamic reticular nucleus demonstrated by a double label autoradiographic technique.Brain Research 138, 407–21.
Montero, V. M. &Scott, G. L. (1981) Synaptic terminals in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus from neurons of the thalamic reticular nucleus: a light and electron microscope autoradiographic study.Neuroscience 12, 2561–77.
Montero, V. M. &Singer, W. (1984) Ultrastructure and synaptic relations of neural elements containing glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) in the perigeniculate nucleus of the cat.Experimental Brain Research 56, 115–25.
O'connell, M., Ohara, P. T. &Lieberman, A. R. (1982) Connections of the thalamic reticular nucleus in the adult rat: a study using horseradish peroxidase (HRP) techniques.Journal of Anatomy 134, 610–11.
Oertel, W. H., Graybiel, A. M., Mugnaini, E., Elde, R. P., Schmechel, D. E. &Kopin, I. J. (1983) Coexistence of glutamic acid decarboxylase and somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in neurons of the feline nucleus reticularis thalami.Journal of Neuroscience 3, 1322–32.
Ohara, P. T. (1981) The thalamic reticular nucleus of the rat: experimental anatomical studies. Ph.D. Thesis, University of London.
Ohara, P. T. (1984) Light (LM) and electron microscopic (EM) examination of the connections of the thalamic reticular nucleus (TRN) with the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (LGNd) and the ventrobasal complex (VB) in the rat studied using degeneration and intracellular labelling techniques.Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 10, 54.
Ohara, P. T. &Lieberman, A. R. (1981) Thalamic reticular nucleus: anatomical evidence that cortico-reticular axons establish monosynaptic contact with reticulo-geniculate projection cells.Brain Research 207, 153–6.
Ohara, P. T., Lieberman, A. R., Hunt, S. P. &Wu, J.-Y. (1983) Neural elements containing glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the rat; immunohistochemical studies by light and electron microscopy.Neuroscience 8, 189–211.
Ohara, P. T., Sefton, A. J. &Lieberman, A. R. (1980) Mode of termination of afferents from the thalamic reticular nucleus in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the rat.Brain Research 197, 503–6.
Papez, J. W. (1956) Central reticular path to intralaminar and reticular nuclei of the thalamus for activating EEG related to consciousness.Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology 8, 117–28.
Parent, A. &Steriade, M. (1984) Midbrain tegmental projections of nucleus reticularis thalami of cat and monkey: a retrograde transport and antidromic invasion study.Journal of Comparative Neurology 229, 548–58.
Peschanski, M. &Besson, J.-M. (1984) Diencephalic connections of the raphé nuclei of the rat brainstem: an anatomical study with reference to the somatosensory system.Journal of Comparative Neurology 224, 509–34.
Peschanski, M., Ralston, H. J. &Roudier, F. (1983) Reticularis thalami afferents to the ventrobasal complex of the rat thalamus: an electron microscope study.Brain Research 270, 325–9.
Peters, A., Palay, S. L. &Webster, H. de F. (1976)The fine structure of the nervous system: The neurons and supporting cells. Philadelphia: Saunders.
Pollin, B. &Rokyta, R. (1982) Somatotopic organization of nucleus reticularis thalami in chronic awake cats and monkeys.Brain Research 250, 211–21.
Reinoso-Suarez, F. (1983) Cajal: a modern insight in neuroscience. InRamon y Cajal's Contributions to the Neurosciences (edited byGrisolia, S., Guerri, C., Samson, F., Norton, S. &Reinoso-Suarez, F.), pp. 3–22. Amsterdam, New York, Oxford: Elsevier.
Rinvik, E. (1972) Organization of thalamic connections from motor and somatosensory cortical areas in the cat. InCorticothalamic Projections and Sensorimotor Activities (edited byFrigyesi, T., Rinvik, E. &Yahr, M. S.), pp. 57–90. New York: Raven Press.
Rinvik, E. (1984) Thalamic commissural connections in the cat.Neuroscience Letters 44, 311–16.
Robertson, R. T. &Rinvik, E. (1973) The Corticothalamic projections from parietal regions of the cerebral cortex. Experimental degeneration studies in the cat.Brain Research 51, 61–79.
Rose, J. E. (1942) The ontogenic development of the rabbit's diencephalon.Journal of Comparative Neurology 77, 61–129.
Rose, J. E. (1952) The cortical connections of the reticular complex of the thalamus.Research Publications of the Association for Nervous and Mental Diseases 30, 454–79.
Rose, J. E. &Woolsey, C. N. (1943) A study of thalamo-cortical relations in the rabbit.Bulletin of the Johns Hopkins Hospital 73, 65–128.
Rose, J. E. &Woolsey, C. N. (1949) Organization of the mammalian thalamus and its relationship to the cerebral cortex.Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology 1, 391–403.
Sanderson, K. J. (1974) Lamination of the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus in carnivores of the weasel (Mustelidae), raccoon (Procyonidae) and fox (Canidae) families.Journal of Comparative Neurology 153, 239–66.
Scheibel, M. E. &Scheibel, A. B. (1966) The organization of the nucleus reticularis thalami: a Golgi study.Brain Research 1, 43–62.
