Abstract
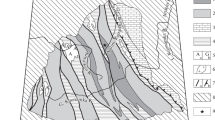
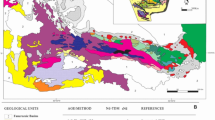
Variably foliated, predominantly granodioritic plutonic rocks from the northern part of the Shaw Batholith in the east Pilbara Archaean craton are dated at 3,499±22 Ma (2σ errors) by a whole-rock Pb-Pb isochron. These rocks intrude the surrounding greenstone sequence, and their age is indistinguishable from that sequence. High strain grey gneisses which occupy much of the western and southern Shaw Batholith are chemically and isotopically similar to the North Shaw suite and are inferred to have been derived from this suite by tectonic processes. Felsic volcanics within the greenstones together with a major portion of the granitic batholiths apparently formed in a calc-alkaline volcanic and plutonic province at ∼3,500 Ma. This volcanic and plutonic suite is similar to modern calc-alkaline suites on the basis of major element, rare earh element and most other trace element contents. The Archaean suite contrasts with modern equivalents only in having lower concentrations of HREE and higher concentrations of Ni and Cr.
The average composition of the North Shaw suite is similar to that of Archaean gneiss belts for most elements and is consistent with the previously formulated hypothesis that the Shaw Batholith is transitional to the upper crustal level of a high-grade gneiss belt. Enrichment of the gneissic crust in the Shaw Batholith in alkali and heat-producing elements is inferred to have taken place by both igneous and hydrothermal processes over a protracted time interval. Late- and post-tectonic adamellite and granite melts intrude the gneissic rocks and there is isotopic evidence consistent with the gneisses being substantially enriched in Rb by pegmatite injection at ∼3,000 Ma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbey S (1980) Studies in “standard samples” for use in the general analysis of silicate rocks and minerals. Part 6: 1979 edition of “usable” values. Geol Surv Can, paper 80-14
Barley ME (1981) Relations between volcanic rocks in the Warrawoona Group: Continuous or cyclic evolution? Spec Publ Geol Soc Aust 7:263–273
Barley ME (1982) Porphyry-style mineralization associated with early Archean calc-alkaline igneous activity, eastern Pilbara, Western Australia, Econ Geol 77:1230–1236
Barley ME, Borley GD, Sylvester GC, Groves DI, Rogers N (in prep) Archaean calc-alkaline volcanism in the Pilbara Block, Western Australia
Barley ME, Dunlop JSR, Glover JE, Groves DI (1979) Sedimentary evidence for an Archaean shallow-water volcanic-sedimentary facies, eastern Pilbara Block, Western Australia. Earth Planet Sci Lett 43:74–84
Barley ME, de Laeter JR (in press) The interpretation of disturbed Rb-Sr whole-rock systems of the Duffer Formation, an early Archaean felsic metavolcanic unit, Eastern Pilbara Block, Western Australia. J Geol Soc Aust
Barton JM, Hunter DR, Jackson MPA, Wilson AC (1980) Rb-Sr age and source of the bimodal suite of the Ancient Gneiss Complex, Swaziland. Nature 283:756–758
Bettenay LF, Bickle MJ, Boulter CA, Groves DI, Morant P, Blake TS, James BA (191) Evoluton of the Shaw Batholith — an Archaean granitoid gneiss dome in the eastern Pilbara, Western Australia. Spec Publ Geol Soc Aust 7:361–372
Bickle MJ, Bettenay LF, Boulter CA, Groves DI, Morant P (1980) Horizontal tectonic interaction of an Archaean gneiss belt and greenstones, Pilbara Block Western Australia. Geology 8:525–529
Bickle MJ, Chapman HJ, Betteney LF, Groves DI, de Laeter JP (1983) Lead ages, reset rubidium-strontium ages and implications for the Archaean crustal evolution of the Diemals area, central Yilgarn Block. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 47:907–914
Bickle MJ, Morant P, Bettenay LF, Boulter CA, Blake TS Groves DI (in prep) Archaean tectonics of the Shaw Bactolith, Pilbara Block, Western Australia: structural and metamorphic tests of the batholith concept. Spec Publ Geol Assoc Can
