Abstract
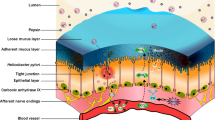
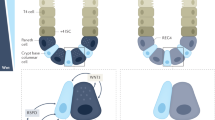
The gastrointestinal epithelium produces a wide variety of peptides which may contribute to protection from injury as well as repair after injury occurs. Restitution, the initial phase of mucosal repair, is accomplished by rapid migration of the epithelium to re-establish surface epithelial continuity. A wide variety of growth factors and cytokines, which are produced both by the epithelium itself and by lamina propria cell populations, promote restitution in models of epithelial injury. These include members of the epidermal growth factor (EGF)/transforming growth factor (TGF)α, and the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) families, as well as a variety of cytokines (interleukin [IL]-1, IL-2, IL-4, IL-15, and interferon γ) which interact with their cognate receptors on the intestinal epithelial basolateral surface. These growth factors and cytokines appear to promote restitution through a TGFβ-dependent pathway and act to both enhance expression of TGFβ and to entrance its bioactivation. In contrast, trefoil peptides, members of a recently recognized family of small proteins produced by goblet cells, both protect the epithelium and promote restitution following secretion onto the apical surface through mechanisms distinct from those peptides acting through TGFβ. Thus, rapid repair after epithelial injury is achieved through complementary mechanisms acting at the basolateral and apical surfaces of the epithelium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waller DA, Thomas NW, Self TJ, et al. Epithelial restitution in the large intestine of the rat following insult with bile salts. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 1988;414:77–81.
Silen W. Gastric mucosal defense and repair. In: Johnson LR (ed.), Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract, 2nd ed. New York: Raven, 1987;1044–1069.
Lacy ER. Epithelial restitution in the gastrointestinal tract. J Clin Gastroenterol 1988;10(Suppl 1):72–77.
Feil W, Lacy ER, Wong YM, et al. Rapid epithelial restitution of human and rabbit colonic mucosa. Gastroenterology 1989;97:685–701.
Rutten MJ, Ito S. Morphology and electrophysiology of guinea pig gastric mucosal repair in vitro. Am J Physiol 1983;244G:171–182.
Moore R, Carlson S, Madera JL. Rapid barrier restitution in an in vitro model of intestinal epithelial injury. Lab Invest 1989;60:237–244.
Nusrat A, Delp C, Madar JL. Intestinal epithelial restitution. J Clin Invest 1992;89:1501–1511.
Ciacci C. Lind SE, Podolsky DK. Transforming growth Factor β regulation of migration in wounded rat intestinal epithelial monolayers. Gastroenterology 1993;105:93–101.
Dignass AU, Podolsky DK. Cytokine modulation of intestinal epithelial cell restitution: Central role of transforming growth factor β. Gastroenterology 1993;105:1323–1332.
Dignass AU, Tsunekawa S, Podolsky DK. Fibroblast growth factors modulate intestinal epithelial cell growth and migration. Gastroenterology 1994;106:1254–1262.
Dignass AU, Lynch-Devaney K, Podolsky DK. Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor modulates intestinal epithelial cell proliferation and migration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1994;202(2):701–709.
Allen A, Bell A, Mantle M, et al. The structure and physiology of gastrointestinal mucus. Adv Exp Med Biol 1982;144:115–133.
Podolsky DK, Isselbacher KJ. Glycoprotein composition of colonic mucosa. Gastroenterology 1984;87:991–998.
Podolsky DK, Isselbacher K. Composition of human colonic mucin. Selective alteration in inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Invest 1983;72:142–153.
Jørgensen KH, Thim L, Jacobsen HE. Pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide (PSP): I. Preparation and initial chemical characterization of a new polypeptide from porcine pancreas. Reg Pep 1982;3:207–219.
Kindon H, deBeaumont M, Lynch-Devaney K, et al. Purification and biochemical characterization of native and recominant intestinal trefoil factor: Protease resistant peptides interact with mucin glycoproteins to promote aggregation. Biochem J 1996.
Rio MC, Bellocq JP, Daniel JY, et al. Breast cancer-associated pS2 protein: Synthesis and secretion by normal stomach mucosa. Science 1988;241:705–708.
Tomasetto C, Rio MC, Gautier C, et al. hSP, the domain-duplicated homolog of pS2 protein, is co-expressed with pS2 in stomach but not in breast carcinoma. Eur Mol Biol Organ J 1990;9:407–414.
Suemori S, Lynch-Devaney K, Podolsky DK. Identification and characterization of rat intestinal trefoil factor: Tissue- and cell-specific member of the trefoil protein family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991;88:11017–11021.
Podolsky DK, Lynch-Devaney K, Stow J, et al. Identification of human intestinal trefoil factor: Goblet cell specific expression of a peptide targeted for apical secretion. J Biol Chem 1993;268:6694–6702.
Rio M-C, Chenard M-P, Wolf C, et al. Induction of pS2 and hSP genes as markers of mucosal ulceration of the digestive tract. Gastroenterology 1991;100:375–379.
Wright NA, Poulsom R, Stamp GS, et al. Trefoil peptide gene expression in gastrointestinal epithelial cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 1993;104:12–20.
Wright NA, Pike C, Elia G. Induction of a novel epidermal growth factor-secreting cell lineage by mucosal ulceration in human gastrointestinal stem cells. Nature 1990;343:82–85.
Dignass AU, Lynch-Devaney K, Kindon H, et al. Trefoil peptides promote epithelial migration through a transforming growth factor β-independent pathway. J Clin Invest 1994;94:376–383.
Hoosein NM, Thim L, Jørgensen KH, et al. Growth stimulatory effect of pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide on cultured colon and breast tumor cells. FEBS Lett 1989;247:303–306.
Jørgensen KH, Thim L, Jacobsen, HE. Pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide (PSP): II. Preparation and initial chemical characterization of a new polypeptide from porcine pancreas. Reg Pep 1982;3:207–219.
Thim L, Jørgensen KH, Jørgensen KD. Pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide (PSP): II. Radioimmunological determination of PSP in porcine tissues, plasma and pancreatic juice. Reg Pep 1982;3:221–230.
Ciacci C, Lind SE, Podolsky DK. Transforming growth factor β regulation of migration in wounded rat intestinal epithelial monolayers. Gastroenterology 1993;105:93–101.
Dignass AU, Tsunekawa S, Podolsky DK. Fibroblast growth factors modulate intestinal epithelial cell growth and migration. Gastroenterology 1994;106:1254–1262.
Dignass AU, Podolsky DK. Cytokine modulation of intestinal epithelial cell restitution: Central role of transforming growth factor β. Gastroenterology 1993;105:1323–1332.
Wright NA, Poulsom R, Stamp G, et al. Trefoil peptide gene expression in gastrointestinal epithelial cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 1993;104:12–20.
Kindon H, Pothoulakis C, Thim L, et al. Trefoil peptides protect intestinal epithelial monolayer/barrier function: Cooperative interaction with mucin glycoprotein. Gastroenterology 1995; 109:516–523.
Mashimo H, Wu DC, Podolsky DK, Fishman MC. Impaired defense of intestinal mucosa in mice lacking intestinal trefoic factor. Science 1996;274:262–265.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Podolsky, D.K. Healing the epithelium: Solving the problem from two sides. J Gastroenterol 32, 122–126 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01213309
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01213309