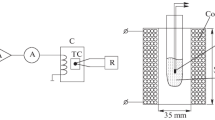
Abstract
Magnetic micro-particles were used to investigate the defence system of the human lungs against foreign material. Afterprimary magnetisation a remanent magnetic field (RMF) of the lung can be measured that allows estimation of the amount of dust retained in the lung. After calibration of the system with a lung phantom the magnetic contamination retained in the lungs of dental technicians and welders was estimated at mean values of 22 and 500 mg respectively. In normal controls only 0.3 mg was found. About 0.5 mg of spherical monodisperse magnetite particles was deposited in the alveolar region of the lung by voluntary inhalation. The decay of the RMF, calledrelaxation, results from a misalignment of the dipole particles due to the activity of pulmonary macrophages. This macrophage activity is characterised by a cellular energyE z. With aseconary magnetisation the lung can be remagnetised by rotation of the dipole particles. This allows an estimation of the intracellular viscoelasticity and the motility of the alveolar macrophages in vivo. Secondary magnetisation and relaxation curves of spherical monodisperse magnetite particles are presented. Intracellular viscosity was estimated to beη ≅ 100 Pa·s at shear rates near 0.01 s−1, the rigidity modulus beingv ≅4–8 Pa. Macrophage activity was described by a cellular energyE z ∼ 5·10−18 J. Additionally, non-magnetic aerosol exposure resulted in a faster relaxation, which was interpreted to be due to activation of the macrophages. The magnetite particles were cleared with a half-time of ≈ 110 days.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramowitz M, Stegun IA (1965) Handbook of mathematical functions. Dover, New York
Bailey MR, Fry FA, James AC (1982) The long-term clearance kinetics of insoluble particles from the human lung. Ann Occup Hyg 26 (1–4):273–290 (Inhaled Particles V)
Bailey MR, Kreyling WG, Andre S, Batchelor A, Collier CG, Drosselmeyer E, Ferron GA, Foster PP, Haider B, Hodgson A, Masse R, Metivier H, Morgan A, Müller H-L, Patrick G, Pearman I, Pickering S, Ramsden D, Stirling C, Talbot RJ (1989) An interspecies comparison of the lung clearance of inhaled monodisperse cobalt oxide particles. I. Objectives and summary of results. J Aerosol Sci 20(2):189–204
Brain JD, Bloom SB, Valberg PA, Gehr P (1984) Correlation between the behavior of magnetic iron oxide particles in the lungs of rabbits and phagocytosis. Exp Lung Res 6:115–131
Cohen D (1973) Ferrimagnetic contamination in the lungs and other organs of the human body. Science 180:745–748
Cohen D, Nemoto I (1984) Ferrimagnetic particles in the lung. I. The magnetising process. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 31(3):261–273
Cohen D, Arai SF, Brain JD (1979) Smoking impairs long-term dust clearance from the lung. Science 294:514–517
Cohen D, Nemoto I, Kaufman L, Arai S (1984) Ferrimagnetic particles in the lung. II. The relaxation process. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 31(3):274–285
Foster PP, Pearman I, Ramsden D (1989) An interspecies comparison of the lung clearance of inhaled monodisperse cobalt oxide particles. II. Lung clearance of inhaled cobalt oxide in man. Aerosol Sci 20(2):189–204
Freedman AP, Robinson SE (1981) Evaluation of magnetopneumography for assessing thoracic accumulation of welding fume particulate and lung dust clearance. In: Ernée SN, Hahlbohm HD, Lübbig H (eds) Biomagnetism, Walter de Gruyter, Berlin, pp 489–495
Freedman AP, Robinson SE, Green FHY (1982) Magnetopneumography as a tool for the study of dust retention in the lungs. Ann Occup Hyg 26(1–4):319–335 (Inhaled Particles V)
Freedman AP, Robinson SE, Street MR (1988) Magnetopneumographic study of human alveolar clearance in health and disease. Ann Occup Hyg 32 [SuppleI]:809–820 (Inhaled Particles VI)
Gebhart J, Heyder J, Roth C, Stahlhofen W (1980) Herstellung und Eigenschaften von Latex-Aerosolen. Staub Reinhaltung Luft 40(1):1–8
Gebhart J, Heigwer H, Heyder J, Roth C, Stahlhofen W (1988) The use of light scattering photometry in aerosol medicine. J Aerosol Med 1:89–112
Gehr P, Bachofen H, Weibel ER (1978) The normal human lung. Ultrastructure and morphometric estimation of diffusion capacity. Respir Physiol 32:345–353
Gehr P, Brain JD, Bloom SB, Valberg PA (1983a) Magnetic particles in the liver: a probe for intracellular movement. Nature 302:336–338
Gehr P, Brain JD, Nemoto I, Bloom SB (1983b) Behavior of magnetic particles in hamster lungs. J Appl Physiol 55(4):1196–1202
