Abstract
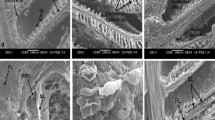
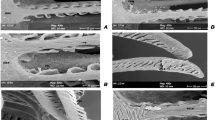
Copper in seawater caused injury to the radioles (gills) of the sabellid polychaete,Eudistylia vancouveri. Light and electron microscopy showed the loss of cellular adhesion and the structural derangement that lead to cell necrosis and death. The progression of injury was related to the uptake of copper into the tissues. Copper was found by X-ray microanalysis to be localized subcellularly in membrane-bound vesicles that are similar to lysosomes. Cell breakdown may result from lysosomal labilization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoyama, H., and T. S. Okada: Mechanisms of cell-to-cell and cell-to-substrate adhesion of human epithelial, Chang conjunctiva cells. Cell. Struct. Funct.2, 281 (1977).
Armstrong, P. B.: On the role of metal cations in cellular adhesion: Effect on cell surface charge. J. Exp. Zool.163, 99 (1966).
Armstrong, P. B., and D. P. Jones: On the role of metal cations in cellular adhesion: Cation specificity. J. Exp. Zool.167, 275 (1968).
Arstila, A. U., P. Hirsimaki, and B. F. Trump: Studies on the subcellular pathophysiology of sublethal chronic cell injury. Betr. Path. Bd.152, 211 (1974).
Baker, J. T. P.: Histological and electron microscopical observations on copper poisoning in the winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus). J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada26, 2785 (1969).
Bayne, B. L., D. R. Livingstone, M. N. Moore, and J. Widdows: A cytochemical and biochemical index of stress inMytilus edulis L. Mar. Pollut. Bull.7, 221 (1976).
Baxter, W. D., and C. A. Currie: Effects of copper on the fine-structure of the liver and gills of the black bullhead (Ictalurus melas). Micron9, 25 (1978).
Betzer, S. B., and P. P. Yevich: Copper toxicity inBusycon canaliculatum L. Biol. Bull.148, 16 (1975).
Bilinski, E., and R. E. Jonas: Effects of cadmium and copper on the oxidation of lactate by rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) gills. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada30, 1553 (1973).
Brown, B. E., and R. C. Newell: The effect of copper and zinc on the metabolism of the musselMytilus edulis. Mar. Biol.16, 108 (1972).
Bryan, G. W.: Some aspects of heavy metal tolerance in aquatic organisms. In A. P. M. Lockwood (ed.): Effects of pollutants on aquatic organisms. London: Cambridge University Press (1976).
Carmichael, N. G., K. S. Squibb, and B. A. Fowler: Metals in the molluscan kidney: A comparison of two closely related bivalve species (Argopecten), using X-ray microanalysis and atomic absorption spectrophotometry. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada36, 1149 (1979).
Collins, M.: Electrokinetic properties of dissociated chick embryo cells. II. Calcium ion binding by neural retinal cells. J. Exp. Zool.163, 39 (1966).
Coombs, T. L.: The nature of zinc and copper complexes in the oyster,Ostrea edulis. Mar. Biol.28, 1 (1974).
Coombs, T. L., and S. G. George: Mechanisms of immobilization and detoxication of metals in marine organisms. In D. S. McLusky and A. J. Berry (eds).: Physiology and behaviour of marine organisms. Oxford: Pergamon Press (1978).
Couch, J. A.: Ultrastructural study of lesions in gills of a marine shrimp exposed to cadmium. J. Invert. Path.29, 267 (1977).
Deman, J. J., E. A. Bruyneel, and M. C. Mareel: A study on the mechanism of intercellular adhesion. Effects of neuraminidase, calcium, and trypsin on the aggregation of suspended HeLa cells. J. Cell. Biol.60, 641 (1974).
Doudoroff, P., and M. Katz: Critical review of literature on the toxicity of industrial wastes and their components to fish. II. The metals, as salts. Sewage Ind. Wastes25, 802 (1953).
Engle, D. W., and B. A. Fowler: Copper and cadmium induced changes in the metabolism and structure of molluscan gill tissue. In W. B. Vernberg, F. P. Thurberg, A. Calabrese, and F. J. Vernberg (eds.): Marine Pollution: Functional responses. New York: Academic Press (1979).
