Summary
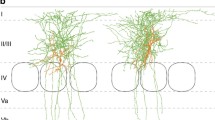
In vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP)-immunoreacted preparations, bipolar neurons are the cells most commonly labelled. The VIP-positive axon terminals form symmetrical synapses, and their most common postsynaptic targets are small and medium sized dendrites. These are of both smooth and spiny types. Additionally, there is a concentration of VIP-positive axon terminals around the cell bodies of pyramidal neurons, and it is suggested that an important function of VIP-labelled bipolar cells is to inhibit vertically oriented groups of pyramidal cells.
In order to further examine the features of axon terminals that label with VIP antibodies, conventionally prepared material was examined by electron microscopy. Those terminals which label with VIP antibody are characterized by irregular profiles of varying sizes and shapes, and by containing closely packed pleomorphic vesicles. Such terminals form symmetrical synapses. The junctions are not well marked by associated cytoplasmic densities, but there is an inherent density within the synaptic cleft. It is suggested that these features characterize all axon terminals in which GABA coexists with peptides in cerebral cortex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Connor, J. R. &Peters, A. (1984) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-immunoreactive neurons in rat visual cortex.Neuroscience 12, 1027–44.
De Lima, A. D. &Morrison, J. H. (1989) Ultrastructural analysis of somatostatin-immunoreactive neurons and synapses in the temporal and occipital cortex of the macaque monkey.Journal of Comparative Neurology 283, 212–27.
Eckenstein, F. &Baughman, R. W. (1984) Two types of cholinergic innervation in cortex, one co-localized with vasoactive intestinal polypeptide.Nature 309, 153–5.
Eldred, W. D., Zucker, C., Karten, H. J. &Yazulla, S. (1983) Comparison of fixation and penetration enhancement techniques for use in ultrastructural immunocyto-chemistry.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 31, 285–92.
Emson, P. C., Gilbert, R. F. T., Loren, I., Fahrenkreig, J., Sundler, F. &Schaffalitzky De Muckadell, O. B. (1979) Development of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) containing neurones in the rat brain.Brain Research 177, 437–44.
Fairén, A., De Felipe, J. &Regidor, J. (1984) Nonpyramidal neurons. General account. InCerebral Cortex, Vol. 1 (edited byPeters, A. &Jones, E. G.) pp. 201–53. New York: Plenum Press.
Fairén, A., Peters, A. &Saldanha, J. (1977) A new procedure for examining Golgi impregnated neurons by light and electron microscopy.Journal of Neurocytology 6, 311–37.
Feldman, M. L. &Peters, A. (1978) The forms of nonpyramidal neurons in the visual cortex of the rat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 179, 761–94.
Fuxe, K., Höfelt, T., Said, S. Z. &Mutt, V. (1977) VIP and the nervous system: immunohistochemical evidence for localization in central and peripheral nerves, particularly intracortical neurons of cerebral cortex.Neuroscience Letters 5, 241–6.
Hajós, F., Zilles, K., Gallatz, K., Schleicher, A., Kaplan, I. &Werner, L. (1988a) Ramification patterns of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP)-cells in the rat primary visual cortex. An immunohistochemical study.Anatomy and Embryology 233, 147–258.
Hajós, F., Zilles, K., Schleicher, A. &Kálán M. (1988b) Types and spatial distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP)-containing synapses in the rat visual cortex.Anatomy and Embryology 178, 207–17.
Harris, K. M., Marshall, P. E. &Landis, D. M. D. (1985) Ultrastructural study of cholecystokinin-immunoreactive cells and processes in area CAI of the rat hippocampus.Journal of Comparative Neurology 233, 147–58.
Hendry, S. H. C., Jones, E. G. &Emson, P. C. (1984) Morphology, distribution and synaptic relations of somatostatin- and neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive neurons in rat and monkey neocortex.Journal of Neuroscience 4, 2497–517.
Hendry, S. H. C. &Jones, E. G. (1985) Morphology of synapses formed by cholecystokinin-immunoreactive axon terminals in regio superior of rat hippocampus.Neuroscience 16, 57–68.
Hendry, S. H. C., Jones, E. G., Defelipe, J., Schmechel, D., Brandon, C. &Emson, P. C. (1984) Neuropeptide-containing neurons of the cerebral cortex are also GABAergic.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 81, 6526–30.
Houser, C. R., Crawford, G. D., Salvaterra, P. M. &Vaughn, J. E. (1985) Immunocytochemical localization of choline acetyltransferase in rat cerebral cortex. A study of colinergic neurons and synapses.Journal of Comparative Neurology 234, 17–34.
Houser, C. R., Vaughn, J. E., Hendry, S. H. C., Jones, E. G. &Peters, A. (1984) GAB neurons in the cerebral cortex. InCerebral Cortex, Vol. 2Functional Properties of Cortical Cells (edited byJones, E. G. &Peters, A.) pp. 63–89. New York: Plenum Press.
Jones, E. G. (1987) GABA-peptide neurons of the primate cerebral cortex. InInhibition in the Brain (edited byRikak, C. E.).Journal of Mind and Behavior 8, 519–36.
Jones, E. G. &Hendry, S. H. C. (1986) Co-localization of GABA and neuropeptides in neocortical neurons.Trends in Neuroscience 9, 71–6.
King, J. C., Lechan, R. M., Kugel, G. &Anthony, E. L. P. (1983) A fixative for immunohistochemical localization of peptides in the central nervous system.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 81, 62–8.
