Abstract
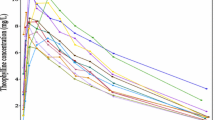
The problems of curve fitting and modeling in pharmacokinetics are discussed. A new nonlinear regression program FUNFIT, written for interactive time sharing, is presented which should be more reliable than programs based on the Gauss-Newton or other related gradient methods. The new program and the well-established program NONLIN were tested on two linear models using human plasma drug level data. FUNFIT found a substantially better solution than NONLIN in the majority of the cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. M. Metzler.A User's Manual for NONLIN, The Upjohn Co., Technical Report 7292/69/7292/005, Kalamazoo, Mich., 1969.
G. W. Booth and T. L. Peterson.Nonlinear Estimation, IBM Share Program, No. 687 WLNL7, 1958.
D. W. Marquardt.Least Squares Estimation of Nonlinear Parameters, IBM Share Library Program, Distribution No. 309401, 1966.
D. A. Meeter.Program GAUSHAUS, Numerical Analysis Laboratory, University of Wisconsin, Madison, 1966.
M. Pfeffer. COMPT: A time-sharing program for nonlinear regression analysis of compartmental models of drug distribution.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 2:137–163 (1973).
M. Berman and M. F. Weiss, Users Manual for SAAM, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., 1968.
J. M. Chambers. Computer system for fitting models to data.Appl. Stat. 18:249–263 (1969).
R. Fletcher.Report R6799, Atomic Energy Research Establishment, Harwell, U.K., 1971.
G. L. Atkins. A versatile digital computer program for nonlinear regression analysis.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 252:405–420 (1971).
W. Murrayet al. Division of Numerical Analysis, National Physical Laboratory, Teddington, Middlesex, U.K.
J. L. Kuester and J. H. Mize.Optimization Technique, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1973, Chap. 6.
H. Eisenpress, A. Bomberault, and J. Greenstadt.Nonlinear Regression Equations and Systems, Estimation and Prediction, 7090 G2IBM0035 IBM, Hawthorne, N.Y.
F. S. Wood.Nonlinear Least Squares Curve-Fitting Program, 360D 13.6.007 IBM/360, 1971.
SHARE Program Library Agency. Triangle Universities Computation Center, P.O. Box 12076, Research Triangle Park, North Carolina 27709.
Nonlinear Parameter Estimation and Programming. Catalog of Programs for IBM System 360 Models 25 and Above, IBM, White Plains, N.Y.
M. J. D. Powell. A hybrid method for non-linear equations. In P. Rabinowitz (ed.),Numerical Methods for Non-linear Algebraic Equations, Gordon and Breach, London, 1970, pp. 87–114.
J. E. Dennis. Some computational techniques for the nonlinear least squares problem. In G. D. Byrne and C. H. Hall (eds.),Numerical Solution of System of Nonlinear Algebraic Equations, Academic Press, New York, 1973, pp. 157–183.
J. E. Dennis. Algorithms for nonlinear problems which use discrete approximations to derivatives.Proc. ACM Natl. Conf. 1970, ACM, New York. Also Tech. Rep. 71-98, Department of Computer Science, Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y., 1971.
H. O. Hartley. The modified Gauss-Newton method for the fitting of nonlinear regression functions by least squares.Technometrics 3:269–280 (1961).
J. M. Chambers. Fitting nonlinear models: Numerical techniques.Biometrica 60:1–13 (1973).
J. H. Neider and R. Mead. A simplex method for function minimization.Comput. J. 7:308–313 (1965).
W. Spendley. Nonlinear least squares fitting using a modified simplex minimization method. In R. Fletcher (ed.),Optimization, Academic Press, New York, 1969, pp. 259–270.
Y. Bard.Nonlinear Parameter Estimation, Academic Press, New York, 1974.
N. R. Draper and A. Smith.Applied Regression Analysis, Wiley, New York, 1966.
H. G. Boxenhaum, S. Riegelman, and R. M. Elashoff. Statistical estimation in pharmacokinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 2:123–147 (1974).
E. Kruger-Thiemer and R. R. Levine. The solution of pharmacological problems with computers part 8: Non first-order models of drug metabolism.Arzneimittel-Forsch. 18:1575–1579 (1968).
J. Wagner.Fundamentals of Clinical Pharmacokinetics, Drug Intelligence Publications, Hamilton, Ill., 1975.
J. Wagner. Do I need a pharmacokinetic model, and, if so, which one?J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 3:457–478 (1975).
J. Wagner.Biopharmaceutics and Relevant Pharmacokinetics, Hamilton Press, Hamilton, Ill., 1971.
M. Berman. The formulation and testing of models.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 108:182–194 (1963).
G. C. Nooney. Mathematical models in medicine: A diagnosis.J. Chron. Dis. 19:325–332 (1966).
M. Berman, E. Shahn, and M. F. Weiss. The routine fitting of kinetic data to models.Biophys. J. 2:275–287 (1962).
J. Hiller. Exponential fitting and general technique of the Prony form. In R. S. Andersen and M. R. Osborne (eds.),Data Representation, University of Queensland Press, Queensland, Australia, 1970, pp. 62–76.
M. G. Kendall.The Advanced Theory of Statistics, Charles Griffin & Co., London, 1963.
C. Daniel and F. S. Wood.Fitting Equations to Data, Wiley, New York, 1971.
H. W. Killifors. On the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normality with mean and variance unknown.J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 62:399–402 (1967).
F. S. Sweed and C. Eisenhart. Tables for testing randomness of grouping in a sequence of alternatives.Ann. Math. Stat. 14:66–87 (1943).
J. Durbin and G. S. Watson. Testing for serial correlation in least squares regression.Biometrica 37:409–428 (1950).
F. J. Anscombe. Rejection of outliers.Technometrics 2:123–147 (1960).
W. G. Hunter and R. Mezaki. A model building technique for chemical engineering kinetics.AIChEJ. 10:315–322 (1964).
G. E. P. Box and W. G. Hunter. The experimental study of physical mechanisms.Technotnetrics d7:23–42 (1965).
G. W. Stewart. A modification of Davidon's minimization method to accept difference approximations of derivatives.J. Assoc. Comput. Mach. 14:72–83 (1967).
R. Fletcher. A survey of algorithms for unconstrained optimization. In W. Murray (ed.),Numerical Methods of Unconstrained Optimization, Academic Press, New York, 1972, pp. 123–129.
R. Fletcher. A review of methods for unconstrained optimization. In R. Fletcher (ed.),Optimization, Academic Press, New York, 1969, pp. 1–12.
K. M. Brown and J. E. Dennis.New Computational Algorithms for Minimizing a Sum of Squares of Non-linear Functions, Yale University Report 71-6, 1971.
M. J. D. Powell. Problems related to unconstrained optimization. In W. Murray,Numerical Methods for unconstrained Optimization, Academic Press, New York, 1972, pp. 29–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedersen, P.V. Curve fitting and modeling in pharmacokinetics and some practical experiences with NONLIN and a new program FUNFIT. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 5, 513–531 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061732
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061732