Abstract
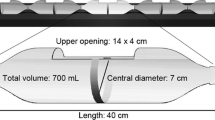
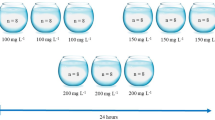
The avoidance behavior of fish is a sensitive indicator to aquatic contaminants such as surfactants, pesticides, and residual chlorine. This paper describes an avoidance test with special reference to monochloramine by medaka (killifish,Oryzias latipes) in a small modular chamber system with a symmetrical parallel-flow. The significant avoidance concentration (P = 0.05) was 5.7 μg/L as combined residual chlorine, which is the lowest among the residual chlorine avoidance concentrations reported in the literature. The avoidance curves of medaka to monochloramine exhibited a similar pattern to those of anionic surfactants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogardus RB, Boies DB, Teppen TC, Horvath FJ (1978) Avoidance of monochloramine: Test tank results for rainbow trout, coho salmon, alewife, yellow perch and spottail shiner. In: Jolley RL, Gorchev H, Hamilton DH Jr (eds) Water Chlorination: Environmental Impact and Health Effects. Vol. 2. Ann Arbor Science, Ann Arbor, Michigan, pp 149–161
Brungs WA (1973) Effects of residual chlorine on aquatic life. J Water Pollut Control Fed 45:2180–2193
Cherry DS, Larrick SR, Dickson KL, Hoehn RC, Cairns J Jr (1977) Significance of hypochlorous acid in free residual chlorine to the avoidance response of spotted bass (Micropterus punctulatus) and rosyface shiner (Notropis rubellus). J Fish Res Board Can 34:1365–1372
Cherry DS, Cairns J Jr (1982) Biological monitoring, part V-preference and avoidance studies. Water Res 16:263–301
Cherry DS, Larrick SR, Giattina JD, Cairns J Jr, Hassel JV (1982) Influence of temperature selection upon the chlorine avoidance of cold-water and warmwater fishes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 39;162–173
Giattina JD, Cherry DS, Larrick SR, Cairns J Jr (1981) Comparison of laboratory and field avoidance behavior of fish in heated chlorinated water. Trans Amer Fish Soc 110:526–535
Giattina JD, Garton RR (1983) A review of the preference-avoidance responses of fishes to aquatic contaminants. In: Gunther FA (ed) Residue Reviews, Vol 87. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 43–90
Hall LW Jr, Burton DT, Margrey SL, Graves WC (1982) A comparison of the avoidance responses of individual and schooling juvenile Atlantic menhaden,Brevoortia tyrannus subjected to simultaneous chlorine and ΔT conditions. J Toxicol Environ Health 10:1017–1026
Hall LW Jr, Margrey SL, Burton DT, Graves WC (1983) Avoidance behavior of juvenile striped bass,Morone saxatilis, subjected to simultaneous chlorine and elevated temperature conditions. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 12:715–720
Hidaka H, Suga M, Tatsukawa R (1983) Quantitative avoidance test of chemicals using the himedaka (Oryzias latipes). J Agric Chem Soc Jap 57:571–579
— (1984a) Avoidance of anionic surfactants in medaka (Oryzias latipes). J Agric Chem Soc Jap 58:1–7
Hidaka H, Hattanda M, Tatsukawa R (1984b) Avoidance of pesticides with medakas (Oryzias latipes) J Agric Chem Soc Jap 58:145–151
Hose JE, Stoffel RJ (1980) Avoidance responses of juvenileChromis punctipinnis to chlorinated seawater. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 25:929–935
Larrick SR, Dickson KL, Cherry DS, Cairns J Jr (1978) Determining fish avoidance of polluted water. Hydrobiologia 61:257–265
Mattice JS, Zittel HE (1976) Site-specific evaluation of power plant chlorination. J Water Pollut Control Fed 48:2284–2308
Meldrim JW, Fava JA Jr (1977) Behavioral avoidance responses of estuarine fishes to chlorine. Chesapeake Sci 18:154–157
Middaugh DP, Crane AM, Couch JA (1977) Toxicity of chlorine to juvenile spot,Leiostomus xanthurus. Water Res 11:1089–1096
Pharmaceutical Society of Japan (1973) Standard Methods of Analysis for Hygienic Chemists—with commentary—. Kanehara Shuppan, Tokyo, pp 710 and 816 (in Japanese)
Scherer E, Nowak S (1973) Apparatus for recording avoidance movements of fish. J Fish Res Board Can 30:1594–1596
Sprague JB, Drury DE (1969) Avoidance reactions of salmonid fish to representative pollutants. In: Jenkins SH (ed) Advances in Water Pollution Research, Vol. 1. Pergamon Press, London, pp 169–179
Stober QJ, Dinnel PA, Hurlburt EF, DiJulio DH (1980) Acute toxicity and behavioral responses of coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) and shiner perch (Cymatogaster aggregata) to chlorine in heated sea-water. Water Res 14:347–354
Tatsukawa R, Hidaka H (1978) Avoidance test of chemical substances by fish—avoidance of detergents by ayu (Plecoglossus altivelis). J Agric Chem Soc Jap 52:263–270
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hidaka, H., Tatsukawa, R. Avoidance test of a fish, medaka (Oryzias latipes), to aquatic contaminants, with special reference to monochloramine. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 14, 565–571 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055386
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055386