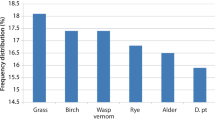
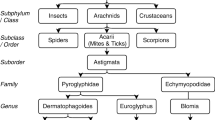
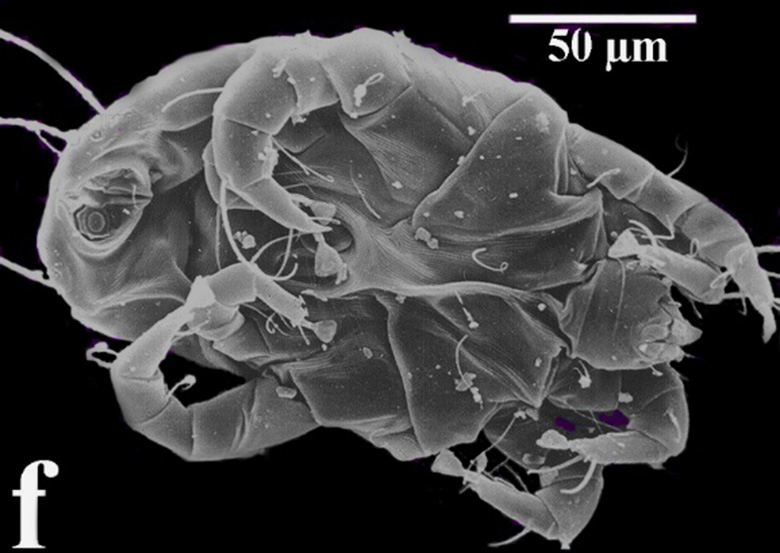
Abstract
For many years it has been suggested that allergens derived from the house dust mite played a major role in the pathogenesis of asthma, eczema and some cases of allergic rhinitis. Recently, house dust mite allergens have been purified and specific immunoassays developed with which exposure to house dust mites and their allergens can be more easily determined. Using these tools, epidemiological studies have provided confirmatory evidence that not only is house dust mite exposure associated with the majority of cases of asthma in children and young adults, but that it is causally related to the development of asthma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnetson, R.S.C., MacFarlane, H.A.F. and Benton, E.C., 1987. House dust mite allergy and atopic eczema. Br. J. Dermatol., 116: 857–860.
Bousquet, J., Chanez, P., Lacoste, J.Y., Barndeon, G., Ghavania, N., Enander, I., Venge, P., Ahlstedt, S., Simony-Lafontaine, J. and Godard, P., 1990. Eosinophilic inflammation in asthma. N. Engl. J. Med., 323: 1033–1039.
Chapman, M.D., Rowntree, S., Mitchell, E.B., Di Prisco Fuenmajor, M.C. and Platts-Mills, T.A.E., 1983. Quantitative assessment of IgG and IgE antibodies to inhalant allergens in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 72: 27–33.
Chapman, M.D., Heymann, P.W., Wilkins, S.R., Brown, M.B. and Platts-Mills, T.A.E., 1987. Monoclonal immunoassays for the major dust mite (Dermatophagoides) allergen,Der p I andDer fI and quantitative analysis of the allergen content of mite and house dust extracts. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 80: 184–194.
Charpin, D., Birnbaum, J., Haddie, E., Genard, G., Toumi, M. and Vervolet, D., 1990. Attitude and allergy to house dust mites: an epidemiological study in primary school children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 85: 185 (abstract).
Clark, P.S., 1987. The diagnosis of perennial rhinitis due to house dust mite (Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus) demonstrated by nasal provocation tests. Ann. Allergy, 59: 25–28.
Deuell, B., Wilson, B., Heymann, P. and Platts-Mills, T., 1991. Atopic dermatitis: The role of dust mite allergy and monitoring of disease activity by assay of IgG in skin scales. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 87: 237 (abstract).
Devlin, J., David, T.J. and Stanton, R.H.J., 1991. Elemental diet for refractory atopic eczema. Arch. Dis. Child., 66: 93–99.
Dilworth, R.J., Chua, K.Y. and Thomas, W.R., 1991. Sequence analysis of cDNA coding for a major house dust mite allergen,Der fI. Clin. Exp. Allergy, 21: 25–32.
