Conclusions
In 10 years of use, the mechanical losses from AN-31 were 40%, AN-2F 30%, KU-2 from the first stage 15%, and none observed for KU-2 in the second stage.
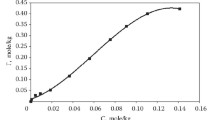
There were considerable reductions in dynamic exchange capacity in the upper layer of the AN-31 (by about 50%) and throughout the AN-2F (by about 60%); the KU-2 in the first stage showed 20% reaction, while that in the second had the capacity of the fresh resin.
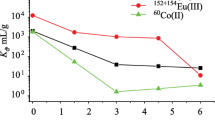
The undesorbed radionuclide concentrations along the filters containing KU-2, AN-31, and AN-2F have been established; the irreversible sorption is up to 4×10−5 Ci/kg.
These exchange materials are suitable as follows for further liquid low-level waste treatment: KU-2 and AN-31 are suitable for further use, while the AN-2F requires replacement by AN-31.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
K. A. Bol'shakov et al., in: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on the Peaceful Uses of Atomic Energy, Geneva, 1958, Papers by Soviet Scientists, Vol. 4 [in Russian], Atomizdat, Moscow (1959), pp. 189–194.
F. V. Rauzen and Z. Ya. Solov'eva, “Changes in ion-exchanger properties on prolonged use with radioactive effluents,” At. Énerg.,21, No. 5, 378–381 (1966).
D. I. Trofimov, Z. A. Aver'kova, et al., “Experience over seven years with Moscow station for purifying and concentrating radioactive effluents”, Proceedings of the International Symposium on Processing Low-Level and Medium Level Radioactive Wastes [in Russian], IAEA, Vienna (1966), pp. 449–475.
N. F. Kuleshov et al., “Results obtained with purifiers at Moscow liquid-waste treatment station with low-level radioactive wastes”, COMECON Symposium Proceedings [in Russian] (1975), pp. 31–38.
G. V. Slavinskaya, L. A. Zeleneva, and N. S. Kuznetsova, “Causes of technological difficulties in operating demineralizing anion-exchange filters,” in: Sorption Theory and Practice, Issue 17 [in Russian], Voronezh. Tekhnol. Inst. (1985), pp. 42–46.
N. K. Galkina et al., “Simulating water purification on anion exchangers”, Khim. Tekhnol. Vody,6, Np. 3, 200–204 (1984).
Ion-Exchanger Catalog [in Russian] NII PM, NIITÉKhIM, Moscow (1980).
A. M. Semushkin, V. A. Yakovlev, and E. V. Ivanova, Infrared Absorption Spectra for Ion-Exchange Materials [in Russian], Khimiya, Leningrad (1980).
Additional information
Translated from Atomnaya Énergiya, Vol. 64, No. 3, pp. 201–206, March, 1988.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martynov, B.V., Baklanov, A.E., Trushkov, N.P. et al. Ion-exchanger properties after prolonged use at Mosocw liquid radioactive waste treatment station. At Energy 64, 249–254 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01123134
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01123134