Abstract
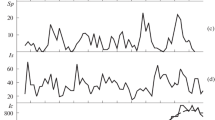
The dynamics of total hospital deaths from different kinds of cardiovascular diseases in one 1000-bed hospital were compared with 10 monthly cosmic/solar and geomagnetic physical activity parameters. Data used were of 180 consecutive months; 15601 deaths including 5667 from cardiovascular diseases were included in this study. It was concluded that the number of monthly hospital deaths shows a highly significant correlation with monthly solar physical activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archer VE (1979) Anencephalus, drinking water, geomagnetism and cosmic radiation. Am J epidemiol 109:88–97
Barnothy NF (1969) Biological effects of magnetic field. Plenum, New York
Bellosi A, Certaines J (1979) Effect of a constant non-uniform magnetic field on leucocyte migration in vitro. Preliminary study. Acta Haematol 8:(2)51–54
Bloxham J, Gubbins D (1989) The evolution of the earth's magnetic field. Sci Am: (Dec) 30–37
Bunning E (1973) The physiological clock. University Press Ltd, London; Springer Verlag, New York Heidelberg Berlin
Dubrov A (1978) The geomagnetic field and life geomagnetobiology. Plenum, London New York
Eigenson MS (1963) The sun, the weather and the climate (in Russian). Hydrometeroizdat, Leningrad
Entrican JH, Douglas AS (1979) Circannual rhtythm of arterial and venous thromboembolic disease. Scot Med J 24:273–278
Friedman H, Becker R, Bachman C (1963) Geomagnetic parameters and psychiatric hospital admission. Nature 200:626–628
Gall S, Ormenyi J (1989) Myocardial infarction and solar activity. 1st International Symposium on Heart Failure — Mechanisms and Management. Jerusalem, Abstract 545
Gibson EG (1973) The quiet sun. Scientific and Technical Information Office, NASA, Washington
Joshua H, Stoupel E (1978) Geomagnetic activity influences on coagulation system in humans. 8th World Congress of Cardiology, Abstract, p 379, Tokyo
Kholodov I (1966) The influence of electromagnetic and magnetic fields on the central nervous system. IPRS-37102, Joint Publication Research Service, Washington DC
Klinowska M (1988) Cetacean “navigation” and the geomagnetic field. J Navigation 4:52–71
Kreiger DT (1975) Rhythms of ACTH and corticosteroid secretion in health and disease, and their experimental modification. J Steroid Biochem 6:785–794
Kuritzky A, Zoldan Y, Herring R, Stoupel E (1987) Geomagnetic activity and severity of migraine attacks. Headache 27(2):87–89
Merlob P, Reisner S, Shimshoni M, Stoupel E (1989) Fetal growth during two extreme periods of solar activity in the 21–22 solar cycle. J Foetal Med 9:1–2, 1–5
Miroschnichenko LI (1981) The sun activity and the earth. Moscow, Nauka
Moore-Ede MC, Czeisler CA, Richardson GS (1983) Circadian time keeping in health and disease. N Eng J Med 308:469–476
Myerson B (1979) Hypothalamic hormones and behavior. Med Biol 572:69–83
Novikova K, Gnevishew N, Tokareva N et al. (1968) The solar activity influence of the natural history of myocardial infarction. Cardiologya 81:109–112
Poumailloux J, viart R (1959) Correlations possibles entre l'incidence des infarctus due myocarde et l'augmentation des activités solaires et geomagnetiques. Bull Acad Med 14:167
Rajaran M, Mitra S (1981) Correlation between convulsive seizure and geomagnetic activity. Neurosci Lett 24:187–191
Reinberg A (1977) Des rhythmes biologiques à la chronobiologie. Gauthier-Villars, Paris
Rozhdestvenshaya E, Novikova R (1969) The influence of solar activity on the blood fibrinolytic system. Med Ref J 10:65–69
Sardon G, Fure M (1927) Les taches solaires et la pathologie humaine. La Presse Medicale, No. 18, Paris
Simpson HW (1981) Chronobiology and medicine. Scot Med J 26:293–295
Smolenskij MM, Tater SE, Bergman SA (1977) Circadian aspects of cardiovascular function. Chronobiologie 3:337–371
Stoupel E (1976) Forecasting in cardiology. Wiley, New York Toronto Jerusalem
Stoupel E (1979) Chronostatistics of cardiovascular deaths. XV International Congress of Therapeutics, Brussels. Abstract, p 121
Stoupel E (1980) Solar terrestial predictions-aspects for preventive medicine. In: Solar-terrestrial predictions proceedings, vol 4, 29–40. NOAA Environmental Research Laboratories, Boulder, Colorado
Stoupel E (1987) Sudden cardiac death and VPC in low geomagnetic activity days. 8th World Symposium on Cardiac Pacing. Pace 10:3, II, 749
Stoupel E (1989) Precipitation of cardiovascular events in different levels of environmental physical activity. 2nd Asian Pacific Symposium on Cardiac Rehabilitation, Jerusalem, Abstract, p 97
Stoupel E, Ashkenazi Y (1989) Circannual rhythmicity in cardiovascular death. 1st International Symposium on Heart Failure Mechanisms and Management. Jerusalem, Abstract 536
Stoupel E, Joshua H (1982) Cardiovascular homeostasis and death occurring at different time, geomagnetic and sun activity. Abstracts, IX World Congress of Cardiology, Moscow, vol I, 0859
Stoupel E, Shimshoni M, Agmon J (1988) Is the localisation of myocardial infarction time related? Clin Cardiol 11:45–49
Stoupel E, Silbergerld A, Gil-Ad I, Keret R, Shimshoni M, Laron Z (1989) Relationship between solar activity and levels of plasma growth hormone and prolactin. Neuroendocrinol Lett 11:291–295
Szceklik E, Mergentaler J, Kotlarek-Haus S, Kuliszkievicz-Janus M, Kucharczyk J, Janus W (1983) Solar activity and myocardial infarction. Cor et Vasa 1:49–55
Tschijevsky A (1976) Terrestrial echo of the solar storms. 2nd edn. Mislj (ed). Moscow
Yakovleva M (1973) The physiologic mechanisms of the effects of electromagnetic fields. Nauka, Leningrad
Van Praag HM, Lewus C, Kahn R (1987) Hormonal probes of central serotonergic activity. Do they really exist? Biol Psychiatry 22:86–98
Zemishlany Z, Davidson M (1988) Searching for biologic markers in schizophrenia. Harefuah 7:64, 344–347
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stoupel, E., Shimshoni, M. Hospital cardiovascular deaths and total distribution of deaths in 180 consecutive months with different cosmic physical activity: a correlative study (1974–1988). Int J Biometeorol 35, 6–9 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01040956
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01040956