Summary
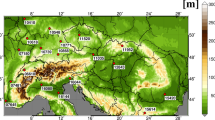
A diagnostic model (DIAMOD) for the atmosphere over Europe is use at the University of Vienna. Central parameters in each diagnostic column (horizontal resolution 100 km, time resolution 12 hours) are the vertical moisture plus heat flux (the total convective heat fluxh) and the vertical rain flux (r); both are functions of pressure. In this study DIAMOD is applied to validate the output of a forecast model for the simulation of acid deposition (EURAD) which is in use at the University of Cologne. The basic equations of both DIAMOD and EURAD models are summarized with emphasis on the sub-gridscale hydrologic components.
First, the nontrivial problem of validating model output versus observations is discussed. Two different validation techniques based upon the budget equations are indentified. The fully prognostic technique compares the forecast of EURAD for the total verification period with the corresponding DIAMOD output. The semiprognostic validation technique involves only one-time-step tendencies. Neither yields an exact correspondence between EURAD and DIAMOD; however, the semiprognostic technique comes somewhat closer to the ideal of an objective validation. The quantities investigated are: The fields, the time tendencies and the fluxesh andr.
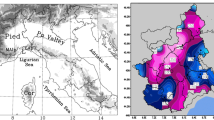
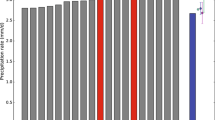
Second, EURAD is validated versus DIAMOD with both techniques for the EUMAC Joint Wet Case (the Chernobyl episode) in April 1986; the output fields include selected profiles ofh(p) over France (a moist night situation) and over Greece (a dry day situation). The comparison demonstrates for both that the EURAD forecasts are acceptable for ther-fluxes but are relatively poor for theh-fluxes. Reasons for the differences are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acs, F., 1994: Berechnung der Komponenten der Energiebilanz an der Erdoberfläche im Modell DIAMOD (personal communication).
Anthes, R. A., 1977: A cumulus parameterization scheme utilizing a one-dimensional cloud model.Mon. Wea. Rev.,105, 270–286.
Anthes, R. A., Kuo, Y.-H., Benjamin, S. G., Li, Y.-F., 1982: The evolution of the mesoscale environment of severe local storms: Preliminary modeling results.Mon. Wea. Rev.,110, 1187–1213.
Anthes, R. A., Hise, E.-Y., Kuo, Y.-H., 1987: Description of the Penn State/NCAR mesoscale model version 4 (MM4). NCAR Tech. Note., NACR/TN-282+STR, 66 pp.
Blackadar, A. K., 1979: High resolution models of the planetary boundary layer. In Pfafflin, J. R., Ziegler, E. N. (eds.)Advances in Environmental Science and Engineering, 1, No. 1, New York: Gordon and Breach Sci. Pub. pp. 50–85.
Bosart, L. F., 1981: The President's Day snowstorm of 18–19 February 1979: A subsynoptic-scale event.Mon. Wea. Rev.,109, 1542–1566.
Bowen, I. S., 1926: The ratio of heat losses by conduction and by evaporation from any water surface.Phys. Rev.,27, 779–787.
Burkhardt, T., 1991: Subgrid-scale vertical heat fluxes for the African region.Meteorol. Atmos. Phys.,46, 155–168.
Chang, J. S., Brost, R. A., Isaksen, I. S. A., Madronich, S., Middleton, P., Stockwell, W. R., Walcek, C. J., 1987: A three-dimensional Eulerian acid deposition model: Physical concepts and formulation.J. Geophys. Res.,92, 14681–14700.
Dent, D., 1988: The ECMWF model: past, present and future. In: Hoffmann, G.-R., Snelling, D. F., (eds.)Multiprocessing in Meteorological Models. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 369–381.
Dorninger, M., Ehrendorfer, M., Hantel, M., Rubel, F., Wang, Y., 1992: A thermodynamic diagnostic model for the atmosphere. Part I: Analysis of the August 1991 rain episode in Austria.Meteorol. Zeitschr., N.F.,1, 87–121.
Ebel, A., Hass, H., Jakobs, H. J., Laube, M., Memmesheimer, M., Oberreuter, A., Geiss, H., Kuo, Y.-H., 1991: Simulation of ozone intrusion caused by a troposphere fold and cut-off low.Atmos. Environ.,25A, 2131–2144.
Ebel, A., Hass, H., Jakobs, H. J., Memmesheimer, M., 1993: Complex chemical transport modelling, its evaluation and application to air pollution episodes. In: Zannetti, P. et al. (eds.)Air Pollution, London: Elsevier, pp. 333–343.
ECMWF, 1993:Validation of Models over Europe. Proceedings of a seminar held at ECMWF, 7–11 September 1992. Vol. I, 285 pp. Vol. II, 279pp.
Ehrendorfer, M., Hantel, M., Wang, Y., 1984: A variational modification algorithm for three-dimensional mass flux non-divergence.Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc.,120, 655–698.