Scheibel, M. E. &Scheibel, A. B. (1972) Specialized organizational patterns within the nucleus reticularis thalami of the cat.Experimental Neurology 34, 316–22.
Schlag, J. &Waszak, M. (1971) Electrophysiological properties of units of the thalamic reticular complex.Experimental Neurology 32, 79–97.
Schmielau, F. (1979) Integration of visual and nonvisual information in nucleus reticularis thalami of the cat. InDevelopmental Neurobiology of Vision (edited byFreeman, R. D.), pp. 205–26. New York: Plenum Publishing Corporation.
Sefton, A. J., Mackay-Sim, A., Baur, L. A. &Cottee, L. J. (1981) Cortical projections to visual centres in the rat: an HRP study.Brain Research 215, 1–13.
Shosaku, A. &Sumitomo, I. (1983) Auditory neurons in the rat thalamic reticular nucleus.Experimental Brain Research 49, 432–42.
Singer, W. (1977) Control of thalamic transmission by corticofugal and ascending reticular pathways in the visual system.Physiological Reviews 57, 386–420.
Sotgiu, M. L., Marini, G., Esposti, D. &Fava, E. (1981) A horseradish peroxidase study of afferent projections to nucleus reticularis thalami in the cat.Archives Italiennes de Biologie 119, 151–59.
Spacek, J. (1982) ‘Free’ postsynaptic-like densities in normal adult brain: their occurrence, distribution, structure and association with subsurface cisterns.Journal of Neurocytology 11, 693–706.
Spacer, J. &Lieberman, A. R. (1974) Ultrastructure and three-dimensional organization of synaptic glomeruli in rat somatosensory thalamus.Journal of Anatomy 117, 487–516.
Spreafico, R., Frassoni, C., Battaglia, G. &Schmechel, D. E. (1984) The intrinsic organization of the nucleus reticularis thalami of the rat: A HRP, Golgi and immunocytochemical study.Neuroscience Letters Supplement 18, S25.
Spreafico, R., Schmechel, D. E., Ellis, L. C. &Rustioni, A. (1983) Cortical relay neurons and interneurons in the n. ventralis posterolateralis of cats: a horseradish peroxidase, electron-microscopic, Golgi and immunocytochemical study.Neurosdence 9, 491–509.
Stanford, L. R., Friedlander, M. J. &Sherman, S. M. (1983) Morphology of physiologically identified W-cells in the C-laminae of the cat's lateral geniculate nucleus.Journal of Neurosdence 6, 578–84.
Steriade, M. (1984) The excitatory-inhibitory response sequence in thalamic and neocortical cells: state-related changes and regulatory sytems. InDynamic Aspects of Neocortical Function (edited byEdelman, G. M., Cowan, W. M. &Gall, W. E.), pp. 107–57. New York: Wiley & Sons.
Steriade, M., Parent, A. &Hada, J. (1984) Thalamic projections of nucleus reticularis thalami of cat: a study using retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase and fluorescent tracers.Journal of Comparative Neurology 229, 531–47.
Steriade, M. &Wyszinski, P. (1972) Cortically elicited activities in thalamic reticularis neurons.Brain Research 42, 514–20.
Sugitani, M. (1979) Electrophysiological and sensory properties of the thalamic reticular neurones related to somatic sensation in rats.Journal of Physiology 290, 79–95.
Sumitomo, I. &Iwama, K. (1977) Some properties of intrinsic neurons of the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the rat.Japanese Journal of Physiology 27, 717–30.
Sumitomo, I., Nakamura, M. &Iwama, K. (1976) Location and function of the so-called interneurons of rat lateral geniculate body.Experimental Neurology 51, 110–23.
Sumitomo, I., Sugitani, M. &Iwama, K. (1977) Disinhibition of perigeniculate reticular neurons following chronic ablation of the visual cortex in rats.Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine 122, 321–9.
Symonds, L. L. &Kaas, J. H. (1978) Connections of striate cortex in the prosimian,Galago senegalensis.Journal of Comparative Neurology 181, 477–512.
Szentágothai, J. (1972) Lateral geniculate body structure and eye movement.Bibliotheca ophthalmologica 82, 178–88.
Waszak, M. (1974) Firing pattern of neurons in the rostral and ventral part of nucleus reticularis thalami during EEG spindles.Experimental Neurology 43, 38–59.
White, E. L. &Rock, M. P. (1980) Three-dimensional aspects and synaptic relationships of a Golgi-impregnated spiny stellate cell reconstructed from serial thin sections.Journal of Neurocytology 9, 615–36.
Yen, C.-T. &Jones, E. G. (1983) Intracellular staining of physiologically identified neurons and axons in the somatosensory thalamus of the cat.Brain Research 280, 148–54.
Yingling, C. D. &Skinner, J. E. (1976) Selective regulation of thalamic sensory relay nuclei by nucleus reticularis thalami.Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology 41, 476–82.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohara, P.T., Lieberman, A.R. The thalamic reticular nucleus of the adult rat: experimental anatomical studies. J Neurocytol 14, 365–411 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01217752
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01217752