Abstract
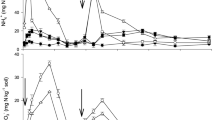
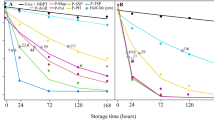
In a field experiment ammonia volatilization and yield response were measured when calcium ammonium nitrate (CAN), urea or urea plus 0.5% w/w N-(n-butyl) thiophosphoric triamide (U + NBPT) were surface-applied to an established perennial ryegrass sward. NBPT lowered cumulative NH3 loss from ventilated enclosures over 13 days from 8.1% of the urea N applied to 1.9% and delayed, by approximately 5 days, the time at which maximum loss occurred. Ammonia volatilization from CAN was low being less than 0.1% of the N applied. However, actual NH3 volatilization loss rates were probably underestimated due to the low air exchange rates used in the ventilated enclosures.
The relative efficiency of urea compared to CAN was 91.2% in terms of dry matter yield. Recovery of N by difference was 57.2% for urea compared with 68.7% for CAN. NBPT improved the yield performance of urea making the amended fertilizer comparable to that of CAN.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beyrouty CA, Nelson DW and Sommers LE (1988) Effectiveness of phosphoroamides in retarding hydrolysis of urea surface-applied to soil with various pH and residue cover. Soil Sci 145: 345–352
Bremner JM and Chai HS (1986) Evaluation of N-butyl phosphorothioic triamide for retardation of urea hydrolysis in soil. Commun in Soil Sci Plant Anal 17: 337–351
Bundy LG and Oberle SL (1988) Evaluation of methods for control of ammonia volatilization from surface-applied urea-containing fertilizers. J Fertilizer Issues 5: 24–30
Buresh RJ, Datta SK de, Padilla JL and Samson MI (1988) Effect of two urease inhibitors on floodwater ammonia following urea application to lowland rice. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52: 856–861
Byrnes BH, Gutser R and Amberger A (1989) Greenhouse study on the effects of the urease inhibitors phenylphosphorodiamidate and N-(n-butyl) thiophosphoric triamide on the efficiency of urea applied to flooded rice. Z Pflanzen Bodenkd 152: 67–72
Chai HS and Bremner JM (1987) Evaluation of some phosphoroamides as soil urease inhibitors. Biol Fertil Soils 3: 189–194
Fenn LB and Hossner LR (1985) Ammonia volatilization from ammonium or ammonium-forming nitrogen fertilizers. Adv Soil Sci 1: 123–169
Hargrove WL (1988) Evaluation of ammonia volatilization in the field. J Prod Agric 1: 104–111
Joo YK, Christians NE and Bremner JM (1987) Effect of N-(n-butyl) thiophosphoric triamide (NBPT) on growth response and ammonia volatilization following fertilization of Kentucky Bluegrass (Poa pratensis L.) with urea. J Fertilizer Issues 4: 98–102
Kissel DE, Brewer HH and Arkin GF (1977) Design and test of a field sampler for ammonia volatilization. Soil Sci Soc Am J 41: 1133–1138
Krogmeier MJ, McCarty GW and Bremner JM (1989) Potential phytotoxicity associated with the use of soil urease inhibitors phenylphosphorodiamidate/N-(n-butyl) thiophosphoric triamide. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 86: 1110–1112
Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food (1988) Fertilizer recommendations for agricultural and horticultural crops. RB209, HMSO, London
Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food (1986) The analysis of agricultural materials. RB427, 3rd Edn., HMSO, London.
Murphy WE (1983) Comparing urea and CAN at different locations. Farm and Food Res 14: 41–43
O'Toole P and Morgan MA (1988) Efficiency of fertilizer urea: The Irish Experience. In Jenkinson DS and Smith KA eds. Nitrogen Efficiency in Agricultural Soils, pp 191–206. Barking: Elsevier Applied Science
Schlegel AJ, Nelson DW and Sommers LE (1986) Field evaluation of urease inhibitors for corn production. Agron J 78: 1007–1012
Stevens RJ, Laughlin RJ and Frost JP (1989) Effect of acidification with sulphuric acid on the volatilization of ammonia from cow and pig slurries. J Agric Sci 113: 389–395
Stevens RJ, Laughlin RJ and Kilpatrick DJ (1989) Soil properties related to the dynamics of ammonia volatilization from urea applied to the surface of acidic soils. Fert Res 20: 1–9
Tecator Application Note (1984) Determination of ammonia nitrogen by flow injection analysis and gas diffusion. AN 50/84
Watson CJ (1990) The influence of soil properties on the effectiveness of phenylphosphorodiamidate (PPD) in reducing ammonia volatilization from surface applied urea. Fert Res 24: 1–10
Van Burg PFJ, Dilz K and Prins WH (1982) Agricultural value of various nitrogen fertilizers. Netherlands Nitrogen Technical Bulletin. No 13, 51 pp
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watson, C.J., Stevens, R.J. & Laughlin, R.J. Effectiveness of the urease inhibitor NBPT (N-(n-butyl) thiophosphoric triamide) for improving the efficiency of urea for ryegrass production. Fertilizer Research 24, 11–15 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01073142
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01073142