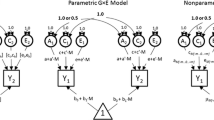
Abstract
The intention of this paper is to show how the methods of nonlinear factor analysis as developed by McDonal (Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 20:205–215, 1967) can be used to study genotype-environment interaction. The method is applied to the interaction of genotype and within-family environmental influences. Simulated twin data are used to illustrate how this type of interaction may be detected and estimated. It is shown that estimates of genetic influences are not affected byG×E interaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartlett, M. S. (1953). Factor analysis in psychology as a statistician sees it. In Uppsala Symposium on Psychological Factor Analysis,Nordisk Psykologi's Monograph Series No. 3, Ejnar Mundsgaards. Copenhagen.
Boomsma, D. I., and Molenaar, P. C. M. (1986). Using LISREL to analyze genetic and environmental covariance structure.Behav. Genet. 16:237–250.
Craig, C. C. (1936). On the frequency function of xy.Ann. Math. Stat. 7:1–15.
Eaves, L. J. (1984). The resolution of genotype×environment interaction in segregation analysis of nuclear families.Genet. Epidemiol. 1:215–228.
Freeman, G. H. (1973). Statistical methods for the analysis of genotype-environment interactions.Heredity 31:339–354.
Fulker, D. W., Wilcock, J., and Broadhurst, P. L. (1972). Studies in genotype-environment interaction. I. Methodology and preliminary multivariate analysis of a dial cross of eight strains of rat.Behav. Genet. 2:261–287.
IMSL, Inc. (1979).IMSL Library Reference Manual Edition 7, IMSL Inc., Houston, Tex.
Jöreskog, K. G., and Sörbom, D. (1981).LISREL: Analysis of Linear Structural Relationships by Maximum Likelihood and Least Squares Methods, National Educational Resources, Chicago.
Lathrope, G. M., and Lalouel, J. M. (1984). Path analysis of family resemblance and geneenvironment interaction.Biometrics 40:611–625.
Lawley, D. N., and Maxwell, A. E. (1971).Factor Analysis as a Statistical Method. Butterworths, London.
Martin, N. G., and Eaves, L. J. (1977). The genetical analysis of covariance structure.Heredity 38:79–95.
Martin, N. G., Eaves, L. J., and Heath, A. C. (1986). Detecting the contributions of measured and unmeasured genotypes and environments and their interactions to liability for a disease (submitted for publication).
McDonald, R. P. (1967). Factor interaction in nonlinear factor analysis.Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 20:205–215.
Plomin, R., DeFries, J. C., and Loehlin, J. C. (1977). Genotype-environment interaction and correlation in the analysis of human behavior.Psychol. Bull..84:309–322.
Rao, D. C., and Morton, N. E. (1974). Path analysis of family resemblance in the presence of gene-environment interaction.Am. J. Hum. Genet. 26:767–772.
Rao, D. C., Morton, N. E., and Yee, S. (1976). Resolution of cultural and biological inheritance by path analysis.Am. J. Hum. Genet. 28:228–242.
Springer, M. D. (1979).The Algebra of Random Variables, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molenaar, P.C.M., Boomsma, D.I. Application of nonlinear factor analysis to genotype-environment interaction. Behav Genet 17, 71–80 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01066011
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01066011