Summary
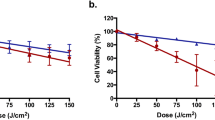
Solar ultraviolet radiation has been associated with the induction of skin cancer. Recent studies have indicated that near-ultraviolet, especially UVB, is mutagenic. Exposure to trivalent inorganic arsenic compounds has also been associated with increased skin cancer prevalence. Trivalent arsenic compounds are not mutagenicper se, but are comutagenic with a number of cancer agents. Here, we test the hypothesis that arsenite enhances skin cancer via its comutagenic action with solar ultraviolet radiation. Irradiation of Chinese hamster V79 cells with UVA (360 nm), UVB (310 nm) and UVC (254 nm) caused a fluence-dependent increase in mutations at thehprt locus. On an energy basis, UVC was the most mutagenic and UVA the least. However, when expressed as a function of toxicity, UVB was more mutagenic than UVC. Nontoxic concentrations of arsenite increased the toxicity of UVA, UVB and UVC. Arsenite acted as a comutagen at the three wavelengths; however, higher concentrations of arsenite were required to produce a significant (P < 0.05) comutagenic response with UVB. The increased mutagenicity of UVB and UVA by arsenite may play a role in arsenite-related skin cancers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arlett CF, Turnbull D, Harcourt SA, Lehmann AR, Colella CM (1975) A comparison of the 8-azaguanine and ouabain-resistance systems for the selection of induced mutant Chinese hamster cells. Mutat Res 33:261–278
Bradley MO, Sharkley NA (1977) Mutagenicity and toxicity of visible fluorescent light to cultured mammalian cells. Nature 266:724–726
Chang CC, Castellazzi M, Glover TW, Trosko JE (1978) Effects of harmon and nonharmon on spontaneous and ultraviolet light-induced mutagenesis in cultured Chinese hamster cells. Cancer Res 38:4527–4533
Coohill TP, Peak MJ, Peak JG (1987) The effects of the ultraviolet wavelengths of radiation present in sunlight on human cells in vitro. Photochem Photobiol 46:1043–1050
Cuzik J, Evans S, Gillman M, Price-Evans DA (1982) Medicinal arsenic and internal malignancies. Br J Cancer 45:904–911
Enninga IC, Groenendijk RTL, Filon AR, van Zeeland AA, Simmons JWIM (1986) The wavelength dependence of u.v.-induced pyrimidine dimer formation, cell killing and mutation induction in human diploid skin fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis 7:1829–1836
Hsie AW, Li AP, Machanoff R (1977) A fluence response study of lethality and mutagenicity of white, black and blue fluorescent light, sunlamp and sunlight irradiation in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mutat Res 45:333–342
Jones CA, Huberman E, Cunningham ML, Peak MJ (1987) Mutagenesis and cytotoxicity in human epithelial cells by far- and near-ultraviolet radiations: action spectra. Radiat Res 110:244–254
Lee TC, Huang RY, Jan KY (1985) Sodium arsenite enhances the cytotoxicity, clastogenicity, and 6-thioguanine-resistant mutagenicity of ultraviolet light in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mutat Res 148:83–89
Li J-H (1989) PhD Thesis. New York University
Li J-H, Rossman TG (1989a) Mechanism of comutagenesis of sodium arsenite withN-methyl-N-nitrosourea. Biol Trace Element Res 21:373–381
Li J-H, Rossman TG (1989b) Inhibition of DNA ligase activity by arsenite: a possible mechanism of its comutagenesis. Mol Toxicol 2:1–9
Lofroth G, Ames BN (1978) Mutagenicity of inorganic compounds inSalmonella typhimurium: Arsenic, chromium, and selenium. Mutat Res 53:65–66
National Research Council (1982) Report on causes and effects of stratospheric ozone reduction: an update. National Academy Press, Washington DC
Okui T, Fujiwara Y (1986) Inhibition of human excision DNA repair by inorganic arsenic and the comutagenic effect in V79 Chinese hamster cells. Mutat Res 172:69–76
Parrish JA, Anderson RR, Urbach F, Pitts D (1978) Biological effects of ultraviolet radiation with emphasis on human responses to long-wave ultraviolet. Plenum Press, New York
Peak MJ, Peak JG (1989) Solar-ultraviolet-induced damage to DNA. Photodermatology 6:1–15
Roberts JD, Kunkel TA (1986) Mutational specificity of animal cell polymerases. Environ Mutagen 8:769–789
Rossman TG, Meyn MS, Troll W (1977) Effects of arsenite on DNA repair inEscherichia coli. Environ Health Perspect 19:229–233
Rossman TG, Stone D, Molina M, Troll W (1980) Absence of arsenite mutagenicity inE. coli and Chinese hamster cells. Environ Mutagen 2:371–379
Setlow RB (1974) The wavelengths in sunlight effective in producing skin cancer: a theoretical analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:3363–3366
Smith KC (1981) Photobiology and photomedicine: the future is bright. J Invest Dermatol 77:2–7
Sterenborg HJCM, van der Leun JC (1990) Tumorigenesis by a long-.wavelength UVA source. Photochem Photobiol 51:325–330
Tseng WP (1977) Effects and dose-response relationships of skin cancer and blackfoot disease with arsenic. Environ Health Perspect 19:109–119
Tyrrell RM (1984) Mutagenic action of monochromatic UV radiation in the solar range on human cells. Mutat Res 129:103–110
Tyrrell RM, Amaudruz F (1984) Alpha polymerase involvement in excision repair of damage induced by solar radiation at defined wavelengths in human fibroblasts. Photochem Photobiol 40:449–451
Zelle B, Reynolds RJ, Kettenhagen MJ, Schuite A, Johman PHM (1980) The influence of the wavelengths of ultraviolet radiation on survival, mutation induction and DNA repair in irradiated Chinese hamster cells. Mutat. Res. 72:491–509
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, JH., Rossman, T.G. Comutagenesis of sodium arsenite with ultraviolet radiation in Chinese hamster V79 cells. Biol Metals 4, 197–200 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01141180
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01141180