Kosaka, T., Kosaka, K., Tateishi, K., Hamaoka, Y., Yanaihara, N., Wu, J.-E. &Hama, K. (1985) GABAergic neurons containing CCK-8-like and/or VIP-like immunoreactivities in the rat hippocampus and dentate gyrus.Journal of Comparative Neurology 239, 420–30.
Kuljis, R. O. &Rakic, P. (1989) Multiple types of neuropeptide Y-containing neurons in primate neocortex.Journal of Comparative Neurology 280, 393–409.
Lorén I., Emson, P. C., Fahrenkrug, J., Bjöklund, A., Alumets, J., Håkanson, R. &Sundler, F. (1979) Distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the rat and mouse brain.Neuroscience 4, 1953–76.
McDonald, J. K. (1984) Osmium ferricyanide fixation improves microfilament preservation and membrane visualization in a variety of animal cell types.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 86, 107–18.
McDonald, J. K., Parnavelas, J. G., Karamanlidis, A. N. &Brecha, N. (1982) The morphology and distribution of peptide-containing neurons in the adult and developing visual cortex of the rat. II. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide.Journal of Neurocytology 11, 825–37.
Meinecke, D. L. &Peters, A. (1987) GABA-immunoreactive neurons in rat visual cortex.Journal of Comparative Neurology 261, 388–404.
Morrison, J. H., Magistretti, P. J., Benoit, R. &Bloom, F. E. (1984) The distribution and morphological characteristics of the intracortical VIP-positive cell: an immuno-histochemical analysis.Brain Research 292, 269–82.
Nunzi, M. G., Gorio, A., Milan, F., Freund, T. F., Somogyi, P. &Smith, A. D. (1985) Cholecystokinin-immunoreactive cells form symmetric synaptic contacts with pyramidal and non-pyramidal neurons in hippocampus.Journal of Comparative Neurology 237, 485–505.
Papadopoulos, G. C., Parnavelas, J. G. &Cavanagh, M. E. (1982) Extensive co-existence of neuropeptides in the rat visual cortex.Brain Research 420, 95–9.
Parnavelas, J. G., Kelly, W., Franke, E. &Eckenstein, F. (1986) Cholinergic neurons and fibers in the rat visual cortex.Journal of Neurocytology 15, 329–36.
Parnavelas, J. G., Sullivan, K., Lieberman, A. R. &Webster, K. E. (1977) Neurons and their synaptic organization in the visual cortext of the rat. Electron microscopy of Golgi preparations.Cell and Tissue Research 183, 499–517.
Peters, A. &Harriman, K. M. (1988) Enigmatic bipolar cell of rat visual cortex.Journal of Comparative Neurology 267, 409–32.
Peters, A. &Harriman, K. M. (1990) Different kinds of axon terminals forming symmetric synapses with the cell bodies and initial axon segments of layer II/III pyramidal cells. I. A morphometric analysis.Journal of Neurocytology 19, 154–74.
Peters, A. &Kara, D. A. (1985a) The neuronal composition of area 17 of rat visual cortex. I. The pyramidal cells.Journal of Comparative Neurology 234, 213–41.
Peters, A. &Kara, D. A. (1985b) The neuronal composition of area 17 of rat visual cortex. II. The nonpyramidal cells.Journal of Comparative Neurology 242, 242–63.
Peters, A. &Kara, D. A. (1987) The neuronal composition of area 17 of rat visual cortex. IV. The organization of pyramidal cells.Journal of Comparative Neurology 260, 573–90.
Peters, A. &Kimerer, L. M. (1981) Bipolar neurons in rat visual cortex: a combined Golgi-electron microscope study.Journal of Neurocytology 10, 921–46.
Peters, A., Meinecke, D. L. &Karamanlidis, A. N. (1987) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide immunoreactive neurons in cat primary visual cortex.Journal of Neurocytology 16, 23–38.
Peters, A., Proskauer, C. C., Feldman, M. L. &Kimerer, L. (1979) The projection of the lateral geniculate nucleus to area 17 of the rat cerebral cortex. V. Degenerating axon terminals synapsing with Golgi impregnated neurons.Journal of Neurocytology 8, 331–57.
Ribak, C. E. (1978) Aspinous and sparsely spinous stellate neurons in the visual cortex of rats contain glutamic acid decarboxylase.Journal of Neurocytology 7, 461–78.
Schober, W., Hedlich, A., Vrensen, G. &Müler, L. (1983) Termination of geniculocortical afferents on bipolar neurons in area 17 of the albino rat: A Golgi/EM study.Journal für Hirnforschung 24, 473–7.
Sims, K. B., Hoffman, D. L., Said, S. I. &Zimmerman, E. A. (1980) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in mouse and rat brain: an immunocytological study.Brain Research 186, 165–83.
Somogyi, P., Hodgson, A. J., Smith, D. A., Nunzi, M. G., Gorio, A. &Wu J. -Y. (1984) Different populations of GABAergic neurons in the visual cortex and hippocampus of cat contain somatostatin- or cholecystokinin-immunoreactive material.Journal of Neuroscience 4, 2590–603.
Westenbroek, R. E., Westrum, L. E., Hendrickson, A. E. &Wu, J.-E. (1988) Ultrastructural localization of immunoreactivity in the developing piriform cortex.Journal of Comparative Neurology 274, 319–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peters, A. The axon terminals of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP)-containing bipolar cells in rat visual cortex. J Neurocytol 19, 672–685 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01188036
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01188036