Summary
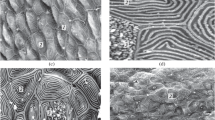
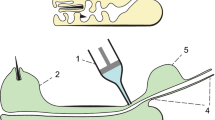
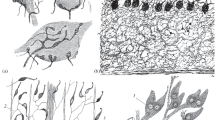
The sensory epithelium lining the ampulla of Lorenzini in the skate was examined by the freeze-fracture technique. Anastomosing tight junctions (zonula occludens) completely encircle the apex of each receptor cell joining it to neighbouring support cells. The tight junctions separate two distinctly different regions of the receptor-cell surface. The apical P-face has numerous large particles while just below the tight junctions of the lateral surface have many smaller particles. On its basal surface each receptor cell makes several evaginating ribbon synapses with an afferent nerve. Three regions of the synaptic evagination can be distinguished on the basis of membrane specializations: 1. At the tip of the evagination a regular array of large particles is found on the P-face of the receptor cell directly opposite a similar regular array of large particles on the P-face of the afferent nerve; 2. just above the tip at a narrow constriction, below which vesicles are not found, a population of large particles on the P-face of the receptor cell opposes a well-defined strip of large particles that cleaves with the E-face of the nerve fibre; 3. at the arch of the synaptic evagination randomly occurring dimples are found on the P-face and protrusions on the E-face of the receptor cell. The density of these protrusions increased in skates that were electrically stimulated. We suggest that the co-extensive arrays of particles at the tip of the ribbon synapse is an intercellular junction; that the active zone of the synapse is at or above the constriction; and that membrane retrieval occurs in the synaptic arch region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akert, K., Sandri, C. &Bennett, M. V. L. (1980) Ultrastructural characteristics of tuberous electroreceptors in a high frequency electric gymnotid,Sternarchus albifrons.Experientia 36, 737.
Barets, A. &Szabo, T. (1962) Appareil synaptique des cellules sensorielle de l'ampoule de Lorenzini chez la torpille,Torpedo marmomta.Journal de Microscopic 1, 47–54.
Bennett, M. V. L. &Clusin, W. T. (1979) Transduction at electroreceptors: origins and sensitivity. InMembrane Transduction Mechanisms (edited byCone, R. A. andDowling, J. E.), pp. 91–116. New York: Raven Press.
Bullock, T. H. (1982) Electroreception.Annual Reviews of Neuroscience 5, 121–70.
Clusin, W. T. &Bennett, M. V. L. (1977a) Calcium-activated conductance in skate electroreceptors. Current clamp experiments.Journal of General Physiology 69, 121–43.
Clusin, W. T. &Bennett, M. V. L. (1977b) Calcium-activated conductance in skate electroreceptors. Voltage-clamp experiments.Journal of General Physiology 69, 145–82.
Clusin, W. T. &Bennett, M. V. L. (1979a) The oscillatory response of skate electroreceptors to small voltage stimuli.Journal of General Physiology 73, 685–702.
Clusin, W. T. &Bennett, M. V. L. (1979b) The ionic basis of oscillatory responses of skate electroreceptors.Journal of General Physiology 73, 703–23.
Clusin, W. T., Spray, D. C. &Bennett, M. V. L. (1975) Activation of a voltage-sensitive conductance by inward calcium current.Nature 256, 425–7.
Derbin, C. (1970) Effets de la section du nerf lateral sur les jonctions sensorineurales des ampoules de Lorenzini de la torpille,Torpedo marmorata.Journal de Microscopie 9, 119–26.
Dotterweich, H. (1931) Bau und Function der Lorenzini'sehen Ampullen.Zoologische Jahrbucher Physiologie 50, 347–417.
Dragsten, P. R., Blumenthal, R. &Handler, J. S. (1981) Membrane asymmetry in epithelia: is the tight junction a barrier to diffusion in the plasma membrane?Nature 294, 718–22.
Franzini-Armstrong, C. (1976) Freeze-fracture of excitatory and inhibitory synapses at crayfish neuromuscular junctions.Journal de Microscopie et de Biologie Cellulaire 25, 217–22.
