Abstract
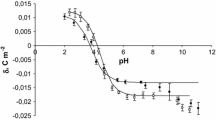
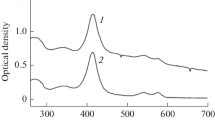
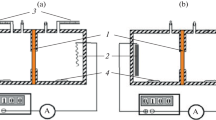
A comparison of water diffusion in human erythrocytes and ghosts revealed a longer relaxation time in ghosts, A comparison of water diffusion in human erythrocytes and ghosts revealed a longer relaxation time in ghosts, corresponding to a decreased exchange rate. However, the diffusional permeability of ghosts was not significantly different from that of erythrocytes . The changes in water diffusion following exposure to p-chloromercuribenzene sulfonate (PCMBS) have been studied on ghosts suspended in isotonic solutions. It was found that a significant inhibitory effect of PCMBS on water diffusion occurred only after several minutes of incubation at 37°C. No inhibition was noticed after short incubation at 0°C as previously used in some labelling experiments. This indicates the location in the membrane interior of the SH groups involved in water diffusion across human erythrocyte membranes. The nuclear magnetic resonance ( n . m . r . ) method appears as a useful tool for studying changes in water diffusiofl in erythrocyte ghosts with the aim of locating the water channel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Macey RI & Farmer REL (1970) Biochim. Biophys. Acta211, 104–106.
Naccache P & Sha'afi RI (1974) J. Cell Physiol.83, 449–456.
Benga GH, Pop VI, Ionescu M, Holmes RP & Popescu O (1982) Cell Biol. Int. Rep.6, 775–781.
Brow PA, Feinstein MB, & Sha'afi RI (1975) Nature254, 523–525.
Sha'afi RI & Feinstein MB (1977) in: Membrane Toxicity (Miller MW & Shamoo AE, eds), pp 67–83, Plenum Press, New York.
Solomon AK, Chasan B, Dix JA, Lukacovic MF, Toon MR & Verkman AS (1983) Ann. NY Acad. Sci.414, 97–124.
Conlon T & Outhred R (1972) Biochim. Biophys. Acta288, 354–361.
Morariu VV & Benga GH (1977) Biochim. Biophys. Acta469, 301–310.
Pirkle JL, Ashley DL & Goldstein JH (1979) Biophys. J.25, 389–406.
Benga GH, Pop VI, Popescu O, Ionescu M & Mihele V (1983) J. Membrane Biol.76, 129–137.
Morariu VV & Benga GH (1984) in: Membrane Processes: Molecular Biology and Medical Applications (Benga Gh, Baum H & Kummerow FA, eds), pp 121–139, Springer Verlag, New York.
Benga Gh & Morariu VV (1977) Nature265, 636–638.
Wood FG & Passow H (1981) in: Techniques in Cellular Physiology, Part I, P112, 1–43.
Antonini E & Brunori M (1971) Hemoglobin and Myoglobin in their Reactions with Ligands, North-Holland Publishing Co., Amsterdam.
Morariu VV, Pop VI, Popescu O & Benga Gh (1981) J. Membrane Biology62, 1–5.
Conlon T & Outhred R (1972) Biochim. Biophys. Acta,288, 408–418.
Farrar TC & Becker ED (1971) Pulse and Fourier Transform NMR, Academic Press, New York.
Brahm J (1982) J. Gen. Physiol.79, 791–819.
Batt ER, Abbott RE & Schachter D (1976) J. Biol. Chem.251, 7184–7190.
Cabantchik ZI & Rothstein A (1974) J. Membrane Biol.14, 227–248.
Rothstein A (1981) in: The Function of Red Blood Cells: Erythrocyte Pathobiology, pp 105–131, Allan R. Liss, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benga, G., Popescu, O. & Pop, V.I. Water exchange through erythrocyte membranes: p-choloromercuribenzene sulfonate inhibition of water diffusion in ghosts studied by a nuclear magnetic resonance technique. Biosci Rep 5, 223–228 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01119591
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01119591