Abstract
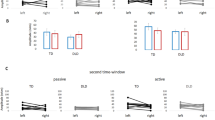
Forty normal-achieving and 33 learning disabled (LD) children were assigned randomly to either a negative ion or placebo test condition. On a dichotic listening task using consonant-vowel (CV) combinations, both groups showed an ioninduced increase in the normal right ear advantage (REA). However, the mechanisms for this effect were different for each group. The LDs showed the effect at the right ear/left hemisphere (enhancement). The normal achievers showed the effect at the left ear/right hemisphere (inhibition). The results are consistent with an activation-inhibition model of cerebral function and suggest a functional relationship between arousal, interhemispheric activation-inhibition, and learning disabilities. The LDs may have an interhemispheric dysfunction. Both groups showed superior right ear report and the normal achiever showed overall superiority. Normal achievers showed higher consonant intrusion scores, probably due to a greater cognitive capacity. Age was a significant covariate reflecting developmental capacity changes. Negative air ions are seen to be a tool with potential theoretical and remedial applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooke WL (1986) Cerbral asymmetries for competitive auditory information processing in disabled and non-disabled readers. Ph D Thesis, Ontario Institute for Studies in Education, University of Toronto, Canada
Denenberg VH (1984) Behavioral asymmetry. In: Geschwind N, Galaburda AM (eds) Cerebral dominance. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Diamond MC, Conner JR Jr, Orenberg EK, Bissell M, Yost M, Krueger A (1980) Eirvironmental influences on serotonin and cyclic nucleotides in rat cerebral cortex. Science 210:652–654
Duffee RA, Koontz RH (1965) Behavioral effects of ionized air on rats. Psychophysiology 1:347–359
Essman WB (1973) Age dependent effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine upon memory consolidation and cerebral protein synthesis. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1:7–14
Essman WB (1974) Brain 5-hydroxytryptamine and memory consolidation. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 11:265–274
Geller E, Ritvo ER, Freeman BJ, Yuwiler A (1982) Preliminary observation on the effect of fenfluramine on blood serotonin and symptoms in three autistic boys. N Engl J Med 307:165–169
Gilbert GO (1973) Effect of negative air ions upon emotionality and brain serotonin levels in isolated rats. Int J Biometeorol 17:267–275
Goldman JD, Thibert RJ, Rourke BP (1979) Platlet serotonin levels in hyperactive children J Pediatr Psychol 4:285–296
Hanley H, Stahl S, Freedman D (1981) Hyperserotonemia and amine metabolites in autistic and retarded children. Arch General Psychiatry 34:521–531
Hawkins LH (1981) The influence of air ions, temperature and humidity on subjective wellbeing and comfort. J Environm Psychol 1:279–292
Hiscock M, Kinsbourne M (1980) Asymmetries of selective listening and attention switching in children. Dev Psychol 16:70–82
Hiscock M, Stewart C (1984) The effect of asymmetrically focused attention upon subsequent ear differences in dichotic listening. Neuropsychologia 22:337–351
Hiscock M, Kinsbourne M, Caplan B, Swanson JM (1979) Auditory attention in hyperactive children: Effects of stimulant medication on dichotic listening performance. J Abnorm Psychol 88:27–32
Hynd GW, Hynd CR, Sullivan HG, Kingsbury TB (1987) Regional cerebral flood flow (rCBF) in developmental dyslexia: Activation during reading in a surface and a deep dyslexic J Learn Disabilities 20:294–300
Irwin M, Belendiuk K, McCloskey K, Freedman DX (1981) Tryptophan metabolism in children with attentional deficit disorder. Am J Psychiatry 138:1082–1085
Jordan J, Sokoloff B (1959) Air ionization, age, and maze learning of rats. J Gerontol 14:344–348
Kershner J (1985) Ontogeny of hemispheric specialization and relationship of developmental patterns to complex reasoning and academic achievement. In: Best C (ed) Developmental neuropsychology and education: Hemispheric specialization and integration: Academic Press, New York
Kimura D (1967) Functional asymmetry of the brain in dichotic listening. Cortex 3:163–178
Kotaka S (1978) Effects of air ions on microorganisms and other biological materials. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol 6:109–149
Krueger AP, Kotaka S (1969) The effects of air ions on brain levels of serotonin in mice. Int J Biometeorol 13:25–38
Krueger AP, Smith RF (1960) The biological mechanisms of air ion action. J Gen Physiol 43:533–540
Krueger AP, Andriese PC, Kotaka S (1963) The biological mechanism of air ion action: The effect CO +2 in inhaled air on the blood level of 5-hydroxytryptamine in mice. Int J Biometeorol 7:3–16
Morton LL, Kershner JR (1984) Negative air ionization improves memory and attention in learning-disabled and mentally retarded children. J Abnorm Child Psychol 12:353–366
Morton LL, Kershner JR (1987) Negative ion effects on hemispheric processing and selective attention in the mentally retarded children. J Ment Defic Res 31:169–180
Obrzut JE, Hynd GW, Obrzut A, Pirozzolo FJ (1981) Effect of directed attention on cerebral asymmetries in normal and learning disabled children. Dev Psychol 17:118–125
Obrzut JE, Hynd GW, Obrzut A (1983) Neuropsychological assessment of learning disabilities: A discriminant analysis J Exp Child Psychol 35:46–55
Obrzut JE, Obrzut A, Bryden MP, Bartels SG (1985) Information processing and speech lateralization in learning disabled children. Brain Language 25:87–101
Oikawa K, Deonauth J, Briedbart S (1979) Mental retardation and elevated serotonin levels in adults. Life Sci 23:341–346
Pare CMB, Sandler M, Stacey RS (1960) 5-hydroxyindoles in mental deficiency. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 23:341–346
Pipe ME, Beale IL (1983) Hemispheric specialization for speech in retarded children. Neuropsychologia 21:91–98
Rogawski MA, Aghajanian GK (1980) Norepinephrine and serotonin: Opposite effects on the activity of lateral geniculate neurons evoked by optic pathway stimulation. Exp Neurol 69:678–694
Schain RJ, Freedman DX (1961) Studies on 5-hydroxyindole metabolism in autistic and other mentally retarded children. J Pediatr 58:315–320
Shucard D Wm, Cummins KR, McGee MG (1984) Event-related brain potentials differentiate normal and disabled readers Brain Language 21:318–334
Silverman D, Kornblueh IH (1957) Effect of artificial ionization of the air on the electroencephalogram. Am J Phys Med 35:352–358
Sulman FG, Levy D, Lukan L, Pfeifer Y, Tal E (1978) Absence of harmful effects of protracted negative air ionization. Int J Biometeorol 22:53–58
Witelson SF (1977) Development dyslexia: Two right hemispheres and none left. Science 195:309–311
Zekulin-Hartley XY (1981) Hemispheric asymmetry in Down's Syndrome children. Can J Behav Sci 13:210–217
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morton, L.L., Kershner, J.R. Differential negative air ion effects on learning disabled and normal-achieving children. Int J Biometeorol 34, 35–41 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01045818
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01045818