Summary
We have identified the processes of mechanoreceptor sensory neurons by intracellular injection of horseradish peroxidase in order to study the structure of synapses which exhibit profound, behaviourally-relevant plasticity. These synapses are located at small, varicose expansions along or at the end of the fine, microtubule-containing neurites, and they are crowded with vesicles some of which are associated with the varicosity membrane at regions of membrane specialization morphologically equivalent to active zones described in other species.
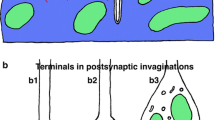
These active zones occur between pre- and postsynaptic processes at two varieties of apposition: a conventional flat one, and a more elaborate indented one. At indented appositions, the presynaptic varicosity is invaginated by a thin (less than 0.25 μm diameter) spine of variable length. The active zones of indented synapses have approximately twice the vesicle frequency of flat synapses, suggesting that indented synapses are more effective.
Sensory neuron terminals are relatively uniform in their structure, having similar concentrations of vesicles and numbers of active zones, and the majority of the processes postsynaptic to them are less than 0.5 μm in diameter. These regularities, and the presence of two strikingly-different types of synaptic apposition, flat and indented, should facilitate structural comparisons of neurons from naive and behaviourally-modified animals. The possible dynamic interconversion of indented and flat appositions at the synaptic terminals of sensory neurons and its behavioural relevance are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, C. H., Castellucci, V. F., Koester, J. andKandel, E. R. (1979) Cellular studies of peripheral neurons in the siphon skin ofAplysia californica.Journal of Neurophysiology 42, 530–57.
Bailey, C. H., Thompson, E. B., Castellucci, V. F. andKandel, E. R. (1976) Fine structure of synapses of identified sensory cells which mediate the gill-withdrawal reflex inAplysia californica.Neuroscience Abstracts 2, 314.
Bailey, C. H., Thompson, E. B., Chen, M. andHawkins, R. (1978) Insights into the morphological basis of presynaptic facilitation in the gill-withdrawal reflex ofAplysia: analysis of the fine structure of a modulatory synapse.Neuroscience Abstracts 4, 187.
Byrne, J. H., Castellucci, V. F., Carew, T. J. andKandel, E. R. (1978a) Stimulus-response relations and stability of mechanoreceptor and motor neurons mediating defensive gill-withdrawal reflex inAplysia.Journal of Neurophysiology 41, 402–17.
Byrne, J., Castellucci, V. andKandel, E. R. (1974) Receptive fields and response properties of mechanoreceptor neurons innervating siphon skin and mantle shelf inAplysia.Journal of Neurophysiology 37, 1041–64.
Byrne, J. H., Castellucci, V. F., andKandel, E. R. (1978b) Contribution of individual mechanoreceptor sensory neurons to defensive gill-withdrawal reflex inAplysia.Journal of Neurophysiology 41, 418–31.
Carew, T. J., Castellucci, V. F. andKandel, E. R. (1971) An analysis of dishabituation and sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex inAplysia.International Journal of Neuroscience 2, 79–98.
Carew, T. J., Castellucci, V. F. andKandel, E. R. (1979) Sensitization inAplysia: Restoration of transmission in synapses inactivated by long-term habituation.Science (in press).
Carew, T. J., Pinsker, H. M. andKandel, E. R. (1972) Long-term habituation of a defensive withdrawal reflex inAplysia.Science 175, 451–4.
Castellucci, V. F., Carew, T. J. andKandel, E. R. (1978) Cellular analysis of long-term habituation of the gill-withdrawal reflex ofAplysia californica.Science 202, 1306–8.
Castellucci, V. F. andKandel, E. R. (1974) A quantal analysis of the synaptic depression underlying habituation of the gill-withdrawal reflex inAplysia.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (U.S.A.) 71, 5004–8.
Castellucci, V. F. andKandel, E. R. (1976) Presynaptic facilitation as a mechanism for behavioral sensitization inAplysia.Science 194, 1176–8.
Castellucci, V., Pinsker, H., Kupfermann, I. andKandel, E. R. (1970) Neuronal mechanisms of habituation and dishabituation of the gill-withdrawal reflex inAplysia.Science 167, 1745–98.
Ceccarelli, B., Hurlbut, W. P. andMauro, A. (1972) Depletion of vesicles from neuromuscular junctions by prolonged tetanic stimulation.Journal of Cell Biology 54, 30–8.
Chan-Palay, V. andPalay, S. L. (1970) Interrelation of basket cell axons and climbing fibers in the cerebellar cortex of the rat.Zeitschrift für Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeschichte 132, 191–227.
