Abstract
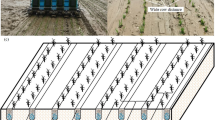
To increase the fertilizer-N efficiency in lowland rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivation, new management practices are needed. Main cause of the present low efficiency is the low N recovery by plants, as a considerable part of the N applied is lost; deep placement techniques improve the recovery. A pneumatic injector, with which urea prills can be point-placed at a depth of 5–10 cm in paddy soils, was tested in 38 on-farm trials in 1989/90, mostly during the wet season. The experiments, located in Africa and Asia, focussed on differences in grain yield between conventional methods of broadcasting urea and injection by the pneumatic injector, at recommended N-rates. The study shows that the pneumatic injector is effective as a tool to improve the N fertilizer efficiency. The average yield increases per region, resulting from the use of the injector, ranged from about 250 to 1300 kg grain ha−1. The value of the yield increase would allow most farmers to recover the costs of the injector within one season, even if labour was hired to carry out the injections. The average labour requirement of the injector was 40 hours ha−1. In Indonesia, injection of prilled urea gave yields similar to those obtained with urea briquettes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buresh RJ and De Datta SK (1990) Denitrification losses from puddled rice soils in the tropics. Biol Fertil Soils 9: 1–13
Cao ZH, De Datta SK and Fillery IRP (1983) Effect of placement methods on floodwater properties and recovery of applied nitrogen (15N-labeled urea) in wetland rice. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48: 196–203
Cao ZH, De Datta SK and Fillery IRP (1984) Nitrogen-15 balance and residual effects of urea-N in wetland rice fields as affected by deep placement techniques. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48: 203–208
De Datta SK and Buresh RJ (1989) Integrated nitrogen management in irrigated rice. Adv Soil Sci 10: 143–169
FAO (1984) Fertilizer application equipment for small farmers. FAO Fertilizer Programme, Rome
Freney JR, Trevit ACF, De Datta SK, Obcemea WN and Real JG (1990) The interdependence of ammonia volatilization and denitirification as nitrogen loss processes in flooded rice in the Philippines. Biol Fertil Soils 9: 31–36
INSFFER (1985) Summary report on the fifth international trial on nitrogen fertilizer efficiency in irrigated wetland rice (1981–1984) International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines
INSFFER (1986) Progress report on the first international trial on the comparison of hand- and machine-applied prilled urea and urea supergranules in lowland rice (1984–1985). International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines
Makken FA and Scholten JHM (1991) Test and introduction of a pneumatic urea injector in wetland rice. Institute for Soil Fertility Research, Haren, The Netherlands
O'Brien DT, Sudjadi M, Sri Adiningsih J and Irawan (1987) Economic evaluation of deep placed urea for rice in farmers' fields: a pilot area approach, Ngawi, East Java, Indonesia. In: Efficiency of nitrogen fertilizers for rice, pp 141–159. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines
Prins WH, Van Brakel GD and Van der Sar T (1984) Pneumatic injector for deep placement of urea in wetland rice soils. Development of the Agricultural Machinery Industry in Developing Countries. Proc 2nd Int Conf Amsterdam 1984, pp 384–390. Pudoc, Wageningen
Prins WH and Rauw GJG (1989) Use of large granular urea (LGU) to improve efficiency of broadcast urea in wetland rice cultivation. Fert Res 19: 21–27
Schnier HF, De Datta SK, Mengel K, Marqueses EP and Faronilo JE (1988) Nitrogen use efficiency, floodwater properties, and nitrogen-15 balance in transplanted lowland rice as affected by liquid urea band placement. Fert Res 16: 241–255
Scholten JHM (1990) Testing the pneumatic urea injector. Agrochemicals News in Brief, Vol. XIII, 3, pp 26–30. ESCAP/FAO/UNIDO, Fertilizer Advisory, Development and Information Network for Asia and the Pacific
Sudjadi M, Prawirasumantri Y and Wetselaar R (1987) Nitrogen fertilizer efficiency in lowland rice in Indonesia. In: Efficiency of nitrogen fertilizers for rice, pp 123–134. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines
Sudjadi M, Putu I, Widjaya-Adhi G and Sri Adiningsih J (1989) Management of nitrogen to improve its use efficiency in lowland and upland soils in Indonesia. In: Van der Heide J (ed) Proc Nutrient management for food crop production in tropical farming systems, Malang, pp 95–107. Institute for Soil Fertility Research, Haren, The Netherlands and Universitas Brawijaya, Malang, Indonesia
Van der Sar T and De Vries HCP (1984) A urea point injector for wetland rice. In: Fertilizer application equipment for small farmers. FAO Fertilizer Programme, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Vlek PLG and Craswell ET (1979) Effect of nitrogen source and management on ammonia volatilization losses from flooded rice-soil systems. Soil Sci Soc Am J 43: 352–358
Yoshida, Shouichi (1981) Fundamentals of rice crop science. pp 135–147. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scholten, J.H.M. Increasing urea-N efficiency for transplanted lowland rice by pneumatic injection: Yield and economics at the farm level. Fertilizer Research 33, 107–114 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01051165
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01051165