Abstract
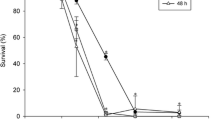
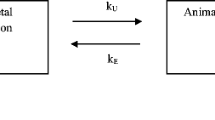
The pH of water affects the accumulation of weak electrolytes by fish in the water. However, the relationships among water pH, weak electrolyte pKa and the rate and extent of accumulation of the weak electrolyte are poorly characterized. To better define these relationships, goldfish were immersed for varying periods of time in solutions of sulfonamides that were buffered at pHvalues from 5.4 to 9.4. Sulfapyridine, sulfisomidine, and sulfadimethoxine were chosen for investigation, because their pKa's, 8.4, 7.4, and 5.9, respectively, bracketed the pH of fish body fluids. Each fish carcass was assayed for the amount of sulfonamide that had accumulated. Several pharmacokinetic models were used to analyze the data. The model that best described the accumulation of the sulfonamides represented the fish as a single compartment having an apparent volume of distribution (V)and clearance constants for absorption of both the nonionized (kHA and ionized (kA)forms. Values of Vwere between 5 and 60% of the body weight of the fish. Values for kA were all approximately 0.2 μl/min/g fish, while values of kHA were 3–100 times larger than the corresponding kA values. The kHA values correlated with the isoamyl acetate/ water partition coefficients of the nonionized forms. The extent of accumulation of the sulfonamides showed two pH-independent regions, with the low pHregion having the greater accumulation. The pHmidway between the two regions was equal to the pKa of the sulfonamide. The accumulation half-lives were 1.5–4.5 hr and independent of the pHof the water.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. S. Kaka and W. L. Hayton. Temperature and surfactant dependence of accumulation of 4-aminoantipyrine and ethanol in fish.J. Pharm. Sci. 67:1558–1563 (1978).
M. Th. M. Tulp, K. Haya, W. G. Carson, V. Zitko, and O. Hutzinger. Effect of salinity on uptake of14C-2,2′,4,5,5′-pentachlorobiphenyl by juvenile Atlantic salmon.Chemosphere. 4:243–249 (1979).
W. Dall and N. E. Milward. Water intake, gut absorption and sodium fluxes in amphibious and aquatic fishes.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 30:247–260 (1969).
G. D. Veith, D. L. De Foe, and V. V. Bergstedt. Measuring and estimating the bioconcentration factor of chemicals in fish.J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 36:1040–1048 (1979).
V. W. Saeger, O. Hicks, R. G. Kaley, P. R. Michael, J. P. Mieure, and E. S. Tucker. Environmental fate of selected phosphate esters.Environ. Sci. Technol. 3:840–844 (1979).
W. B. Neely, D. R. Branson, and G. E. Blau. The use of the partition coefficient to measure the bioconcentration potential of organic chemicals in fish.Environ. Sci. Technol. 8:1113–1115 (1974).
H. Könemann and K. van Leeuwen. Toxicokinetics in fish: accumulation and elimination of six chlorobenzenes by guppies.Chemosphere. 9:3–19 (1980).
W. B. Neely. Estimating rate constants for the uptake and clearance of chemicals by fish.Environ. Sci. Technol. 13:1506–1510 (1979).
A. Spacie and J. R. Hamelink. Dynamics of trifluralin accumulation in river fishes.Environ. Sci. Technol. 13:817–822 (1979).
G. Levy and S. P. Gucinski. Studies on biologic membrane permeation kinetics and acute toxicity of drugs by means of goldfish.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 146:80–86 (1964).
J. B. Hunn and J. L. Allen. Movement of drugs across the gills of fishes.Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. 14:47–54 (1974).
T. Bergsjo and T. H. Bergsjo. Absorption from water as an alternative method for the administration of sulphonamides to rainbow trout,Salmo gairdneri. The significance of the pKa value of the sulphonamides and the pH and salt content of the water.Acta. Vet. Scand. 19:102–109 (1978).
K. Kobayashi and T. Kishino. Effect of pH on the toxicity and accumulation of pentachlorophenol in goldfish.Bull. Japn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 46:167–170 (1980).
J. Rieder. Quantitative determination of the bacteriostatically active fraction of sulfonamides and the sum of their inactive metabolites in the body fluids.Chemotherapy 17:1–21 (1972).
W. S. Hoar and D. J. Randall.Fish Physiology, Vol. IV. Academic Press, New York, 1970, p. 258.
F. B. Eddy, J. P. Lomholt, R. E. Weber, and K. Johansen. Blood respiratory properties of rainbow trout kept in water of high CO2 tension.J. Exp. Biol. 67:37–41 (1977).
C. M. Metzler, G. L. Elfring, and A. J. McEwen. A package of computer programs for pharmacokinetic modeling.Biometrics 30:562–563 (1974).
H. Akaike. A new look at the statistical model identification.IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 19:716–723 (1974).
D. S. Riggs.The Mathematical Approach to Physiological Problems. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 1963, p. 51.
Y. Sakiya and Y. Miyauchi. Kinetics on uptake of drugs in goldfish. IV. Contribution of the stationary layer to drug absorption from the gill.Chem. Pharm. Bull. 27:1366–1372 (1979).
T. Koizumi, T. Arita, and K. Kakemi. Absorption and excretion of drugs. XIX. Some pharmacokinetic aspects of absorption and excretion of sulfonamides. (1). Absorption from rat stomach.Chem. Pharm. Bull. 12:413–420 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lo, IH., Hayton, W.L. Effects of pH on the accumulation of sulfonamides by fish. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 9, 443–459 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01060888
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01060888