Abstract
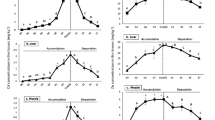
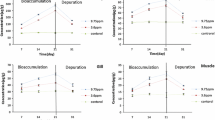
Cadmium uptake rates in various tissues ofPandalus montagui exposed to sea water containing 37 μgCd/L for 14 days ranged from 0.002–0.06 μg/g dry tissue/hr. During depuration for 57 days, the levels in most tissues decreased slightly, but continued to rise in the hepatopancreas indicating Cd redistribution. Exposure to 65 μg Zn/L produced no substantial change in Zn content of the tissues. An increase occurred in eggs and hepatopancreas during the first six days of depuration. During exposure to Cd and Zn combined (40 μg Cd/L + 70 μg Zn/L), tissue Zn levels responded as with Zn alone. In the presence of Zn, Cd concentration was doubled in the hepatopancreas, depressed by one-third in the carcass, and did not change in the other tissues. Increased amounts of Zn (up to 410 μg Zn/L) had no effect on the Cd levels of the tissues except that the Cd level in the hepatopancreas was depressed, although the level was still greater than in the case of exposure to Cd alone. The possible role of metallothionein is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blau, G., and G. Agin: A users manual for BIOFAC: A computer program for characterizing the roles of uptake and clearance of chemicals in aquatic organisms. Dow Chemical Co., Midland, MI (1978).
Casterline, Jr., J. L., and G. Yip: The distribution and binding of cadmium in oyster, soybean, and rat liver and kidney. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.3, 319 (1975).
Dethlefsen, V.: Uptake, retention, and loss of cadmium by brown shrimp (Crangon crangon). Meeresforsch.26, 137 (1977/78).
Establier, R., M. Gutiérrez, and A. Rodriguez: Acumulación de cadmio en el músculo y hepatopancreas del langostino (Penaeus kerathurus) y alteraciones histopatológicas producidas. Invest. Pesq.42, 299 (1978).
Hill, C. H., and G. Matrone: Chemical parameters in the study ofin vivo andin vitro interactions of transition elements. Fed. Proc. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol.29, 1474 (1970).
Jackim, J., G. Morrison, and R. Steele: Effects of environmental factors on radiocadmium uptake by four species of marine bivalves. Mar. Biol.40, 303 (1977).
Magos, L., and M. Webb: Theoretical and practical considerations on the problem of metal-metal interaction. Environ. Health Perspect.25, 151 (1978).
McLeese, D. W., C. D. Metcalfe, and D. S. Pezzack: Uptake of PCBs from sediment byNereis virens andCrangon septemspinosa. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.9, 509 (1980).
Nimmo, D. W. R., D. V. Lightner, and L. H. Bahner: Effects of cadmium on the shrimps,Penaeus duorarum, Palaemonetes pugio andPalaemonetes vulgaris. In F. J. Vernberg, A. Calabrese, F. P. Thurberg, and W. B. Vernberg (eds): Physiological responses of marine biota to pollutants, p. 131. New York: Academic Press (1977).
Olafson, R. W., A. Kearns, and R. G. Sim: Heavy metal induction of metallothionein synthesis in the hepatopancreas of the crabScylla serrata. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.62B, 417 (1979).
Preston, A.: Heavy metals in British waters. Nature242, 95 (1973).
Schroeder, H. A., A. P. Nason, I. H. Tipton, and J. A. Balassa: Essential trace elements in man: Zinc. Relation to environmental cadmium. J. Chron. Dis.20, 179 (1967).
Talbot, V., and R. J. Magee: Naturally-occurring heavy metal binding proteins in invertebrates. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.7, 73 (1978).
Vaasjoki, R., and J. K. Miettinen: Zn/Cd and Zn/Hg metalloprotein interactions in rainbow trout studied by gel chromatography and isoelectric focusing. In S. S. Brown (ed): Clinical chemistry and chemical toxicology of metals, p. 71. Amsterdam: Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press (1977).
Webb, M.: Protection by zinc against cadmium toxicity. Biochem. Pharmacol.21, 2767 (1972).
Zitko, V. Relationships governing the behavior of pollutants in aquatic ecosystems and their use in risk assessment. Can. Tech. Rep. Aquat. Sci., In press (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ray, S., McLeese, D.W., Waiwood, B.A. et al. The disposition of cadmium and zinc inPandalus montagui . Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 9, 675–681 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055543
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055543