Abstract
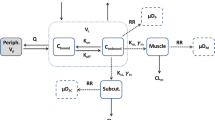
Single 30- mg doses of chlordiazepoxide HCl were administered to six healthy human subjects by the intravenous, oral, and intramuscular routes. Plasma concentration- time curves following intravenous administration were satisfactorily described by a biexponential equation consistent with a two-compartment open model system. Mean values of half-lives for the so-called distribution and elimination phases were 0.252 and 9.39 hr, respectively. The mean values for the volume of the central compartment (V 1) and volume of distribution\((V_{d_\beta } )\) were 18.0 and 30.9% of body weight, respectively. Following oral administration, the drug was rapidly and completely absorbed. Absorption was first order (t1/2≈27 min), and three of the six subjects showed a discernible lag time of approximately 20 min. Drug absorption following intramuscular administration was comparatively slow. A two- compartment “muscle model” comprised of precipitated and solubilized drug in the muscle was found to satisfactorily characterize the absorption process following administration by this route.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. H. Sternbach. The discovery of Librium.Agents and Actions 2:193–196 (1972).
Physicians' Desk Reference, 29th ed., Medical Economics Co., Oradell, N.J., 1975, p. 1245.
C. Abruzzo, I. Bekersky, S. Cotler, C. Coutinho, R. Lucek, and V. Toome. Data on file, Hoffmann-La Roche Inc., Nutley, N.J.
T. Fujita, J. Iwasa, and C. Hansch. A new substituent constant,π, derived from partition coefficients.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 86:5175–5180 (1964).
T. C. McIlvaine. A buffer solution for colorimetric comparison.J. Biol. Chem. 49:183–186 (1921); throughDocumenta Geigy Scientific Tables, 7th ed. (K. Diem and C. Lentner, eds.), Ciba-Geigy Ltd., Basel, Switzerland, 1970, pp. 280–282.
R. A. Giannella, S. A. Broitman, and N. Zamcheck. Gastric acid barrier to ingested microorganisms in man: Studiesin vivo andin vitro.Gut 13:251–256 (1972).
S. A. Kaplan and S. Cotler. Use of cannulated everted intestinal sac for serial sampling as a drug absorbability (permeability) screen.J. Pharm. Sci. 61:1361–1365 (1972).
A. H. Anton. The relation between the binding of sulfonamides to albumin and their antibacterial efficacy.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 129:282–290 (1960).
M. Rowland. Influence of route of administration on drug availability.J. Pharm. Sci. 61:70–74 (1972).
M. A. Schwartz. Pathways of metabolism of the benzodiazepines. In S. Garattini, E. Mussini, and L. O. Randall (eds.),The Benzodiazepines, Raven Press, New York, 1973, pp. 53–74.
W. R. Dixon, M. A. Brooks, E. Postma, M. R. Hackman, and M. A. Schwartz. Identification and determination ofN-desmethyl-diazepam in plasma following chronic administration of chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride (Librium) to man.Fed. Proc. 33:472, Part I (1974).
S. A. Kaplan, M. Lewis, M. A. Schwartz, E. Postma, S. Cotler, C. W. Abruzzo, T. L. Lee, and R. E. Weinfeld. Pharmacokinetic model for chlordiazepoxide-HCl in the dog.J. Pharm. Sci. 59:1569–1574 (1970).
M. A. Schwartz and E. Postma. MetabolicN-demethylation of chlordiazepoxide.J. Pharm. Sci. 55:1358–1362 (1966).
M. A. Schwartz, E. Postma, and Z. Gaut. Biological half-life of chlordiazepoxide and its metabolite, demoxepam, in man.J. Pharm. Sci. 60:1500–1503 (1971).
L. A. Gottschalk, R. Biener, and E. C. Dinovo. Effect of oral and intramuscular routes of administration on serum chlordiazepoxide levels and the prediction of these levels from predrug fasting serum glucose concentrations.Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 8:697–702 (1974).
D. J. Greenblatt, R. I. Shader, and J. Koch-Weser. Slow absorption of intramuscular chlordiazepoxide.New Engl. J. Med. 291:1116–1118 (1974).
D. J. Greenblatt, R. I. Shader, and J. Koch-Weser. Pharmacokinetic determinants of the response to single doses of chlordiazepoxide.Am. J. Psychiat. 131:1395–1397 (1974).
D. J. Greenblatt, R. I. Shader, J. Koch-Weser, and K. Franke. Clinical pharmacokinetics of chlordiazepoxide.Psychopharmacol. Bull. 11(4):34–35 (1975).
D. J. Greenblatt, R. I. Shader, K. Franke, and J. Koch-Weser. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous chlordiazepoxide.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 17:235 (1975).
