Abstract
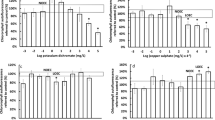
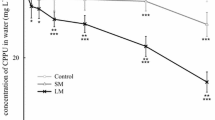
An assay based on inhibition of a-glucosidase biosynthesis (AGB) inBacillus licheniformis was used to test the toxicity of sediment elutriates from hazardous waste sites in Florida. The assay gave the same general classification of toxicity as Microtox in 85% of the 66 elutriates screened. For the ten most inhibitory elutriates, the AGB assay consistently gave lower EC50s than Microtox. These samples were the highest in concentrations of cadmium, copper, lead, zinc of all those screened, suggesting that the AGB assay is particularly sensitive to heavy metals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bitton G, Dutka BJ (1986) Toxicity testing using microorganisms, Vol 1. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Campbell M, Bitton G, Koopman B, Delfino JJ (1992) Preliminary comparison of sediment extraction procedures and exchange solvents for hydrophobic compounds based on inhibition of bioluminescence. Environ Toxicol Water Qual 7:329–338
Daniels SA, Munawar M, Mayfield CI (1989) An improved elutriation technique for the bioassessment of sediment contaminants. Hydrobiologia 188/189:619–631
Dutton RJ (1988) Enzyme biosynthesis in bacteria as a basis for toxicity testing. Doctoral Dissertation. University of Florida, Gainesville, FL
Dutton RG, Bitton G, Koopman B, Agami O (1990) Effect of environmental toxicants on enzyme biosynthesis: A comparison of β-ga-lactosidase, α-glucosidase and tryptophanase. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 19:395–398
Krawczyk DF (1984) Biological methods for determining toxicity of contaminated freshwater sediments to invertebrates. Environ Toxicol Chem 3:617–630
Ludwig DD, Sherrard JH, Amende RA (1989) Evaluation of the standard elutriate test as an estimator of contamination release at dredging sites. Res J Wat Pollut Control Fed 61:619–631
Microbics Corp (1982) Microtox Systems Operation Manual, No. 015-555-879. 2233 Faraday, Suite B. Carlsbad, CA
Nebeker AV, Cairns MA, Gakstater JH, Malueg KW, Schuytema GS, Krawczwk DF (1984) Biological methods for determining toxicity of contaminated freshwater sediments to invertebrates. Environ Toxicol Chem 3:617–630
Reinhartz A, Lampert I, Herzberg M, Fish F (1987) A new short term sensitive bacterial assay kit for the detection of toxicants. Toxicol Assess 2:193–206
Ross PE, Henebry MS (1989) Use of four microbial tests to assess the ecotoxicological hazard of contaminated sediments. Toxicol Asses 4:1–21
USEPA (1983) Methods for chemical analysis of water ans waste. EPA-600/4-79-020. US Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, OH
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campbell, M., Bitton, G. & Koopman, B. Toxicity testing of sediment elutriates based on inhibition of alpha-glucosidase biosynthesis inBacillus licheniformis . Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 24, 469–472 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01146163
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01146163