GulleY, R. L. &Reese, T. S. (1976) Intercellular junctions in the reticular lamina of the organ of Corti.Journal of Neurocytology 5, 479–507.
Heuser, J. E. &Reese, T. S. (1977) Structure of the synapse. InHandbook of Physiology -The Nervous System, Vol. 1 (edited byKandel, E.). pp. 261–94. Washington DC: American Physiological Society.
Heuser, J. E. &Reese, T. S. (1979) Changes in the structure of presynaptic membranes during transmitter secretion. InNeurobiology of Chemical Transmission (edited byOtsuka, M. &Hall, Z.), pp. 3–11. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Heuser, J. E. &Reese, T. S. (1981) Structural changes after transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction.Journal of Cell Biology 88, 564–80.
Kalmijn, A. J. (1966) Electroreception in sharks and rays.Nature 212, 1232–3.
Kalmijn, A. J. (1974) The detection of electric fields from inanimate sources other than electric organs. InHandbook of Sensory Physiology. Vol III 3, Electroreceptors and other Specialized Receptors in Lower Vertebrates (edited byFessard, A.), pp. 12–58. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Landis, D. M. D. &Reese, T. S. (1974) Differences in membrane structure between excitatory and inhibitory synapses in cerebellar cortex.Journal of Comparative Neurology 155, 93–126.
Landis, D. M. D., Reese, T. S. &Raviola, E. (1974) Differences in membrane structure between excitatory and inhibitory components of the reciprocal synapse in the olfactory bulb.Journal of Comparative Neurology 155, 67–92.
Murray, R. W. (1962) The responses of the ampullae of Lorenzini of elasmobranchs to electrical stimulation.Journal of Experimental Biology 39, 119–28.
Obara, S. &Bennett, M. V. L. (1972) Mode of operation of ampullae of Lorenzini of the skate,Raja. Journal of General Physiology 60, 534–57.
Osborne, M. P. (1977) Role of vesicles with some observations on vertebrate sensory cells. InSynapses: Proceedings of an International Symposium (edited byCottrell, G. A. &Usherwood, P. N. R.), pp. 40–63. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Pumplin, D. W., Reese, T. S. &Llinas, R. (1981) Are the presynaptic membrane particles the calcium channels?Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 78, 7210–3.
Raviola, E. &Gilula, N. B. (1975) Intramembrane organization of specialized contacts in the outer plexiform layer of the retina.Journal of Cell Biology 65, 192–222.
Rheuben, M. B. &Reese, T. S. (1978) Three-dimensional structure and membrane specializations of moth excitatory neuromuscular synapses.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 65, 95–111.
Saito, K. (1980) Fine structure of the sensory epithelium of the guinea pig organ of Corti: afferent and efferent synapses of hair cells.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 71, 222–32.
Schaeffer, S. F. &Raviola, E. (1978) Membrane recycling in the cone cell endings of the turtle retina.Journal of Cell Biology 79, 802–25.
Schaeffer, S. F., Raviola, E. &Heuser, J. E. (1982) Membrane specializations in the outer plexiform layer of the turtle retina.Journal of Comparative Neurology,204, 253–67.
Sejnowski, T. J. &Yodlowski, M. L. (1978) A freeze-fracture study of the skate electroreceptor.Biological Bulletin 155, 465.
Staehelin, L. A. (1974) Structure and function of intercellular junctions.International Review of Cytology 39, 191–283.
Szabo, T. (1972) Ultrastructural evidence for a mechanoreceptor function of the ampullae of Lorenzini.Journal de Microscopie 14, 343–50.
Szabo, T. (1974) Anatomy of the specialized lateral line organs of electroreceptors. InHandbook of Sensory Physiology. Vol III 3. Electroreceptor and other Specialized Receptors in Lower Vertebrates (edited byFessard, A.), pp. 12–58. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Waltman, B. (1966) Electrical properties and fine structure of the ampullary canals of Lorenzini.Acta Physiologica Scandanavica 66 Suppl. 264, 1–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sejnowski, T.J., Yodlowski, M.L. A freeze-fracture study of the skate electro receptor. J Neurocytol 11, 897–912 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01148307
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01148307