Chapman HJ, Bickle MJ, de Laeter JR, Bettenay LF, Groves DI, Andersen LS, Binns RA, Gorton M (1981) Rb-Sr geochronology of granitic rocks from the Diemals area, central Yilgarn Block, Western Australia. Spec Publ Geol Soc Aust 7:173–186
Collerson KD, Fryer BJ (1978) The role of fluids in the formation and subsequent development of early continental crust. Contrib Mineral Petrol 67:151–167
Collerson KD, McCulloch MT (1983) Field and Sr-Nd isotopic constraints on Archaean crust and mantle evolution in the East Pilbara Block, Western Australia. Geol Soc Aust, Abstr Ser 9:167–168
Cooper JA, James PR, Rutland RWR (1982) Isotopic dating and structural relationships of granitoids and greenstones in the east Pilbara, Western Australia. Precamb Res 18:199–236
Davy R, Lewis JD (1981) The geochemistry of the Mount Edgar Batholith, Pilbara area, Western Australia. Spec Publ Geol Soc Aust 7:373–383
de Jong WK (1973) Tables of influence coefficients. X-ray Spectrometry 2:151–158
de Laeter JR, Abercrombie IE (1970) Mass spectrometric isotope dilution analyses of rubidium and strontium in standard rocks. Earth Planet Sci Lett 9:327–330
de Laeter JR, Libby WG, Trendall AF (1981) The older Precambrian geochronology of Western Australia. Spec Publ Geol Soc Aust 7:145–157
Dostal J, Zentilli M, Caelles JC, Clark AH (1977) Geochemistry and origin of volcanic rocks of the Andes, (26°–28°S). Contrib Mineral Petrol 63:113–128
Dunlop JSR, Buick R (1981) Archaean epiclastic sediments derived from mafic volcanics, North Pole, Pilbara Block, Western Australia. Spec Publ Geol Soc Aust 7:225–233
Eriksson KA (1981) Archaean platform-to-trough sedimentation east Pilbara Block, Australia. Spec Publ Geol Soc Aust 7:235–244
Ewing TE (1979) Two calc-alkaline volcanic trends in the Archean: trace element evidence. Contrib Mineral Petrol 70:1–7
Frey FA, Chappell BW, Roy SD (1978) Fractionation of rare-earth elements in the Tuolumne intrusive series, Sierra Nevada batholith, California. Geology 6:239–242
Glikson AY (1979) Early Precambrian tonalite-trondhjemite sialic nuclei. Earth Science Reviews 15:1–73
Hamilton PJ, Evensen NM, O'Nions RK, Glikson AY, Hickman AH (1981) Sm-Nd dating of the North Star Basalt, Warrawoona Group, Pilbara Block, Western Australia. Spec Publ Geol Soc Aust 7:187–192
Hawkesworth CJ, O'Nions RK (1977) The petrogenesis of some Archaean volcanic rocks from southern Africa. Jour Petrol 18:487–520
Heier KS (1973) Geochemistry of granulite facies rocks and problems of their origin. Phil Trans R Soc Lond A273:429–442
Hickman AH (1981) Crustal evolution of the Pilbara Block, Western Ausralia. Spec Publ Geol Soc Aust 7:57–69
Hickman AH, Lipple SL (1975) Explanatory notes on the Marble Bar 1∶250000 geological sheet, Western Australia. Geol Surv West Aust Rec 1974/20
Jacobs JW, Korotev RC, Blanchard DP, Hasin LA (1977) A welltested procedure for instrumental neutron activation analysis of silicate rocks and minerals. J Radioanal Chem 40:93–114
Jacobsen SB, Wasserburg CJ (1979) The mean age of mantle and crustal reservoirs, J Geophys Res 84:7411–7427
Jahn BM, Glikson AY, Peucat JJ, Hickman AH (1981) REE geochemistry and isotopic data of archaean silicic volcanics and granitoids from the Pilbara Block, Western Australia: implications for early crustal evolution. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45:1633–1652
Larsen ES (1948) Batholith and associated rocks of Corona Elsinore and San Luis Rey quadrangles, Southern California. Geol Soc Am Mem 29:182 p
Lopez-Escobar L, Frey FA, Oyarzũn J (1979) Geochemical characteristics of Central Chile (33°–34°S) granitoids. Contrib Mineral Petrol 70:439–450
Lopez-Escobar L, Frey FA, Vergara M (1977) Andesites and highalumina basalts from the central-south Chile high Andes: geochemical evidence bearing on their petrogenesis. Contrib Mineral Petrol 63:199–228
Lopez-Escobar L, Oyarzũn JM (1974) Uranium in calc-alkaline granitoids of Central Chile. Pacific Geology 8:47–50
Moorbath S (1976) Age and isotope constraints for the evolution of Archaean crust. In: Windley BF (ed) The early history of the earth. Wiley, London: 351–360
