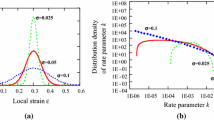
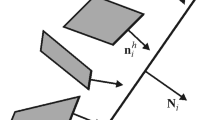
Summary
Kinetics is studied during the martensitic transformation on both the micro- and macro-level from the thermomechanical point of view. A variant, a smallest microstructure element in an alloy, is assumed to transform at a burst when a transformation condition expressed by means of the driving force is satisfied. It has a micro-fraction showing 1 (transformed) or 0 (yet untransformed). The macrofraction, which represents a certain extent of transformation in a representative volume composed of a large enough number of variants, is derived by performing an ensemble average of the micro-fraction over the representative volume. The progress of the macro-fraction during thermomechanical loading is shown to be governed by a differential equation, the solution of which could be reduced to the conventional transformation kinetics discussed in the fields of metallurgy and transformation thermomechanics. A linear relation is derived between the increments of the macroscopic transformation strain and of the macro-fraction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tanaka, K., Nagaki, S.: A thermomechanical description of materials with internal variables in the process of phase transitions. Ing. Arch.51, 287–299 (1982).
Tanaka, K., Kobayashi, S., Sato, Y.: Thermomechanics of transformation pseudoelasticity and shape memory effect in alloys. Int. J. Plasticity2, 59–72 (1986).
Abeyaratne, R., Knowles, J. K.: A continuum model of a thermoelastic solid capable of undergoing phase transitions. J. Mech. Phys. Solids.41, 541–571 (1993).
Fischer, F. D., Berveiller, M., Tanaka, K., Oberaigner, E. R.: Continuum mechanical aspects of phase transformations in solids. Arch. Appl. Mech.64, 54–85 (1993).
Olson, G. B., Roitburd, A. L.: Martensitic nucleation. In: Martensite (Olson, G. B., Owen, W. S., eds.), pp. 149–174. Materials Park, Ohio: ASM International 1993.
Grujicic, M., Ling, H. C., Haezebrouck, D. M., Owen, W. S.: The growth of martensite. In: Martensite (Olson, G. B., Owen, W. S., eds.), pp. 175–196. Materials Park, Ohio: ASM International 1993.
Heidug, W., Lehner, F. K.: Thermodynamics of coherent phase transformations in nonhydrostatically stressed solids. Pure Appl. Geophys.123, 91–98 (1985).
Abeyaratne, R., Knowles, J. K.: On the driving traction acting on a surface of strain discontinuity in a continuum. J. Mech. Phys. Solids38, 345–360 (1990).
Liu, I.-S.: On interface equilibrium and inclusion problems. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn.4, 177–186 (1992).
Raniecki, B., Tanaka, K.: On the thermodynamic driving force for martensitic transformations. In: Residual stresses — 3 Hujiwara, H., Abe, T., Tanaka, K., eds.), Vol. 1, pp. 196–201. London, New York: Elsevier 1992.
Lexcellent, C., Torra, V.: Micromechanics of shape memory alloys Cu−Zn−Al single crystal: Experiments and modelling. In: MECAMAT 93, Int. Seminar on Micromechanics of Materials, pp. 234–245. Paris: Editions Eyrolles 1993.
Tamura, I.: Deformation-induced martensitic transformation and transformation-induced plasticity in steels. Metal Sci.16, 245–253 (1982).
Wang, Z. G., Inoue, T.: Analyses of temperature, structure and stress during quenching of steel with consideration for stress dependence of transformation kinetics. J. Soc. Mater. Sci. Jpn.32, 991–996 (1983).
Nishiyama, Z.: Martensitic transformation. New York: Academic Press 1978.
Kaufmann, L., Hilbert, M.: Thermodynamics of martensitic transformation. In: Martensite (Olson, G. B., Owen, W. S., eds.), pp. 41–58. Materials Park, Ohio: ASM International 1993.
Magee, C. L.: The nucleation of martensite. In: Phase transformations (Aaronson, H. I., ed.), pp. 115–156. Materials Park, Ohio: ASM 1969.
De Groot, S. R., Mazur, P.: Non-equlibrium thermodynamics. Amsterdam: North-Holland 1962.
Inoue, T., Raniecki, B.: Determination of thermal-hardening stresses in steels by use of thermoplasticity theory. J. Mech. Phys. Solids26, 187–212 (1978).
Tanaka, K., Sato, Y.: A mechanical view of transformation-induced plasticity. Ing. Arch.55, 147–155 (1985).
Tanaka, K.: A phenomenological description on thermomechanical behavior of shape memory alloys. J. Pressure Vessel Tech.112, 158–163 (1990).
Fischer, F. D., Tanaka, K.: A micromechanical model for the kinetics of martensitic transformation. Int. J. Solids Struct.29, 1723–1728 (1992).
Marchand, J. P.: Distributions, and outline. Amsterdam: North-Holland 1962.
Koistinen, D. P., Marburger, R. E.: A general prescribing the extent of the austenite-martensite transformation in pure iron-carbon alloys and plain carbon steel. Acta Metall.7, 59 (1959).
Hill, R.: Elastic properties of reinforced solids: some theoretical principles. J. Mech. Phys. Solids11, 357–372 (1963).
Mori, T., Wakashima, K.: Successive iteration method in the evaluation of averaged field in elastically inhomogeneous materials. In: Micromechanics and inhomogeneity (Weng, G. J., Taya, H., Abe, H., eds.), pp. 269–282. New York: Springer (1990).
Kröner, E.: Statistical continuum mechanics. Wien, New York: Springer 1972.
Patoor, E., Eberhardt, A., Berveiller, M.: Thermomechanical behavior by martensitic transformation in single and polycrystals. In: Proc. 8th RISO Int. Symp., pp. 465–470, Riso 1987.
Wakashima, K., Tsukamoto, H., Choi, B. H.: Elastic and thermoelastic properties of metal matrix composite with discontinuous fibers or particles. In: Proc. Korea-Japan Metal Symp. Composite Materials, Seoul/Korea, pp. 102–112, 1988.
Benveniste, Y., Dvorak, G. J.: On a correspondence between mechanical and thermal effects in two-phase composite. In: Micromechanics and inhomogeneity (Wang, G. J., Taya, H., Abe, H., eds.), pp. 65–82. New York: Springer 1990.
Eshelby, J. D.: The determination of the elastic field on an ellipsoidal inclusion and related problems. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser.A241, 376–396 (1957).
Withers, P. J., Stobbs, W. M., Pedersen, O. B.: The application of the Eshelby method of internal stress determination to short fibre metal matrix composites. Acta Metall.37, 3061–3084 (1989).
Tanaka, K., Hasegawa, D., Böhm, H. J., Fischer, F. D.: Overall thermomechanical behavior of shape memory alloys; a micromechanical approach based on mean field theory. Mat. Sci. Res. Int.1, 23–30 (1995).
Patel, J. R., Cohen, M.: Criterion for the action of applied stress in the martensitic transformation. Acta Metall.1, 531–538 (1953).
Gautier, E., Zhang, X. M., Simon, A.: Role of internal stress state on transformation induced plasticity and transformation mechanisms during the progress of stress induced phase transformation. In: International Conference on Residual Stresses (ICRS2), (Beck, G., Denis, S., Simon, A., eds.), pp. 777–783. London, New York: Elsevier 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, K., Oberaigner, E.R. & Fischer, F.D. Kinetics on the micro- and macro-levels in polycrystalline alloy materials during martensitic transformation. Acta Mechanica 116, 171–186 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01171428
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01171428