Abstract
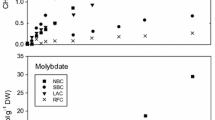
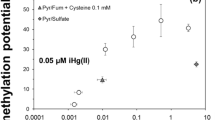
The transformation of MeHg under anaerobic conditions in axenic cultures ofDesulfovibrio desulfuricans strain LS is compared to that in anoxic marine sediments contaminated by Hg of industrial origin. MeHg was added to cultures ofD. desulfuricans strain LS and incubated at 28°C for two weeks. Significant amounts of dimethylmercury and metacinnabar were produced. These two Hg compounds were formed from the slow decomposition of the intermediate dimethylmercury-sulfide. Other collateral compounds, such as methane and ionic Hg, were also detected during the MeHg degradation process. On the other hand a sample of fresh sediment (1.5 g d.w.) was spiked with 10 μg of MeHg and 2 mmoles.ml−1 of pyruvate, as carbon source for sulfate-reducing bacteria. After 9 days of incubation at 28°C, significant amounts of dimethylmercury were produced. A lower content of this volatile species was found in a subsample of sediment supplemented with sodium molybdate, which is a strong inhibitor of sulfatereducing activity. A kinetic study showed the disappearance of monomethylmercury from the sediment and the formation of dimethylmercury over the incubation period. The environmental significance of dimethylmercury and dimethylmercury-sulfide in the natural biogeochemical cycle of Hg is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andren, A.W. and R.C. Harris; 1973,Nature,245: 256.
Baldi, F., M. Pepi and M. Filippelli; 1993,Appl. Environ. Microbiol.,59: 2479.
Baldi, F. and M. Filippelli; 1994, InHg Pollution: Integration and Synthesis. Watras. C. and J.W. Huckabee (eds.) Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton FL, (in press).
Ballantine, D. S. and W. H. Zoller; 1984,Anal. Chem. 56: 1288.
Berman, M., T. Chase and R. Bartha; 1990,Appl. Environ. Microbiol.,56: 298.
Bisogni, J.J. and A.W. Lawrence; 1975,J. Water Pollut. Control Fed.,47: 135.
Bloom, N.S.; 1989,Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci.,46: 1131.
Choi, S.C. and R. Bartha; 1993,Appl. Environ. Microbiol.,59: 290.
Choi, S.C., Chase T.J.R, and R. Bartha; 1994,Appl. Environ. Microbiol.,60: 1342.
Compeau, G.C. and R. Bartha; 1984,Appl. Environ. Microbiol.,48: 1203.
Compeau, G.C. and R. Bartha; 1985,Appl. Environ. Microbiol.,50: 498.
Compeau, G.C. and R. Bartha; 1987,Appl. Environ. Microbiol.,53: 261.
Cossa, D. and J. M. Martin; 1993., Water Resources Report, CEC, Brussels 1993.
Cossa, D. J. M. Martin and J Sanjuan; 1994,Mar. Pollut. Bull. (in press).
Craig, P.J. and P.D. Bartlett; 1978,Nature,275: 635.
D'Itri, P.A. and F.M. D'Itri; 1977, Hg contamination: a human tragedy, John Wiley & Sons, New York, London, Sydney, Toronto.
Filippelli, M.; 1987,Anal. Chem.,59: 116.
Filippelli, M., F. Baldi, E.F. Brinckman and G.J. Olson; 1992,Environ. Sci. Technol.,26: 1457.
Filippelli, M. and F. Baldi; 1993,Appl. Organomet. Chem.,7: 487.
Filippelli, M.; 1994,Appl. Organomet. Chem. (in press).
Hamdy, M. K. and O. R. Noyes; 1975,Appl. Microbiol.,30: 424.
Imura, N., E. Sukegawa, S.K. Pan, K. Nagao, J.Y. Kim, T. Kwan and T. Ukita; 1972,Science,172: 1248.
Jensen, S. and A. Jernelöv; 1969,Nature,223: 753.
Mason, R.P. and W.F. Fitzgerald; 1993,Deep-Sea Res.,40: 1897.
Mason, R.P., K.R. Rolfhus and W.F. Fitzgerald; 1994,Wat. Air Soil Pollut., in press.
Padberg, S., Å. Iverfeldt, Y.H. Lee, F. Baldi, M. Filippelli, K. May and M. Stoeppler; In:Hg as a global pollutant: Toward integration and synthesis. J. Huckabee and C. Watras (ed.) Lewis Publishers, Chelsea, Mich. (in press).
Quevauviller, P., O.X.F. Donnard, J.C. Wassermann, F.M. Martin and J. Schneider; 1992,Appl. Organometal. Chem.,6: 221.
Rapsomanikis, S., Donnard, O.F.X. and Weber J.H.; 1986,Anal. Chem.,58: 35.
Rowland, I.R., M.J. Davies, and P. Grasso; 1977,Nature,265: 718.
Schwarzenbach, G. and M. Schellenberg; 1965,Helv.Chim.Acta 48: 28.
Vonk, J. W. and A. K. Sijpesteijn; 1973,Antoine van Leeuwenhoek,39: 505.
Westöö, G.; 1966,Acta Chem. Scand.,22: 2277.
Wollast, R., G. Billen, and F. T. Mackenzie; 1974, In:Ecological and Toxicological Research. McIntyre and Mills, eds. Plenum Press, New York, p. 145.
Wood, J. M., F.S. Kennedy and C.G. Rosen; 1968,Nature,220: 173.
Wood, J.M. and H.K. Wang; 1983,Environ. Sci. Technol.,17: 582.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baldi, F., Parati, F. & Filippelli, M. Dimethylmercury and dimethylmercury-sulfide of microbial origin in the biogeochemical cycle of HG. Water Air Soil Pollut 80, 805–815 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01189732
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01189732