Abstract
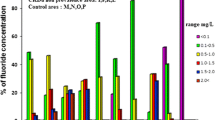
In a village affected by the endemic Balkan nephropathy (BN), concentrations of different forms of nitrogen in well-water were examined. While the amounts of exchangeable ammonium and nitrate were mostly within permissible limits, nitrite content was often extremely high. The increased nitrite concentration and diminished nitrate/nitrite ratio were found in 9 (out of 10) wells used by households with BN affected members, and in 6 (out of 10) wells used by BN-free house-holds. The differences are not statistically significant, but this clue should be followed. Though not likely to be a direct cause of BN, these parameters may well serve as indicators of factors causally related to the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Council of European Communities (1980) EC Directive relating to the quality of water intended for human consumption. 778/EEC
Danilović V (1958) Chronic nephritis due to ingestion of lead-contaminated flour. Brit Med J 1:27–28
Fraser P, Chilvers C, Beral V, Hill MJ (1980) Nitrate and human cancer: A review of the evidence. Int J Epidemiol 9:3–11
Hall PW, Dammin GJ (1978) Balkan nephropathy. Nephron 22:281–300
Hall PW, Vasiljević M (1973) Beta-2-microglobulin excretion as an index of renal tubular disorders with special reference to endemic Balkan nephropathy. J Lab Clin Med 81:897–904
Hill MJ, Hawksworth G (1972) Bacterial production of nitrosaminesin vitro andin vivo. In: Bogovski P, Preussmann R, Walker EA (eds) N-nitroso compounds, analysis and formation. IACR Sci Publ, Lyon, pp 116–121
Jevtić Z, Tasić M (1977) Investigation of drinking water in endemic nephropathy foci. Proceedings of the 3rd Symposium on endemic nephropathy. Galenika, Beograd, pp 102–108 (in Serbo-Croatian)
Keeney DR, Bremner JM (1966) Determination and isotope-ratio analysis of different forms of nitrogen in soils: 4. Exchangeable ammonium, nitrate, and nitrite by direct-distillation methods. Soil Sci Soc Amer Proc 30:583–587
Magee PN, Barnes JM (1967) Carcinogenic nitroso compounds. Adv Cancer Res 10:163–246
Perić J (1985) Hydrogeological field investigations and endemic nephropathy. Third Symposium on Endemic Nephropathy. Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts, Belgrade, pp 105–122 (in Serbian)
Radovanović Z, Krajinović S, Petković S, Hall PW (1981) Papillary transitional cell tumours, Balkan nephropathy, and beta-2-microglobulin. The Lancet ii:689
Radovanović Z, Djordjević G, Raičević R, Velimirović D, Velimirović A, Janković S, Miljković V (1985a) Endemic nephropathy in a selected locality-implications of a crosssectional study. Med Invest 18:75–80 (in Serbian and English)
Radovanović Z, Krajinović S, Janković S, Hall PW, Petković S (1985b) Family history of cancer among cases of upper urothelial tumours in a Balkan nephropathy area. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 110:181–183
Shuval HY, Gruener N (1977) Health effects of nitrates in water. US Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, Ohio
Tančev I, Evstatiev P, Dorosiev D, Penčeva Ž, Cvetkov G (1956) Investigations of nephritis in Vratza area. Savr Med 7, 9:14–29 (in Bulgarian)
Wolstenholme GEW, Knight J (eds) (1967) The Balkan nephropathy. CIBA Foundation study group No. 30. Churchill Ltd, London
World Health Organization (1965) The “endemic nephropathy” of south-eastern Europe. Bull WHO 32:431–448
-(1974) WHO meeting of investigators on endemic nephropathy. Belgrade, NCD/WP/74 (mimeo)
— (1977) Environmental health criteria. Nitrates, nitrites, and N-nitroso compounds. WHO, Geneva
Živković N (1985) Collection of sanitary regulations of SFR Yugoslavia and SR Serbia. Official news of SFRY, Belgrade (in Serbo-Croatian)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radovanović, Z., Stevanović, D. Different forms of mineral nitrogen in drinking water and the Balkan nephropathy. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 17, 813–815 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061986
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061986