Abstract
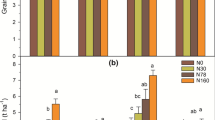
Application of 120 kg urea-N ha−1 to lowland rice grown in a highly percolating soil in 10 equal split doses at weekly intervals rather than in 3 equal split doses at 7, 21 and 42 days after transplanting did not significantly increase rice grain yield and N uptake. Results suggest that leaching losses of N were not substantial. In lysimeters planted with rice, leaching losses of N as urea, NH +4 , and NO -3 beyond 30 cm depth of a sandy loam soil for 60 days were about 6% of the total urea-N and 3% of the total ammonium sulphate-N applied in three equal split doses. Application of urea even in a single dose at transplanting did not result in more N leaching losses (13%) compared to those observed from potassium nitrate (38%) applied in three split doses. Nitrogen contained in potassium nitrate was readily leached during the first week of its application. More N was lost from the first dose of N applied at transplanting than from the second or third dose. Data pertaining to yield, N uptake and per cent N recovery by rice revealed that the performance of different fertilizer treatments was inversely related to susceptibility of N to leaching.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardakani MS, Volz MG and McLaren AD (1975) Consecutive steady state reactions of urea, ammonium and nitrite N in soil. Can J Soil Sci 55: 83–91
Bauder JW and Montgomery BR (1980) N-source and irrigation effects on nitrate leaching. Agron J 72: 593–596
Bremner JM and Keeney DR (1965) Steam distillation method for determination of ammonium, nitrate and nitrite. Anal Chem Acta 32: 425–495
Buresh RJ, Austin ER and Craswell ET (1982) Analytical methods in15N research. Fert Res 3: 37–62
Douglas LA and Bremner JM (1970) Extraction and colorimetric determination of urea in soils. Soil Sci Soc Amer Proc 34: 859–862
Katyal JC, Bijay-Singh, Vlek PLG and Craswell ET (1985a) Fate and efficiency of nitrogen fertilizers applied to wetland rice. II. Punjab, India. Fert Res 6: 279–290
Katyal JC, Bijay-Singh, Sharma VK and Craswell ET (1985b) Efficiency of some modified urea fertilizers for wetland rice grown on a permeable soil. Fert Res 8: 137–146
Martin JW, Leonard WH and Stamp DL (1976) Principles of field crop production. p. 547–548, Macmillan Publ Co, New York
Meelu OP and Gupta RK (1980) Time of fertilizer N application in rice culture. Int Rice Res Newsletter 5: 3
Reddy KR (1982) Nitrogen cycling in a flooded-soil ecosystem planted to rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Soil 67: 209–220
Rekhi RS, Meelu OP and Gupta RK (1982) Lysimeter studies on recovery of15N-labelled urea in wetland rice. Plant Soil 66: 57–67
Vlek PLG and Craswell ET (1979) Effect of nitrogen source and management on ammonia volatilization losses from flooded rice soil systems. Soil Sci Soc Amer J 43: 352–358
Wagenet RJ, Biggar JW and Nielsen DR (1977) Tracing the transformation of urea fertilizer during leaching. Soil Sci Soc Am J 41: 896–902
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bijay-Singh, Yadvinder-Singh, Khind, C.S. et al. Leaching losses of urea-N applied to permeable soils under lowland rice. Fertilizer Research 28, 179–184 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01049748
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01049748