Fowler, B. A., D. A. Wolfe and W. F. Hettler: Mercury and iron uptake by cytosomes in mantle epithelial cells of quahog clams (Mercenaria mercenaria) exposed to mercury. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada32, 1767 (1975).
Gardner, G. R., and P. P. Yevich: Histological and hematological responses of an estuarine teleost to cadmium. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada27, 2185 (1970).
George, S. G., B. J. S. Pirie, and T. L. Coombs: Absorption, accumulation and excretion of ironprotein complexes byMytilus edulis (L). International Conference on Heavy Metals in the Environment, Symposium Proceedings, Vol. II, Pt. 2 (1975).
—, —, —: The kinetics of accumulation and excretion of ferric hydroxide inMytilus edulis (L.) and its distribution in tissues. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol.23, 71 (1976).
George, S. G., B. J. S. Pirie, A. R. Cheyne, T. L. Coombs, and P. T. Grant: Detoxication of metals by marine bivalves: An ultrastructural study of the compartmentation of copper and zinc in the oysterOstrea edulis. Mar. Biol.45, 147 (1978).
Goldfischer, S., B. Shiller, and I. Sternlieb: Copper in hepatocyte lysosomes of the toad,Bufo marinus L. Nature228, 172 (1970).
Howard, A. G., and G. Nickless: Heavy metal complexation in polluted molluscs. II. Oysters (Ostrea edulis andCrassostrea gigas). Chem.-Biol. Interactions17, 257 (1977).
—, —: Heavy metal complexation in polluted molluscs. III. Periwinkles (Littorina littorea), cockles (Cardium edule) and scallops (Chalamys opercularis). Chem.-Biol. Interactions23, 227 (1978).
Huang, R. T. C.: Cell adhesion mediated by glycolipids. Nature276, 624 (1978).
Hughes, G. M., S. F. Perry, and V. M. Brown: A morphometric study of effects of nickle, chromium and cadmium on the secondary lamellae of rainbow trout gills. Water Res.13, 665 (1979).
Jha, R. K.: An improved polychrome staining method for thick epoxy sections. Stain. Tech.51, 159 (1976).
Lake, P. S., and V. J. Thorp: The gill lamellae of the shrimpParatya tasmaniensis (Atyidae: Crustacea). Normal ultrastructure and changes with low levels of cadmium. Proc. Eighth Int. Congr. Electron Microsc. Canberra2, 448 (1974).
LaRoche, G., G. R. Gardner, R. Eisler, E. H. Jakim, P. P. Yevich, and G. E. Zaroogian: Analysis of toxic responses in marine poikilotherms. In G. E. Glass (ed.): Bioassay techniques and environmental chemistry. Ann Arbor: Ann Arbor Science Publishers (1973).
Lauwerys, R., and J-P. Buchet: Study on the mechanism of lysosome labilization by inorganic mercuryin vitro. Eur. J. Biochem.26, 535 (1972).
Ledgerwood, R. D., and G. W. Brown, Jr.: Cadmium induced aneurysms in gill lamellae. In 1972 Research in fisheries. College of Fisheries Contribution 375, University of Washington, Seattle, WA (1973).
Lindquist, R. R.: Studies on the pathogenesis of hepatolenticular degeneration. III. The effect of copper on rat liver lysosomes. Am. J. Path.53, 903 (1968).
Loose, L. D., J. B. Solkworth, and D. Warrington: Cadmium-induced phagocyte toxicity. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.20, 582 (1978).
Malenkov, A. G., and A. G. Melikyants: Ion permeability and strength of cell contacts. Ion permeability and mechanical properties of cell contacts in small intestine epithelium. J. Membrane Biol.36, 97 (1977).
McGuire, E. J.: A possible role for carbohydrates in cell-cell adhesion. In C. F. Fox (ed.): Membrane research. New York: Academic Press (1972).
Moore, M. W., and A. R. D. Stebbing: The quantitative cytochemical effects of three metal ions on a lysosomal hydrolase of a hydroid. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K.56, 995 (1976).
