Abstract
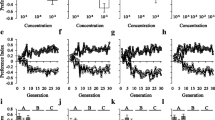
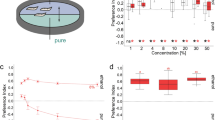
The experiments usedDrosophila melanogaster lines previously selected for increased knockdown resistance to ethanol. Selected lines utilized ethanol as a metabolic resource to a greater extent than unselected lines. Lines were characterized by their olfactory responses to ethanol, ethyl acetate, and acetaldehyde in a wind tunnel. Selected lines were less attracted to ethanol than unselected lines but did not differ consistently in their responses to other chemicals. This suggests that increased tolerance and utilization of ethanol are not necessarily accompanied by increased attraction to this chemical.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cavener, D. (1979). Preference for ethanol inDrosophila melanogaster associated with the alcohol dehydrogenase polymorphism.Behav. Genet. 9:359–365.
Cohan, F. M., and Graf, J. (1985). Latitudinal cline inDrosophila melanogaster for knock-down resistance to ethanol fumes and for rates of response to selection for further resistance.Evolution 39:278–293.
Cohan, F. M., and Hoffmann, A. A. (1986). Genetic divergence under uniform selection. II. Different responses to selection for knockdown resistance to ethanol amongDrosophila melanogaster populations and their replicate lines.Genetics 114:145–163.
Depiereux, E., Hougouto, N., Lechien, J., Libion-Mannaert, M., Lietaert, M.-C., Feytmans, E., and Elens, A. (1985). Larval behavioral response to environmental alcohol in relation to alcohol dehydrogenase activity level inDrosophila melanogaster.Behav. Genet. 15:181–188.
Dixon, W. J. (ed.) (1981).BMDP Statistical Software, University of California Press, Berkeley.
Fienberg, S. E. (1981).The Analysis of Cross Classified Categorical Data, MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass.
Fuyama, Y. (1978). Behavior genetics of olfactory response inDrosophila. II. An odorant-specific variant in natural populations ofD. melanogaster.Behav. Genet. 8:406–414.
Gelfand, L., and McDonald, J. (1980). Relationship between ADH activity and behavioral response to environmental alcohol inDrosophila.Behav. Genet. 10:237–249.
Gelfand, L., and McDonald, J. (1983). Relationship between alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) activity and behavioral response to environmental alcohol in fiveDrosophila species.Behav. Genet. 13:281–293.
Gibson, J. B., and Oakeshott, J. G. (1982). Tests of the adaptive significance of the alcohol dehydrogenase polymorphism inDrosophila melanogaster: Paths, pitfalls and prospects. In Barker, J. S. F., and Starmer, W. T. (eds.),Ecological Genetics and Evolution, Academic Press, Sydney, pp. 291–306.
Gibson, J. B., Lewis, N., Adena, M. A., and Wilson, S. R. (1979). Selection for ethanol tolerance in two populations ofDrosophila melanogaster segragating ADH allozymes.Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 32:387–398.
Hoffmann, A. A. (1983). Bidirectional selection for olfactory response to acetaldehyde and ethanol inDrosophila melanogaster.Genet. Sel. Evol. 15:501–518.
Hoffmann, A. A. (1985). Interspecific variation in the response ofDrosophila to chemicals and natural fruit odours in a wind tunnel.Aust. J. Zool. 33:451–460.
Hoffmann, A. A., Parsons, P. A., and Nielsen, K. M. (1984). Habitat selection: Olfactory response ofDrosophila melanogaster depends on resources.Heredity 53:139–145.
Parsons, P. A., and Spence, G.E. (1981). Longevity, resource utilization and larval preference inDrosophila: Inter- and intraspecific variation.Aust. J. Zool. 29:671–678.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants GM22221 and GM08511.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffmann, A.A., Cohan, F.M. Olfactory responses ofDrosophila melanogaster selected for knockdown resistance to ethanol. Behav Genet 17, 307–312 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01065509
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01065509