Abstract
In situ contaminant and water quality studies were conducted with striped bass prolarvae,Morone saxatilis, in two major spawning areas of the Chesapeake Bay in 1990 to explore the possible effects of water quality and contaminants conditions on survival. Three 96-hin situ survival studies with striped bass prolarvae were conducted at three stations in the Potomac River and three stations in the upper Chesapeake Bay during a major portion of the spawning season (13–20°C). Water quality parameters, inorganic contaminants and organic contaminants were monitored in the water column at these three stations during the experiments. Concentrations of 10 metals associated with precipitation events occurring at field sites on the Potomac River and upper Chesapeake Bay were also determined.
Survival of prolarvae ranged from 2 to 17.5% in all three 96-h tests conducted in the Potomac River. Control survival was greater than 79%. Survival of prolarvae during experiment 3 (all stations combined for each experiment) was significantly lower than survival of prolarvae during experiment 1. The low survival of prolarvae during experiment 3 occurred concurrently with a reported “fish kill” on the Potomac River. Chromium (14 μg/L) and zinc (119 μg/L) concentrations exceeding U.S. EPA water quality criteria were reported from a 48-h composite sample taken during experiment 3. Lower than normal pH conditions (6.8 and 6.9) were also documented during this experiment. Arsenic, chromium, and zinc may have been stressful.
Survival of prolarvae at the three stations during upper Chesapeake Bay tests ranged from 36 to 52.5% for 96-h exposures but was slightly lower (23–34.5%) during a 120-h exposure. Control survival was >81% in all experiments. Survival of prolarvae during all experiments in the upper Bay was similar to natural survival that occurs with this life stage. Adverse water quality and contaminant conditions were not reported in the upper Chesapeake Bay striped bass spawning area.
Detectable concentrations of cadmium (0.80 and 0.89 μg/L), aluminum (5.4 μg/L), chromium (1.1 μg/L), and zinc (2.5 μg/L) were reported in acidic precipitation samples (pH 3.4) collected from the Potomac River site. Surface water concentrations of these metals did not increase in the Potomac River study area after the precipitation events. The following metals were detected in acidic precipitation (pH 4.06–5.12) in the upper Chesapeake Bay: 22.1 μg/L Al; 1.1, 1.8, 2.3 μg/L Cd; 1.2 μg/L Cu; 2.7 and 3.1 μg/L Pb and 4.6 μg/L Zn. Concentrations of Al (22.1 μg/L) and Pb (3.1 μg/L) in precipitation corresponded with increased concentrations in the surface waters at a nearby station in the upper Chesapeake Bay study area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boreman J, Austin HM (1985) Production and harvest of anadronmous striped bass stocks along the Atlantic coast. Trans Am Fish Soc 144:3–7
Burton DT (1982) An evaluation of the potential toxicity of treated bleached kraft mill effluent to the early life stages of striped bass (Morone saxatilis). Report JHU/APL CPE-8204, Laurel, MD
Church TM, Tramontano JM, Scudlark JR, Jickells TD, Tokos JJ Jr., Knap AH (1984) The wet deposition of trace metals to the western Atlantic Ocean at the Mid-Atlantic coast and on Bermuda. Atmos Environ 18:2657–2664
Columbia National Fisheries Research Laboratory (CNFRL) (1983) Impacts of contaminants on early life stage of striped bass. U.S. Dept. of Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service, Columbia, MO
Dahlberg MD (1979) A review of survival of fish eggs and larvae in relation to impact assessments. Mar Fish Rev 41:1–12
Dey WD (1981) Mortality and growth of young-of-the-year striped bass in the Hudson River estuary. Trans Am Fish Soc 110:151–157
Finger SE, Livingstone AC, Olson SJ (1990) Influence of contaminants on survival of striped bass in Chesapeake Bay tributaries. In: Weaver JE (ed) Second US-USSR Symposium on Reproduction, Rearing and Management of Anadromous Fishes, February 7–10, 1990, Seattle WA. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
Geiger JG, Parker NC (1985) Survey of striped bass hatchery management in the southeastern United States. Prog Fish Cult 47:1–13
Goodyear CP (1985) Toxic materials, fishing and environmental variation: Simulated effects on striped bass population trends. Am Fish Soc 114:107–113
Hall LW Jr (1984) Field assessment of striped bass,Morone saxatilis, larval survival as related to contaminants and changes in water quality parameters. Final report, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, National Fisheries Center, Leetown, WV
Hall LW Jr, Bushong SJ, Ziegenfuss MC, Hall WS, Herman RL (1988) Concurrent mobile on-site and in situ striped bass contaminant and water quality studies in the Choptank River and upper Chesapeake Bay. Environ Toxicol Chem 7:815–830