Newman, M. W., and S. A. MacLean: Physiological response of the cunner,Tautogolabrus adspersus, to cadmium. VI. Histopathology. In Physiological response of the cunner,Tautogolabrus adspersus, to cadmium, NOAA Tech. Rep. NMFS SSRF 683 (1974).
Nimmo, D. W. R., D. V. Lightner, and L. H. Bahner: Effects of cadmium on the shrimps,Penaeus duorarum, Palaemonetes pugio andPalaemonetes vulgaris. In F. J. Vernberg, A. Calabrese, F. P. Thurberg, and W. B. Vernberg (eds.): Physiological responses of marine biota to pollutants. New York: Academic Press (1977).
Oppenheimer, S. B.: Cell surface carbohydrates in adhesion and migration. Amer. Zool.18, 13 (1978).
Passow, H., A. Rothstein, and T. W. Clarkson: The general pharmacology of heavy metals. Pharmacol. Rev.13, 185 (1961).
Pearson, P. and M. B. Mathews: Endoskeletal cartilage in a marine polychaete,Eudistylia polymorpha. Biol. Bull.132, 244 (1967).
Raymont, J. E. G.: Discussion appended to J. E. G. Raymont and J. Shields. 1964. Toxicity of copper and chromium in the marine environment. In E. A. Pearson (ed.): Advances in water pollution research. New York: MacMillan (1964).
Richardson, K. C., I. Jarett, and E. H. Finke: Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron miscroscopy. Stain. Tech.35, 313 (1960).
Roesijadi, G.: Influence of copper on the clam,Protothaca staminea: Effects on gills and occurrence of copper-binding proteins.Biol. Bull 158, 233 (1980).
Schulz-Baldes, M.: Lead transport in the common musselMytilus edulis. In D. S. McLusky and A. J. Berry (eds.): Physiology and behavior of marine organisms. Oxford: Pergamon Press (1978).
Skidmore, J. F.: Respiration and osmoregulation in rainbow trout with gills damaged by zinc sulphate. J. Exp. Biol.52, 481 (1970).
Sternlieb, I., and S. Goldfischer: Heavy metals and lysosomes. In J. T. Dingle and R. T. Dean (eds.): Lysosomes in biology and pathology. Vol 5. Amsterdam: North Holland (1976).
Strik, J. J. T. W. A., H. H. de Iongh, J. W. A. van Rijn van Alkemade, and T. P. Wuite: Toxicity of chromium (VI) in fish, with special reference to organoweights, liver and plasma enzyme activities, blood parameters and histological alterations. In J. H. Koeman and J. J. T. W. A. Strik (eds.): Sublethal effects of toxic chemicals on aquatic animals. Amsterdam: Elsevier (1975).
Tapp, R. L., and A. Hockaday: Combined histochemical and x-ray microanalytical studies on the copper-accumulating granules in the mid-gut of larvalDrosophila. J. Cell. Sci.26, 201 (1977).
Ueda, M. J., and M. Takeichi: Two mechanisms in cell adhesion revealed by effects of divalent cations. Cell. Struct. Funct.1, 377 (1976).
Vernberg, W. B., and F. J. Vernberg: Environmental physiology of marine animals. Berlin: Springer-Verlag (1972).
Viarengo, A., M. Pertica, G. Mancinelli, S. Palmero, and M. Orunesu: Rapid induction of copper binding proteins in the gills of metal exposed mussels. In R. Gilles (ed.): Proceedings of the first meeting of the European society of comparative physiology and biochemistry. Oxford: Pergamon Press (In press).
Young, J. S., R. L. Buschbom, J. M. Gurtisen, and S. P. Joyce: Effects of copper on the sabellid polychaete,Eudistylia vancouveri: I. Concentration limits for copper accumulation. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.8, 97 (1979a).
Young, J. S., J. M. Gurtisen, C. W. Apts, and E. A. Crecelius: The relationship between the copper complexing capacity of sea water and copper toxicity in shrimp zoeae. Marine Environ. Res.2, 265 (1979b).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Young, J.S., Adee, R.R., Piscopo, I. et al. Effects of copper on the sabellid polychaete,Eudistylia vancouveri. II. Copper accumulation and tissue injury in the branchial crown. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 10, 87–104 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01057578
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01057578