Abstract
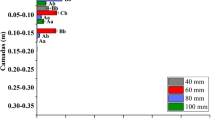
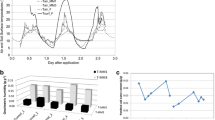
When the insecticide/nematicide aldicarb was incubated in three greenhouse soils at 20°C, the transformation rates of the parent compound and its first oxidation product aldicarb-sulfoxide were high, while the amounts of aldoxycarb (=aldicarb-sulfone) remained low. The transformation and movement of aldicarb and its oxidation products in a simplified greenhouse-soil system were simulated with a computation model. When the highest transformation rates were introduced into the computations in combination with high irrigation rates, the computed leaching was only 0.006% of the dose, with a maximum concentration of 0.15μg L−1 in the tile-drain water. With lower transformation rates, the computed leaching was 1.39% of the dose with a maximum concentration of 21.0μg L−1, but in combination with a lower irrigation rate the leaching was computed to be much less. Water from drain pipes and pits was sampled in three greenhouses that had received regular applications of aldicarb: the concentrations measured by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) varied from less than 1μg L−1 to more than 30μg L−1. Most of the concentrations measured in water courses in an area with many greenhouses were low, but some were high, ranging up to 21μg L−1. Ways of reducing the discharge of the oxidation products of aldicarb from greenhouse soils to water courses are suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Briggs GG, Bromilow RH, Evans AA (1982) Relationships between lipophilicity and root uptake and translocation of non-ionized chemicals by barley. Pestic Sci 13:495–504
Bromilow RH, Baker RJ, Freeman, MAH, Görög K (1980) The degradation of aldicarb and oxamyl in soil. Pestic Sci 11:371–378
Dekker A, Houx NWH (1983) Simple determination of oxime carbamates in soil and environmental water by high pressure liquid chromatography. J Environ Sci Health B18:379–392
Felsot A, Dahm PA (1979) Sorption of organophosphorus and carbamate insecticides by soil. J Agric Food Chem 27:557–563
Heywood DL (1975) Degradation of carbamate insecticides in soil. In: Coulston F, Korte F (eds) (Environ Quality Safety 4) Thieme, Stuttgart, 128–133
IBM (1975) Continuous System Modeling Program III (CSMP III). Program Reference Manual. Program No 5734-XS9. Data Processing Division, White Plains, NY 206 pp.
Leistra M (1978) Computed redistribution of pesticides in the root zone of an arable crop. Plant Soil 49:569–580
Moreale A, van Bladel R (1981) Adsorption de 13 herbicides et insecticides par le sol. Relation solubilité-réactivité. Revue de l'Agriculture 34:939–952
Smelt JH, Leistra M, Houx NWH, Dekker A (1978a) Conversion rates of aldicarb and its oxidation products in soils. I. Aldicarb sulphone. Pestic Sci 9:279–285
— (1978b) Conversion rates of aldicarb and its oxidation products in soils. II. Aldicarb sulphoxide. Pestic Sci 9: 286–292
— (1978c) Conversion rates of aldicarb and its oxidation products in soils. III. Aldicarb. Pestic Sci 9:293–300
Toksöz S, Kirkham D (1971) Steady drainage of layered soils. I. Theory. J Irrig Drainage Div IR1:1–18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leistra, M., Dekker, A. & van der Burg, A.M.M. Leaching of oxidation products of aldicarb from greenhouse soils to water courses. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 13, 327–334 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055283
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055283