Di Nicolo, R., Nelson, R.P., Fernandez-Caldas, E., Trudeau, W., Swanson, M., Bonini, L.V., Perez, A., Arthur, P., Lockey, R. and Good, R.A. 1991. Allergen-specific IgE levels in children presenting to the emergency room with acute asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 87: 234 (abstract).
Djukanovic, R., Roche, W.R., Wilson, J.W., Beasley, C.R.W., Twentyman, O.P., Howarth, P.H. and Holgate, S.T., 1990. Mucosal inflammation in asthma. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis., 142: 434–457.
Dowse, G.K., Smith, D., Turner, K.J. and Alpers, M.P., 1985. Prevalence and features of asthma in a sample survey of urban Goroka, Papua New Guinea. Clin. Allergy, 15: 429–438.
Ehnert, B., Lau-Schadendorf, S., Weber, A., Buettner, P., Schou, C. and Wahn, U., 1992. Reducing domestic exposure to dust mite allergen reduces bronchial hyperreactivity in sensitive children with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 90: 135–138.
Herxheimer, H. and Schaefer, O., 1975. Asthma in Canadian Eskimos. N. Engl. J. Med., 291: 1419 (letter).
Hill, A.B., 1965. The environment and disease: Association or causation? Proc. R. Soc. Med., 58: 295–300.
Hosen, H., 1988. The diagnosis of perennial rhinitis due to the house dust mite demonstrated by nasal provocative tests. Ann. Allergy, 60: 462 (letter).
Kern, R.A., 1921. Dust sensitization in bronchial asthma. Med. Clin. North Am., 5: 751–758.
Lau, S., Falkenhorst, G., Weber, A., Werthmann, I., Lind, P., Buettner-Goetz, P. and Wahn, U., 1989. High mite-allergen exposure increases the risk of sensitisation in atopic children and young adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 84: 718–725.
Lobitz, W.C. and Jillson, O.F., 1958. Anecdotes of an agnostic allergist. Arch. Dermatol., 78: 458.
Marsh, D.G., 1975. Allergens and the genetics of allergy. In: M. Sela (Editor), The Antigens, Vol. 3. Academic Press, New York, NY, pp. 271–295.
Mitchell, E.B., Crow, J., Chapman, M.D., Jouhal S.S., Pope, F.M. and Platts-Mills, T.A.E., 1982. Basophils in allergen induced path test sites in atopic dermatitis. Lancet, 1: 127–130.
Miyamoto, T., Oshima, S., Ishizaki, T. and Sato, S., 1968. Allergenic identity between the common floor mite (Dermatophagoides farinae Hughes 1961) and house dust as a causative agent in bronchial asthma. J. Allergy, 42: 14–28.
O'Hallaran, M.T., Yunginger, J.W., Offord, K.P., Somers, M.J., O'Connel, E.J., Ballard, D.J. and Sachs, M.I., 1991. Exposure to an aeroallergen as a possible precipitating factor in respiratory arrest in young patients with asthma. N. Engl. J. Med., 324: 359–363.
Ohman, S. and Johansson, S.G., 1974. Allergen specific IgE in atopic dermatitis. Acta Dermatol. Venerol., 54: 283–290.
Ohman, J.L., Nadakavukaren, J.J., Sparrow, D. and MacDonald, M.R., 1991. Mite sensitization and current smoking are related to new onset asthma in older males. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 87: 719 (abstract).
Perason, R.S.B., 1973. Asthma in Barbados, Clin. Allergy 3: 289–297.
Peat, J.K., Britton, W.J., Salome, C.M. and Woolcock, A.J., 1987. Bronchial hyperresponsiveness in two populations of australian schoolchildren. III Effect of exposure to environmental allergens. Clin. Allergy, 17: 297–300.
Platts-Mills, T.A.E. and De Weck, A.L., 1989. Report of an international workshop. Dust mite allergens and asthma: a worldwide problem. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 83: 416–427.
Platts-Mills, T.A.E., Tovey, E.R., Mitchell, E.B., Moszoro, H., Nock, P. and Wilkins, S.R., 1982. Reduction of bronchial hyperreactivity during prolonged allergen avoidance. Lancet, 2: 675–678.
Platts-Mills, T.A.E., Hayden, M.L., Chapman, M.D. and Wilkins, S.R., 1987. Seasonal variation in dust mite and grass pollen allergen in dust from the houses of patients with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 79: 781–791.
