Abstract
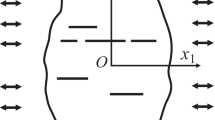
For the purpose of clarifying the micro fracture of continuous fiber unidirectionally reinforced composite materials, the problem of an edge crack perpendicular to a long reinforced phase is considered on the basis of the plane strain theory of elasticity. The stress intensity factor at the tip of the crack, and the stresses on the interface between the matrix and the reinforced phase and in the reinforced phase are discussed. In the analysis, the method of continuous distributions of dislocations is used. Then, a singular integral equation is derived and is solved by the technique developed by Erdogan and Gupta.
From the numerical results it was concluded that:
-
(1)
The stress intensity factor decreases monotonically as the crack tip approaches the reinforced phase. That is, the presence of the reinforced phase can result in crack arrest.
-
(2)
When the crack tip exists near the reinforced phase, the normal stress on the interface between the matrix and the reinforced phase has a maximum at the intersection of the extension of the edge crack and the reinforced phase, while the shear stress on the interface and the normal stress in the reinforced phase take, respectively, maxima at symmetric points with respect to the crack surface in the immediate vicinity of the intersection.
-
(3)
The maximum values of the stresses on the interface and in the reinforced phase increase monotonically as the crack tip approaches the reinforced phase.
Résúme
En vue de clarifier la micro-rupture de matériaux composites renforcés par des fibres, on considère le problème d'une fissure de bord normale à une longue section de renforcement, en se basant sur la théorie de l'état plan de déformation de l'élasticité. Sont discutés le facteur d'intensité des contraintes à l'extrémité de la fissure, et les contraintes à l'interface entre la matrice et la section de renforcement, ainsi que dans cette portion même. Dans l'analyse, on utilise la méthode de la distribution continue des dislocations. On en tire une équation intégrale singulière, qui est résolue selon la technique proposée par Erdogan et Gupta.
On conclut des résultats numériques que:
-
- le facteur d'intensité de contraintes décroît continûment lorsque l'extrémité de l'entaille se rapproche de la portion de renforcement: la présence de celle-ci peut donc agir comme arrêt de fissuration.
-
- Lorsque l'extrémité de la fissure se trouve au voisinage du renforcement la tension normale dans l'interface entre la matrice et la fibre passe par un maximum au niveau du plan de la fissure, tandis que les tensions de cisaillement sur l'interface, et de traction sur la fibre passant respectivement par des maxima en des points symétriques par rapport au plan de la fissure, dans le voisinage immédiat de son intersection avec la fibre.
-
- La valeur maximum des contraintes dans l'interface et dans la portion de renforcement augmente de manière régulière lorsque l'extrémité de la fissure se rapproche de cette portion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.C. Sih and V.P. Tamuzs (eds.),Fracture of Composite Materials, Sijthoff and Noordhoff, The Netherlands (1979).
G.C. Sih and V.P. Tamuzs (eds.),Fracture of Composite Materials, Martinus Nijhoff, The Netherlands (1982).
G.A. Cooper and A. Kelly,Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 15 (1967) 279–297.
A.H. Pacella and F. Erdogan,International Journal of Solids and Structure 10 (1974) 807–819.
B. Harris,Metal Science 14 (1980) 351–362.
J.A. Mandel, S.C. Pack and S. Tarazi,Engineering Fracture Mechanics 16 (1982) 741–754.
F. Erdogan and G.D. Gupta,Quarterly of Applied Mathematics 32 (1972) 525–534.
N.I. Muskhelishvili,Some Basic Problems of the Mathematical Theory of Elasticity, Noordhoff, The Netherlands (1963).
O. Tamate and N. Iwasaka,International Journal of Solids and Structures 11 (1975) 1257–1268.
S. Krenk,Quarterly of Applied Mathematics 32 (1975) 479–484.
H. Tada, P. Paris and G. Irwin,The Stress Analysis of Cracks Handbook, Del Research, Pennsylvania (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujino, K., Sekine, H. & Abé, H. Analysis of an edge crack in a semi-infinite composite with a long reinforced phase. Int J Fract 25, 81–94 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01141552
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01141552