Coggeshall, R. E. (1967) A light and electron microscope study of the abdominal ganglion ofAplysia californica.Journal of Neurophysiology 30, 1263–87.
Coggeshall, R. E. andFawcett, D. W. (1964) The fine structure of the central nervous system of the leech,Hirudo medicinalis.Journal of Neurophysiology 27, 229–89.
Cottrell, G. A. andOsborne, N. N. (1970) Subcellular localization of serotonin in an identified serotonin-containing neuron.Nature 225, 470–2.
Couteaux, R. (1961) Principaux critères morphologiques et cytochimiques utilisables aujourd'hui pour définir les divers types de synapses. InActualités Neurophysiologiques, troisième série (edited byMonnier, A. M.), pp. 145–173, Paris: Masson et Cie.
Eccles, J. C., Ito, M. andSzentÁgothai, J. (1967)The Cerebellum as a Neuronal Machine. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Eisenstadt, M., Goldman, J. E., Kandel, E. R., Koike, H., Koester, J. andSchwartz, J. H. (1973) Instrasomatic injection of radioactive precursors for studying transmitter synthesis in identified neurons ofAplysia californica.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (U.S.A.) 70, 3371–5.
Geffen, L. andLivett, B. G. (1971) Synaptic vesicles in sympathetic neurons.Physiological Reviews 51, 98–157.
Gillette, R. andPomeranz, B. (1975) Ultrastructural correlates of interneuronal function in the abdominal ganglion ofAplysia californica.Journal of Neurobiology 6, 463–74.
Goldman, J. E., Kim, K. S. andSchwartz, J. H. (1976) Axonal transport of3H-serotonin in an identified neuron ofAplysia californica.Journal of Cell Biology 70, 304–18.
Graham, R. C. andKarnovsky, M. J. (1966) The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 14, 291–302.
Graubard, K. (1975) Voltage attenuation withinAplysia neurons: the effect of branching pattern.Brain Research 88, 325–32.
Graubard, K. (1978) Serial synapses inAplysia.Journal of Neurobiology 9, 325–8.
Gray, E. G. (1959) Axo-somatic and axo-dendritic synapses of the cerebral cortex: an electron microscope study.Journal of Anatomy (London) 83, 420–33.
Hamlyn, L. M. (1962) The fine structure of the mossy fibre endings in the hippocampus of the rabbit.Journal of Anatomy (London) 96, 112–20.
Hawkins, R., Castellucci, V. andKandel, E. R. (1976) Identification of individual neurons mediating the heterosynaptic facilitation underlying behavioral sensitization inAplysia.Neuroscience Abstracts 2, 325.
Hawkins, R., Klein, M. andKandel, E. R. (1978) Single identified neurons produce presynaptic facilitation of the gill-withdrawal reflex by increasing Ca++ conductance in sensory neurons ofAplysia.Neuroscience Abstracts 4, 196.
Hawkins, R., Tomosky-Sykes, T., Castellucci, V. andKandel, E. R. (1977) Properties of identified neurons mediating the heterosynaptic facilitation underlying behavioral sensitization inAplysia.Proceedings of the International Union of Physiological Sciences (Abstracts) 13, 312.
Heuser, J. E. andReese, T. S. (1973) Evidence for recycling of synaptic vesicle membrane during transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction.Journal of Cell Biology 57, 315–44.
Heuser, J. E. andReese, T. S. (1977) Structure of the synapse. InHandbook of Physiology The Nervous System Vol. 1 Part 1 (edited byKandel, E. R.). pp. 261–294. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkens.
Howes, E. A., Mclaughlin, B. J. andHeslop, J. P. (1974) The autoradiographical association of fast transported material with dense core vesicles in the central nervous sytem ofAnodonta cygnea L.Cell and Tissue Research 153, 545–58.
Jourdan, F. andNicaise, G. (1971) L'ultrastructure des synapses dans le ganglion pleural de l'Aplysie.Journal de Microscopie (Paris) 11, 69–70.
Kandel, E. R. (1976)The Cellular Basis of Behavior. San Francisco: Freeman.
King, D. G. (1976a) Organization of crustacean neuropil. I. Patterns of synaptic connections in lobster stomatogastric ganglion.Journal of Neurocytology 5, 207–37.
King, D. G. (1976b) Organization of crustacean neuropil. II. Distribution of synaptic contacts on identified motor neurons in lobster stomatogastric ganglion.Journal of Neurocytology 5, 239–66.