Platts-Mills, T.A.E., Chapman, M.D., Pollart, S.M., Heymann, P.W. and Luczynska, C.M., 1990. Establishing health standards for indoor foreign proteins related to asthma: Dust mite, cat, cockroach. Toxicol. Ind. Health, 6: 197–208.
Pollart, S.M., Reid, M.J., Fling, J.A., Chapman, M.D. and Platts-Mills, T.A., 1988. Epidemiology of emergency room asthma in northern California: association with IgE antibody to rye grass pollen. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 82: 224–230.
Price, J.A., Pollock, J., Little, S.A., Longbottom, J.L. and Warner, J.O., 1990. Measurements of airborne mite allergen in homes of asthmatic children. Lancet, 336: 895–897.
Rawle, F.R., Mitchell, E.B. and Platts-Mills, T.A.E., 1984. T cell responses to the major allergen from the house dust miteDermatophagoides pteronyssinus, antigen P1: comparison of patients with asthma, atopic dermatitis, and perennial rhinitis. J. Immunol., 133: 195–201.
Roberts, D., 1984. House dust avoidance and atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol., 110: 735–736.
Rothman, K.J., 1986. Causal inference in epidemiology. In: Modern Epidemiology. Little, Brown and Company, Boston/Toronto, pp. 7–21.
Sarsfield, J.K., 1974. Role of house-dust mites in childhood asthma. Arch. Dis. Child., 49: 711–716.
Smith, J.M. and Springett, V.H., 1979. Atopic disease and month of birth. Clin. Allergy, 9: 153–157.
Smith, J.M., Disney, M.E., Williams, J.D. and Goels, Z.A., 1969. Clinical significance of skin reactions to mite extracts in children with asthma. Br. Med. J., 1: 723–726.
Sporik, R., Holgate, S.T., Platts-Mills, T.A.E. and Cogswell, J.J., 1990. Exposure to house-dust mite allergen (Der p I) and the development of asthma in childhood. A prospective study. N. Engl. J. Med., 323: 502–507.
Sporik, R., Platts-Mills, T.A.E. and Cogswell, J.J., 1991. Exposure and sensitisation of children admitted to hospital with asthma to house dust mite allergen (Der p I). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 87: 291 (abstract.).
Tovey, E.R., Chapman, M.D., Wells, C.W. and Platts-Mills, T.A., 1981. The distribution of dust mite allergen in the houses of patients with asthma. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis., 124: 630–635.
Trudinger, M., Chua, K.Y. and Thomas, W.R., 1991. cDNA coding the major mite allergenDer fII. Clin. Exp. Allergy, 21: 33–37.
Tuft, L.A., 1949. Importance of inhalant allergens in atopic dermatitis. J. Invest. Dermatol., 12: 211–219.
van der Brempt, X., Haddi, E., Michel-Nguyen, A., Fayon, J.P., Soler, M., Charpin, D. and Vervloet, D., 1991. Comparison of the ACAREX test with monoclonal antibodies for quantification of mite allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 87: 130–132.
van Leeuwen, W.S., 1927. Asthma and tuberculosis in relation to climate allergens. Br. Med. J., 2: 344–347.
Voorhorst, T., Spieksma, F.Th.M., Varekamp, H., Leupen, M.J. and Lyklema, A.W., 1967. The house dust mite (Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus) and the allergens it produces: identity with the house dust allergen. J. Allergy, 39: 325–339.
Warner, J.O., 1976. Significance of late reactions after bronchial challenge with house dust mite. Arch. Dis. Child., 51: 905–911.
Zeiger, R.S., 1988. The development and prevention of allergic disease in childhood. In: E. Middleton, C.E. Reed, E.F. Ellis, N.F. Adkinson and J.W. Yunginger (Editors), Allergy: Principles and Practice, 3rd edition. Mosby, pp. 930–968.
Zimmerman, T., 1987. Reduzierung der Hausstaubmilben Allergene nach Zimmer und Bettsäuberung. Untersuchung mit echem Teglstreifer System (Acarex). Allergologie, 10: 3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sporik, R., Platts-Mills, T.A.E. Epidemiology of dust-mite-related disease. Exp Appl Acarol 16, 141–151 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01201497
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01201497