Moorbath S, Taylor PN (1981) Isotopic evidence for continental growth in the Precambrian. In: Kröner A (ed) Precambrian plate-tectonics. Elsevier, Amsterdam: 491–525
O'Nions RK, Evensen NM, Hamilton PJ (1979) Geochemical modelling of mantle differentiation and crustal growth. J Geophys Res 84:6091–6101
O'Nions RK, Pankhurst RJ (1978) Early Archaean rocks and geochemical evolution of the Earth's crust. Earth Planet Sci Lett 38:211–236
Oversby VM (1976) Isotopic ages and geochemistry of Archaean acid igneous rocks from the Pilbara, Western Australia. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 40:817–829
Pidgeon RT (1978a) 3450 m.y. old volcanics in the Archaean layered greenstone succession of the Pilbara Block, Western Australia. Earth Planet Sci Lett 37:421–428
Pidgeon RT (1978b) Geochronological investigation of granite batholiths of Archaean granite-greensone terrain of the Pilbara Block. In: Smith IEM, Williams JG (eds) Proceedings of the 1978 Archaean Geochemistry Conference. Univ Toronto Press, Toronto: 360–362
Steiger RH, Jäger E (1977) Subcomission on geochronology: convention on the use of decay constants in geo- and cosmochronolgy. Earth Planet Sci Lett 36:359–362
Tarney J, Dalziel IWD, de Wit MJ (1976) Marginal basin “Rocas verdes” complex from S. Chile: a model for Archaean greenstone belt formation. In: Windley BF (ed.) The early history of the Earth. Wiley, London: 131–146
Tatsumoto M, Knight RJ, Allegré CJ (1973) Time differences in the formation of meteorites as determined from the ratio of lead-207 to lead-206. Science 180:1279–1283
Taylor SR, Gorton MP (1977) Geochemical application of spark source mass spectrography — 111. element sensitivity, precision and accuracy. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 41:1375–1380
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1981) The composition and evolution of the continental crust: rare earth element evidence from sedimentary rocks. Phil Trans R Soc Lond A301:381–399
Thorpe RS, Potts PJ, Francis PW (1976) Rare earth data and petrogenesis of andesite from the North Chilean Andes. Contrib Mineral Petrol 54:65–78
Weaver BW, Tarney J (1980) Continental crust composition and nature of the lower crust: constraints from mantle Nd-Sr isotope correlation. Nature 286:342–346
Weaver BL, Tarney J (1981) Lewisian gneiss geochemistry and Archaean crustal development models. Earth Planet Sci Lett 55:171–180
Wells PRA (1980) Thermal models for the magmatic accretion and subsequent metmorphism of continental crust. Earth Planet Sci Lett 46:253–265
Williams IS, Page RW, Froude D, Foster JJ, Compston W (1983) Early crustal components in the Western Australian Archaean: Zircon U-Pb ages by ion microprobe analysis from the Shaw Batholith and Narryer metamorphic belt. Geol Soc Aust Abstr Ser 9:169–171
Willis JP, Erlank AJ, Gurney JJ, Theil RH, Ahrens LH (1972) Major, minor and trace element data for some Apollo 11, 12, 14 and 15 samples. Proceedings of the Lunar Science Conference, Geochim Cosmochim Acta, supplement 3, 2:1269–1273
Wilson JF, Bickle MJ, Hawkesworth CJ, Martin A, Nisbet EG, Orpen JL (1978) Granite-greenstone terrains of the Rhodesian Archaean Craton. Nature 271:23–27
Windley BF (1977) The evolving continents. Wiley, London: p 385
Wood DA, Joron JL, Treuil M, Norry M, Tarney J (1979) Elemental and Sr isotope variations in basic lavas from Iceland and the surrounding ocean floor. Contrib Mineral Petrol 70:319–339
York D (1969) Least squares filing of a straight line with correlated errors. Earth Planet Sci Lett 5:320–324
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bickle, M.J., Bettenay, L.F., Barley, M.E. et al. A 3500 Ma plutonic and volcanic calc-alkaline province in the Archaean East Pilbara Block. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 84, 25–35 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01132327
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01132327