Klein, M. andKandel, E. R. (1978) Presynaptic modulation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ current: Mechanism for behavioral sensitization inAplysia californica.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (U.S.A.) 75, 3512–6.
Ko, C. P. andRoper, S. (1978) Disorganized and ‘excessive’ reinnervation of frog cardiac ganglia.Nature 274, 286–8.
Koike, H., Eisenstadt, M. andSchwartz, J. H. (1972) Axonal transport of newly synthesized acetylcholine in an identified neuron ofAplysia.Brain Research 37, 152–9.
Krasne, F. B. andStirling, C. A. (1972) Synapses of crayfish abdominal ganglia with special attention to afferent and efferent connections of the lateral giant fibers.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 127, 526–44.
Kupfermann, I., Carew, T. J. andKandel, E. R. (1974) Local, reflex and central commands controlling gill and siphon movements inAplysia.Journal of Neurophysiology 37, 996–1019.
Muller, K. J. andMcmahan, U. J. (1976) The shapes of sensory and motor neurons and the distribution of their synapses in ganglia of the leech: A study using intracellular injection of horseradish peroxidase.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B194, 481–99.
Palay, S. L. (1956) Synapses in the central nervous system.Journal of Biophysical and Biochemical Cytology 2, Suppl., 193–202.
Palay, S. L. (1958) The morphology of synapses in the central nervous system.Experimental Cell Research Suppl.5, 275–93.
Pentreath, V. W. (1976) Ultrastructure of terminals of an identified 5-hydroxy-tryptamine-containing neuron marked by intracellular injection of radioactive 5-hydroxy-tryptamine.Journal of Neurocytology 5, 43–61.
Pentreath, V. W. andBerry, M. S. (1975) Ultrastructure of the terminals of an identified dopamine-containing neuron marked by intracellular injection of radioactive dopamine.Journal of Neurocytology 4, 249–60.
Peters, A., Palay, S. L. andWebster, H. Def. (1976)The Fine Structure of the Nervous System. The Neurons and Supporting Cells. Philadelphia: Saunders.
Pfenninger, K. (1977) Cytology of the chemical synapse: Morphological correlates of synaptic function. InNeurotransmitter Function: Basic and Clinical Aspects (edited byFields, W. S.), pp. 27–57, Miami: Symposia Specialists.
Pinsker, H., Hening, W. A., Carew, T. J. andKandel, E. R. (1973) Long-term sensitization of a defensive withdrawal reflex inAplysia.Science 182, 1039–42.
Pinsker, H., Kupfermann, I., Castellucci, V. andKandel, E. R. (1970) Habituation and dishabituation of the gill-withdrawal reflex inAplysia.Science 167, 1740–2.
Purves, D. andMcmahan, U. J. (1972) The distribution of synapses on a physiologically identified motor neuron in the central nervous system of the leech: an electron microscopic study after injection of the fluorescent dye Procion yellow.Journal of Cell Biology 55, 205–20.
Raisman, G. (1969) Neuronal plasticity in the septal nuclei of the adult rat.Brain Research 14, 25–48.
Raisman, G. andField, P. M. (1973) A quantitative investigation of the development of collateral reinnervation after partial deafferentation of the septal nuclei.Brain Research 50, 241–64.
Sandemen, D. C. andMendum, C. M. (1971) The fine structure of the central synaptic contacts on a identified crustacean motoneuron.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 119, 515–25.
Schubert, D., LaCorbiere, M., Whitlock, C. andStallcup, W. (1978) Alterations in the surface properties of cells responsive to nerve growth factor.Nature 273, 718–23.
Shkolnik, L. J. andSchwartz, J. H. (1978) Genesis and development of serotonergic vesicles in the identified giant cerebral neuron (GCN) ofAplysia.Neuroscience Abstracts 4, 249.
Thompson, E. B. andBailey, C. H. (1979) Two different and compatible intraneuronal labels for ultrastructural study of synaptically related cells.Brain Research (in press).
Thompson, E. B., Schwartz, J. H. andKandel, E. R. (1976) A radioautographic analysis in the light and electron microscope of identifiedAplysia neurons and their processes after intrasomatic injection of3H-L-fucose.Brain Research 112, 251–81.
Van Harreveld, A. andTrubatch, J. (1975) Synaptic changes in frog brain after stimulation with potassium chloride.Journal of Neurocytology 4, 33–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bailey, C.H., Thompson, E.B., Castellucci, V.F. et al. Ultrastructure of the synapses of sensory neurons that mediate the gill-withdrawal reflex inAplysia . J Neurocytol 8, 415–444 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01214801
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01214801