Abstract
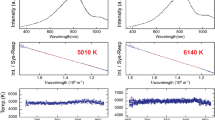
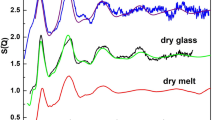
The solubility mechanism of fluorine in quenched SiO2-NaF and SiO2-AlF3 melts has been determined with Raman spectroscopy. In the fluorine abundance range of F/(F+Si) from 0.15 to 0.5, a portion of the fluorine is exchanged with bridging oxygen in the silicate network to form Si-F bonds. In individual SiO4-tetrahedra, one oxygen per silicon is replaced in this manner to form fluorine-bearing silicate complexes in the melt. The proportion of these complexes is nearly linearly correlated with bulk melt F/(F+Si) in the system SiO2-AlF3, but its abundance increases at a lower rate and nonlinearly with increasing F/(F+Si) in the system SiO2-NaF. The process results in the formation ofnonbridging oxygen (NBO), resulting in stabilization of Si2O 2−5 units as well as metal (Na+ or Al3+) fluoride complexes in the melts. Sodium fluoride complexes are significantly more stable than those of aluminum fluoride.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brawer SA, White WB (1975) Raman spectroscopic investigation of the structure of silicate glasses. I. The binary silicate glasses. J Chem Phys 63:2421–2432
Danckwerth P (1981) Phase relations in the system Na2O-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O-HF at 15 kbar. Carnegie Inst Washington Yearb 80:350–352
Davidon WC (1966) Variable metric method for minimization. ANL 5990, Argonne National Laboratory
Dumas P, Corset J, Carvalho W, Levy Y, Neuman Y (1982) Fluorine-doped vitreous silicate analysis of fiber optics preforms by vibrational spectroscopy. J Non-Cryst Solids 47:239–242
Fletcher R, Powell MJD (1963) A rapidly converging descent method for minimization. Computer J 6:163–168
Furukawa T, Fox KE, White WB (1981) Raman spectroscopic investigation of the structure of silicate glasses. III. Raman intensities and the structural units in sodium silicate glasses. J Chem Phys 75:3226–3237
Gilbert B, Mamantov G, Begun GM (1975) Raman spectra of aluminum containing melts and the ionic equilibrium in molten cryolite type mixtures. J Chem Phys 62:950–955
Hariyama C, Camp FE (1969) The effect of fluorine and chlorine substitution and fining of soda-lime and potassium-barium silicate glass. Glass Technol 10:123–127
Hartwig CM (1977) The radiation-induced formation of hydrogen and deuterium compounds in silica as observed by Raman scattering. J Chem Phys 66:227–239
Kogarko LN, Kriegman LD (1973) Structural position of fluorine in silicate melts (according to melting curves). Geochem Int 9:34–40
Kovalenko NI (1978) The reactions between granite and aqueous hydrofluoric acid in relation to the origin of fluorine-bearing granites. Geochem Int 14:108–118
Kozakevitch P (1954) Sur la viscosite des laitiers de hauts four-neaux. Rev Metall 51:569–587
Long DA (1977) Raman spectroscopy. McGraw-Hill, New York
Manning DAC (1981) The effect of fluorine on liquidus phase relationships in the system Qz-Ab-Or with excess water at 1 kb. Contrib Mineral Petrol 76:206–215
Matson JF, Sharma SK, Philpotts JA (1983) The structure of high-silica alkali-silicate glasses — a Raman spectroscopic study. J Non-Cryst Solids 58:323–352
McMillan P, Piriou B, Navrotsky A (1982) A Raman spectroscopic study of glasses along the joins silica-calcium aluminate, silica-sodium aluminate and silica-potassium aluminate. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 46:2021–2037
Mysen BO, Virgo D, Scarfe CM (1980) Relations between the anionic structure and viscosity of silicate melts — a Raman spectroscopic study. Am Mineral 65:690–711
Mysen BO, Finger LW, Seifert FA, Virgo D (1982a) Curve-fitting of Raman spectra of amorphous materials. Am Mineral 67:686–696
Mysen BO, Virgo D, Seifert FA (1982b) The structure of silicate melts: implications for chemical and physical properties of natural magma. Rev Geophys 20:353–383
Phillips JC (1984) Microscopic origin of anomalously narrow Raman lines in network glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 63:347–355
Powell MJD (1964a) An efficient method for finding a minimum of a function of several variables without calculating derivatives. Computer J 7:155–162
Powell MJD (1964b) A method for minimizing a sum of non-linear functions without calculating derivatives. Computer J 7:303–307
Rabinovitch EM (1983) On the structural role of fluorine in glass. Phys Chem Glasses 24:54–56
Seifert FA, Mysen BO, Virgo D (1981) Quantitative determination of proportions of anionic units in silicate melts. Carnegie Inst Washington Yearb 80:301–302
Seifert FA, Mysen BO, Virgo D (1982) Three-dimensional network melt structure in the systems SiO2-NaAlO2, SiO2-CaAl2O4 and SiO2-MgAl2O4. Am Mineral 67:696–718
Seifert FA, Mysen BO, Virgo D (1983) Raman study of densified vitreous silica. Phys Chem Glasses 24:141–145
Shinozaki N, Okusi H, Mizoguchi K, Suginohara Y (1977) Electrical conductivity and IR spectra of Na2O-SiO2-NaF melts. Japan Inst Metall J 41:607–612
Takusagawa N (1980) Infrared absorption spectra and structure of fluorine-containing alkali silicate glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 42:35–40
Walrafen GE (1967) Raman spectral studies of the effects of temperature on water structure. J Chem Phys 54:114–126
Wyllie PJ, Tuttle OF (1961) Experimental investigation of silicates containing two volatile components. II. The effects of NH3 and HF in addition to water on the melting temperatures of granite and albite. Am J Sci 259:128–143
Yamamoto K, Nakashini T, Kasahara H, Abe K (1983) Raman scattering of SiF4 molecules in amorphous, fluorinated silicon. J Non-Cryst Solids 59 and 60:213–216
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mysen, B.O., Virgo, D. Interaction between fluorine and silica in quenched melts on the joins SiO2-AlF3 and SiO2-NaF determined by raman spectroscopy. Phys Chem Minerals 12, 77–85 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01046830
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01046830