Summary
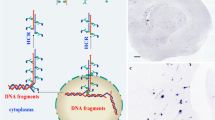
A full-length cDNA clone encoding the constant region of T cell receptor β chain was labelled by random priming DNA with digoxigenin-dUTP. The probe was used to estimate the relative amount of the receptor β chain mRNA byin situ hybridization on frozen sections from human thymus and lymph nodes. The hybridization was visualized in blue using an anti-digoxigenin antibody conjugated with alkaline phosphatase and a subsequent enzyme-catalysed colour reaction. The distributions of the signal in tissue sections were as expected. Moreover, labelled cells showed hybrids both in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus, and strongly and weakly stained cells were clearly distinguishable. The results indicate that this method ofin situ hybridization should be useful in the detection of specific mRNA in frozen sections.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuto, O., Campen, T. J., Royer, H. D., Hussey, R., Poole, C. B. &Reinherz, E. (1985) Molecular analysis of T cell receptor(Ti) variable region (V) gene expression.J. Exp. Med. 161, 1326–43.
Bauman, J. G. J., Wiegant, J. &Van Duijn, P. (1981) Cytochemical hybridization with fluorochrome-labelled RNA II. Applications.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 29, 238–46.
Bentley, L. J., Singer, R. H. (1985) Quantitative analysis ofin situ hybridization methods for the detection of actin gene expression.Nucleic Acid Res. 13, 1777–99.
Bentley, L. J., Villnave, C. A. &Singer, R. H. (1988) Sensitive, high-resolution chromatin and chromosome mappingin situ: presence and orientation of two closely integrated copies of EBV in a lymphoma line.Cell 52, 51–61.
Bloch, B., Popovici, T., Le Guellec, D., Norman, D. E., Chouham, S., Guitteny, A. F. &Bohlen, P. (1986)In situ hybridization histochemistry for the analysis of gene expression in the endocrine and central nervous tissues. A three year experience.J. Neurosci. Res. 16, 183–200.
Brigati, D. J., Myerson, D., Leary, J. J., Spalholz, B., Travis, S. Z., Fong, C. K. Y., Hsiung, G. D. &Ward, D. C. (1983) Detection of viral genomes in cultura cells and paraffin-embedded tissue sectioning using biotin-labeled hybridization probes.Virology 126, 32–50.
Buongiorno-Nardelli, M., &Amaldi, F. (1969) Autoradiographic detection of molecular hybrids between rRNA and DNA in tissue sections.Nature 225, 946–8.
Caccia, N. &Mak, T. W. (1989) T cell receptors. InT Cells. Vol. 7, pp. 39–76. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Coghlan, J. P., Penschow, J. D., Hudson, P. H. &Niall, H. D. (1984) Hybridization histochemistry: use of recombinant DNA for tissue localization of specific mRNA population.Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 6, 63–78.
de Frutos, R., Kimura, K. &Peterson, K. R. (1989)In situ hybridization of Drosophila polytene chromosomes with digoxygenin-dUTP-labeled probes.Trends in Gen. 5, 366.
Farquharson, M., Harvie, R. &McNicol, A. M. (1990) Detection of messenger RNA using a digoxigenin end labelled oligodeoxynucleotide probe.J. Clin. Pathol. 43, 424–8.
Farr, G. A., Anderson, S. K., Marrac, P. &Kappler, J. (1985) Expression of antigen-specific, major histocompatibility complex-restricted receptors by cortical and medullary thymocytesin situ.Cell. 43, 543–50.
Gall, J. G. &Purdene, M. C. (1969) Formation and detection of RNA: DNA hybrid molecules in cytological preparations.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 63, 378–83.
Garson, J. A., Van den Berghe, A. &Kemshead, J. T. (1987a) Novel non-isotopicin situ hybridization technique detects small (1 Kb) unique sequences in routinely G-banded human chromosomes: fine mapping of N-myc and B-NGF genes.Nucleic Acid Res. 15, 4761–70.
Garson, J. A., Van den Berghe, J. A. &Kemshead, J. T. (1987b) High-resolutionin situ hybridization technique using biotinylated N MYC oncogene probe reveals periodic structure of HSRs in human neuroblastoma.Cytogenet Cell. Genet. 45, 10–15.
Godard, C. &Jones, K. W. (1979) Detection of AKR mouse cells byin situ hybridization.Nucleic Acids Res. 6, 2849–57.
Guitteny, A. F., Fouqueb, B., Mougin, C., Teoule, R. &Bloch, B. (1988) Histological detection of messenger RNAs with biotinylated synthetic oligonucleotide.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 36, 536–71.
Herrington, C. S., Burns, J., Graham, A. K., Evans, M. F. &McGee, J. O'D. (1989a) Interphase cytogenetics using biotin and digoxygenin-labelled probes I: relative sensitivity of both reporter molecules for HPV 16 detection in CaSKi cells.J. Clin. Pathol. 41, 592–600.
Herrington, C. S., Burns, J., Graham, A. K., Bhatt, B. &McGee, J.O'D. (1989b) Interphase cytogenetics using biotin and digoxygenin labelled probes II: simultaneous detection of two nucleic acid species in individual nuclei.J. Clin. Pathol. 42, 601–6.
Huang, W. M., Gibson, S. J., Facer, P., Gu, J. &Polak, M. (1983) Improved section adhesion for immunocytochemistry using high molecular weight polymers of L-lysine as a slide coating.Histochemistry 77, 275–9.
Landegent, J. E., Jansen In De Wal, N., Baan, R. A., Hoeijmakers, J. H. J. &Van der Ploeg, M. (1984) 2-acetylaminofluorene-modified probes for the indirect-hybridocytochemical detection of specific nucleotide sequences.Exp. Cell Res. 153, 61–72.
Lewis, M. E., Sherman, T. G. &Watson, S. J. (1985)In situ hybridization histochemistry with sythetic oligonucleotides. Strategies and methods.Peptides 6, 75.
Maggiano, N., Larocca, L. M., Piantelli, M., Acuto, O. &Musiani, P. (1987) Expression of T-cell receptor-α and -β subunits in human thymocytes. An immunocytologic study.J. Immunol. 139, 1438–45.
Manuelidis, L., Langer-Safer, P. R. &Ward, D. C. (1982) High-resolution mapping of satellite DNA using biotin-labelled DNA probes.J. Cell Biol. 95, 619–25.
McCabe, J., Morrel, J. I., Ivell, R., Schmale, H., Richter, D. &Pfaff, D. W. (1986).In situ hybridization technique to localize rRNA in mammalian neurons.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 34, 45–50.
Royer, H. D., Ramarli, D., Acuto, O., Campen, T. J. &Reinherz, E. L. (1985) Genes encoding the T-cell receptor-α and -β subunits are transcribed in an ordered manner during intrathymic ontogeny.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 5510–14.
Shroyer, K. P. &Nakane, P. K. (1982) Use of DNP-labelled cDNA forin situ hybridization.J. Cell. Biol. 97, 337a.
Taylor, C. L. (1986) Lymphoma/hematopathology. InImmunomicroscopy: a Diagnostic Tool for the Surgical Pathologist. Vol. 19, pp. 70–115. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Company.
Tchen, P., Fuchs, R. P. P., Sage, E. &Leng, M. (1984) Chemically modified nucleic acids as immunodetectable probes in hybridization experiments.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 3466–70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maggiano, N., Larocca, L.M., Piantelli, M. et al. Detection of mRNA and hnRNA using a digoxigenin labelled cDNA probe byin situ hybridization on frozen tissue sections. Histochem J 23, 69–74 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01047110
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01047110