D. J. Greenblatt, R. I. Shader, J. S. Harmatz, K. Franke, and J. Koch-Weser. Influence of magnesium and aluminium hydroxide mixture on chlordiazepoxide absorption.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 19:234–239 (1976).
L. Z. Benet. General treatment of linear mammillary models with elimination from any compartment as used in pharmacokinetics.J. Pharm. Sci. 61:536–541 (1972).
C. M. Metzler, G. L. Elfring, and A. J. McEwen.A User's Manual for NONLIN and Associated Programs, Upjohn Co., Kalamazoo, Mich., April 20, 1974.
H. O. Hartley. The modified Gauss-Newton method for the fitting of non-linear regression functions.Technometrics 3:269–280 (1961).
A. J. Sedman and J. G. Wagner. CSTRIP, a Fortran IV computer program for obtaining initial polyexponential parameter estimates.J. Pharm. Sci. 65:1006–1010 (1975).
H. G. Boxenbaum, S. Riegelman, and R. M. Elashoff. Statistical estimations in pharmacokinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 2:123–148 (1974).
S. Riegelman, J. C. K. Loo, and M. Rowland. Shortcomings in pharmacokinetic analysis by conceiving the body to exhibit properties of a single compartment.J. Pharm. Sci. 57:117–123 (1968).
A. Rescigno and G. Segre.Drug and Tracer Kinetics, Blaisdell, Waltham, Mass., 1966, pp. 91–94.
W. G. Kramer, R. P. Lewis, T. C. Cobb, W. F. Forester, Jr., J. A. Visconti, L. A. Wanke, H. G. Boxenbaum, and R. H. Reuning. Pharmacokinetics of digoxin: Comparison of a two- and a three-compartment model in man.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 2:299–312 (1974).
J. G. Wagner.Biopharmaceutics and Relevant Pharmacokinetics, Drug Intelligence Publications, Hamilton, Ill., 1971, p. 295.
S. Riegelman, J. Loo, and M. Rowland. Concept of a volume of distribution and possible errors in evaluation of this parameter.J. Pharm. Sci. 57:128–133 (1968).
M. Gibaldi, R. Nagashima, and G. Levy. Relationship between the drug concentration in plasma or serum and amount of drug in the body.J. Pharm. Sci. 58:193–197 (1969).
M. Gibaldi and D. Perrier. Drug elimination and apparent volume of distribution in multicompartment systems.J. Pharm. Sci. 61:952–954 (1972).
C. V. Greenway and R. D. Stark. Hepatic vascular bed.Physiol. Rev. 51:23–65 (1971).
A. E. Till, L. Z. Benet, and K. C. Kwan. An integrated approach to the pharmacokinetic analysis of drug absorption.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 2:525–544 (1974).
J. C. K. Loo and S. Riegelman. New method for calculating the intrinsic absorption rate of drugs.J. Pharm. Sci. 57:918–928 (1968).
H. G. Boxenbaum and S. A. Kaplan. Potential source of error in absorption rate calculations.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 3:257–264 (1975).
M. Berman. The formulation and testing of models.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 108:182–194 (1963).
J. G. Wagner. Intrasubject variation in elimination half-lives of drugs which are appreciably metabolized.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 1:165–173 (1973).
W. J. Westlake. Problems associated with analysis of pharmacokinetic models.J. Pharm. Sci. 60:882–885 (1971).
W. J. Waddell and T. C. Butler. Calculation of intracellular pH from the distribution of 5,5-dimethyl-2,4-oxazolidinedione (DMO): Application to skeletal muscle of the dog.J. Clin. Invest. 38:720–729 (1959).
E. D. Robin, R. J. Wilson, and P. A. Bromberg. Intracellular acid-base relations and intracellular buffers.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 92:539–546 (1961).
W. O. Fenn. Carbon dioxide and intracellular homeostasis.Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 92:547–558 (1961).
H. G. Boxenbaum, K. A. Geitner, M. L. Jack, W. R. Dixon, and S. A. Kaplan. Pharmacokinetic and biopharmaceutic profile of chlordiazepoxide HCl in healthy subjects: Multiple-dose oral administration.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 5:25–39 (1977).
H. B. Kostenbauder, R. P. Rapp, J. P. McGovren, T. S. Foster, D. G. Perrier, H. M. Blacker, W. C. Hulon, and A. W. Kinkel. Bioavailability and single-dose pharmacokinetics of intramuscular phenytoin.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 18:449–456 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boxenbaum, H.G., Geitner, K.A., Jack, M.L. et al. Pharmacokinetic and biopharmaceutic profile of chlordiazepoxide HCl in healthy subjects: Single-dose studies by the intravenous, intramuscular, and oral routes. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 5, 3–23 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01064806
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01064806