Hall LW Jr, Hall WS, Bushong SJ, Herman RL (1987b) In situ striped bass (Morone saxatilis) contaminant and water quality studies in the Potomac River. Aquat Toxicol 10:73–99
Hall LW Jr, Horseman LO, Zeger S (1984) Effects of multiple organic and inorganic contaminants on fertilization, hatching success and prolarval survival of striped bass,Morone saxatilis. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 13:723–729
Hall LW Jr, Pinkney AE, Herman RL, Finger SE (1987a) Survival of striped bass larvae and yearlings in relation to contaminants and water quality in the upper Chesapeake Bay. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 16:391–400
Hall LW Jr, Pinkney AE, Horseman LO, Finger SE (1985) Mortality of striped bass larvae in relation to contaminants and water quality in a Chesapeake Bay tributary. Trans Am Fish Soc 114:861–868
Hall LW Jr, Ziegenfuss MC, Bushong SJ, Unger MA (1989) Studies of contaminant and water quality effects on striped bass prolarvae and yearlings in the Potomac River and upper Chesapeake Bay. Trans Am Fish Soc 118:619–629
Hall LW Jr, Ziegenfuss MC, Bushong SJ, Sullivan JA, Unger MA (1992a) In situ striped bass (Morone saxatilis) contaminant and water quality studies in the Potomac River and upper Chesapeake Bay in 1989. Aquatic Toxicol 22:181–222
Hall LW Jr, Ziegenfuss MC, Fischer SA, Sullivan JA, Palmer DM (1992b) In situ striped bass contaminant and water quality studies in the Potomac River and upper Chesapeake Bay in 1990. Report, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, National Fisheries Center, Leetown, WV
Horning WB, Weber CI (1985) Short term methods for estimating the chronic toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to Freshwater organisms. EPA/600/4-85/014, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, OH
Hughes, JS (1973) Acute toxicity of thirty chemicals to striped bass,Morone saxatilis. Report, Louisiana Wildlife and Fisheries Commission, Baton Rouge, LA
Lal K, Laskev R, Juljis A (1977) Acclimation and rearing of striped bass larvae in sea water. Calif Fish Game 63:210–218
Maryland Department of Natural Resources (1989) Striped bass studies. Final Report Federal Aid Project F-42-R-1, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Newton Corner, MA
Mehrle DM, Buckley D, Finger SE (1986) Impacts of contaminants on striped bass in Chesapeake Bay: A summary of research on water quality/contaminant interactions in laboratory and field studies. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, National Fisheries Contaminants Research Center, Columbia, MO
National Fisheries Contaminants Research Center (NFCRC) (1986) Impacts of contaminants on striped bass in Chesapeake Bay. Progress Report, U.S. Dept. of Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service, Columbia, MO
Polgar TT (1977) Striped bass ichthyoplankton abundance, mortality, and production estimation for the Potomac River population. In: Van Winkle (ed) Proceedings of the conference on assessing the effects of power-plant-induced mortality on fish populations. Pergamon Press, NY, pp 110–126
Rago P (1990) Preliminary summary of Fish and Wildlife Service Research Program FY-1990. Report, Presented to Planning and Coordination Group of the Emergency Striped Bass Study on May 31, 1990, Washington, DC
Tramontano JM, Scudlark JR, Church TM (1987) A method for collecting, handling and analysis of trace metals in precipitation. Environ Sci Technol 21:749–753
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1979) Methods for chemical analysis of water and wastes. EPA 600/4-79-020, USEPA, Cincinnati, OH
— (1984) Guidelines establishing test procedures for the analysis of pollutants under the Clean Water Act. Federal Register 49(209)43234–43442
— (1987) Water quality criteria summary. USEPA, Office of Water Regulations and Standards, Criteria and Standards Division, Washington, DC
Wolfe DA (1977) Fate and effects of petroleum hydrocarbons in marine organisms and ecosystems. Pergamon Press, NY
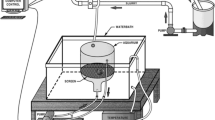
Ziegenfuss MC, Hall LW Jr, Bushong SJ, Sullivan JA, Unger MA (1990) A remotein situ apparatus for ambient toxicity testing of larval and yearling fish in river or estuarine systems. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:1311–1315
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hall, L.W., Ziegenfuss, M.C., Fischer, S.A. et al. The influence of contaminant and water quality conditions on larval striped bass in the Potomac River and upper Chesapeake Bay in 1990: Anin situ study. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 24, 1–10 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061082
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061082