Emanuel, K. A., Raymond, D. J., 1993: The representation of cumulus convection in numerical models.Meteorological Monograph. 24, 46, 246.
Fritsch, J. M., Maddox, R. A., 1981: Convective driven mesoscale weather system aloft. Part I: Observation.J. Appl. Meteor.,20, 9–19.
Grell, G., Kuo, Y.-H., Pasch, R. J., 1991: Semiprognostic test of cumulus parameterization schemes in the middle latitudes.Mon. Wea. Rev.,119, 5–31.
Gyakum, J. R., 1983: On the evolution of the QE II storm Parts I, II.Mon. Wea. Rev.,111, 1137–1173.
Haimberger, L., Hantel, M., Dorninger, M., 1995: A thermodynamic diagnostic model for the atmosphere. Part III: DIAMOD with orography and new error model. Meteorol. Zeitschr. (in print).
Hantel, M., 1981: ALPEX: Subsynoptische Vertikaltransporte.Annalen der Meteorologie (N.F.),19, 79–80.
Hantel, M., Emeis, S., 1985: A diagnostic model for synoptic heat budgets.Arch. Met. Geoph. Biokl. Serie A,33, 407–420.
Hantel, M., 1986: Rain in the free atmosphere from synoptic data.Meteorol. Rdsch.,39, 102–111.
Hantel, M., 1987: Subsynoptic vertical heat fluxes from high-resolution synoptic budgets.Meteorol. Atmos. Phys.,36, 24–44.
Hantel, M., Ehrendorfer, M., Haimberger, L., 1993: A thermodynamic diagnostic model for the atmosphere. Part II: The general theory and its consequences.Meteorol. Zeitschr., N.F.,6, 255–271.
Hass, H., Memmeshimer, M., Geiß, H., Jakobs, H. J., Laube, M., Ebel, A., 1990: Simulation of the Chernobyl radioactive cloud over Europe using the EURAD model.Atmos. Environ.,24A, 673–692.
Hollingsworth, A., 1994: Validation and diagnosis of atmospheric models.Dyn. Atmos. Oceans,20, 227–246.
Klinker, E., Sardeshmukh, P. D., 1992: The diagnosis of mechanical dissipation in the atmosphere from large-scale balance requirements.J. Atmos. Sci.,49, 608–627.
Kuo, H. L., 1974: Further studies of parameterization of the effect of cumulus convection on large-scale flow.J. Atmos. Sci.,31, 1232–1240.
Kuo, Y. H., Anthes, R. A., 1982: Numerical simulation of a Mei-Yu system over southeastern Asia.Pap. Meteor. Res.,5, 15–36.
Kuo, Y. H., Anthes, R. A., 1984: Semiprognostic tests of Kuo-type cumulus parameterization schemes in an extratropical convective system.Mon. Wea. Rev.,112, 1498–1509.
Lord, S. J., 1982: Interaction of a cumulus cloud ensernble with the large-scale environment. Part III: Semiprognostic test of the Arakawa-Schubert parameterization.J. Atimos. Sci.,39, 88–103.
Maddox, R. A., 1980: Mesoscale convective complexes.Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc.,61, 1374–1387.
Reed, R. J., 1979: Cyclogenesis in polar air streams.Mon. Wea. Rev.,107, 38–52.
Rubel, F., Wang, Y., Hantel, M., Ehrendorfer, M., 1993: Verification of the hydrological cycle in the EURAD-model. In: Bonell, P. M. et al. (eds.)Photo-Oxidants: precursors and Products. Proceedings of EUROTRAC-Symposium '92, Garmisch-Partenkirchen. SPB Academic Publishing, The Hauge, 454–457.
Rubel, F., 1994: Diagnose vertikaler Niederschlagsflüsse. Dissertation, University of Vienna, 175 pp.
Sanders, F., Gyakum, J. R., 1980: Synoptic-dynamic climatology of the “Bomb”.Mon. Wea. Rev.,108, 1589–1606.
Stull, R. B., 1988.An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meterology. Dordrecht: Kluwer, 666pp.
Tiedtke, M., 1989: A comprehensive mass flux scheme for cumulus parameterization in large-scale models.Mon. Wea. Rev.,117, 1779–1800.
Wang, Y., 1994: Semiprognostischer Test der Cumulusparametrisierung mit dem Kuo-Schema über Europa. Dissertation, University of Vienna, 109 pp.
Wang, Y., Hantel, M., 1994: Convective fluxes and cumulus parameterization in the EURAD model-A contribution to subproject EUMAC. In: Borrell, P. M., et al., (eds.)The Proceedings of EUROTRAC-Symposium '94. SPB Academic Publishing, The Hague, 850–855.
Yanai, M., Esbensen, S., Chu, J.-H., 1973: Determination of bulk properties of tropical cloud clusters from large scale heat and moisture budgets.J. Atmos. Sci.,30, 611–627.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 11 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hantel, M., Jakobs, H.J. & Wang, Y. Validation of parameterized convective fluxes with DIAMOD. Meteorl. Atmos. Phys. 57, 201–227 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01044161
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01044161