Gehr P, Brain JD, Nemoto I, Bloom SB (1985) Organelle movements of alveolar macrophages studied by cytomagnetometry. In: Weinberg H, Stroink G, Katila T (eds) Biomagnetism, applications & theory. Pergamon Press, New York, pp 395–400
Kalliomäki PL, Alkano K, Korhonen O, Mattsson T, Vaaranen V, Koponen M (1978) Amount and distribution of welding fume lung contaminant among arc welders. Scand J Work Environ Health 4:122–130
Kreyling WG, Ferron GA (1984) Production of cobalt oxide aerosols with a modified spinning top aerosol generator. J Aerosol Sci 15(3):851–857
Mak-List (1991) Maximale Arbeitsplatzkonzentrationen und Biologische Arbeitsstofftoleranzwerte. Kommission zur Prüfung gesundheitsschädlicher Arbeitsstoffe der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG). VCH, Weinheim
Möller W, Stahlhofen W (1989) Magnetic material in the lungs of dental technicians. J Aerosol Sci 20(8):1345–1348
Möller W, Stahlhofen W (1991) In vivo measurement of hydrodynamic properties and activity of alveolar macrophages. In: Hoke M, Erne SN, Okada YC, Romani GL (eds) Biomagnetism- Clinical aspects. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 655–660
Möller W, Stahlhofen W, Roth C (1990) Improved spinning top aerosol generator for the production of high concentrated ferrimagnetic aerosols. J Aerosol Sci 21 (supple 1):S435-S438
Möller W, Guzijan V, Pohlit W, Stahlhofen W, Wenisch T, Wiegand J (1992 a) Cytomagnetometry with ferrimagnetic micro-particles - influence of particle size and dispersity. J Aerosol Sci 23 (suppl 1):S519-S522
Möller W, Stahlhofen W, Wiegand J (1992b) Measurement of the hydrodynamic properties of highly viscous solutions with ferrimagnetic particles. J Aerosol Sci 23 (suppl 1):S421–S424
Nemoto I (1982) A model for magnetisation and relaxation of ferrimagnetic particles in the lung, IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 29:745–752
Nemoto I (1989) Estimation of the energy of cytoplasmic movement by magnetometry: effects of temperature and intracellular concentration of ATP. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 36(6):598–607
Stahlhofen W, Möller W (1988) Description of a biomagnetic method for detection of the behaviour of magnetic aerosols in the human lungs. J Aerosol Sci 19(7):1087–1091
Stahlhofen W, Möller W (1990) Using spherical magnetic particles for testing the intracellular viscosity. J Aerosol Sci 21 (supple 1):S435-S438
Stahlhofen W, Möller W (1991) Magnetopneumography with spherical monodisperse ferrimagnetic particles. In: Hoke M, Erne SN, Okada YC, Romani GL (eds) Biomagnetism - clinical aspects. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 661–666
Stahlhofen W, Möller W (1992) Investigation of the defense system of the human lungs with ferrimagnetic particles, J Aerosol Med 5(4):221–228
Stahlhofen W, Gebhart J, Heyder J, Stuck B (1979) Herstellung von monodispersen Fe2O3-Testaerosolen mit Hilfe der Zentrifugälzerstdubung. Staub Reinhaltung Luft 3:73–108
Stahlhofen W, Gebhart J, Heyder J (1980) Experimental determination of the regional deposition of aerosol particles in the human respiratory tract. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 41:385–398
Stahlhofen W, Möller W, Godleski J (1990) Relaxation measurements with spherical magnetic particles in the human lungs. J Aerosol Sci 21(3):355–362
Storey JR (1983) Magnetic sensors with good signal-to-interference discrimination. Nuovo Cimento 2D(2):153–165
Valberg PA (1984) Magnetometry of ingested particles in pulmonary macrophages. Science 224:513–516
Valberg PA, Brain JD (1988) Lung particle retention and lung macrophage function evaluated using magnetic aerosols. J Aerosol Med 1:331–339
Valberg PA, Butler JP (1987) Magnetic particle motions within living cells. I. Physical theory and technique. Biophys J 52:537–550
Valberg PA, Butler JP (1990) Intracellular movement and intracellular viscosity: What can magnetic microparticles tell us? Comments Theor Biol 2:75–79
Valberg PA, Feldman HA (1987) Magnetic particle motions within living cells. II. Measurement of cytoplasmic viscosity and motile activity. Biophys J 52:551–561
Wilkinson WL (1960) Non-Newtonian fluids. Pergamon Press, London
Zaner KS, Valberg PA (1989) Viscoelasticity of F-actin measured with magnetic microparticles. J Cell Biol 109:2233–2243
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor Wolfgang Jacobi on the occasion of his 65th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stahlhofen, W., Möller, W. Behaviour of magnetic micro-particles in the human lung. Radiat Environ Biophys 32, 221–238 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209772
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209772